Abstract
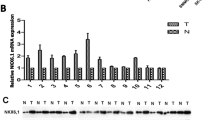
Naked cuticle 1 (NKD1), a negative regulator of the Wnt signaling pathway, is abnormally expressed in many types of malignant tumors. Yet the role and mechanism of NKD1 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell proliferation and its relationship with HCC patients’ prognosis have been poorly characterized. In the present study, real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was used to examine the mRNA expression patterns of NKD1 in the tissues of 60 patients with HCC and corresponding adjacent non-tumor tissues and found that NKD1 mRNA expression in HCC tissues was relatively lower than that in non-tumor tissues and negatively correlated with tumor size. Kaplan–Meier survival curves uncovered that patients with lower NKD1 expression had a poorer post-operative prognosis than those with higher expression. In addition, over-expression of NKD1 inhibited the HCC cell proliferation ability, whereas knockdown of NKD1 had the opposite effect. In vivo assays showed that mice injected with SMMC-7721 + control cells had bigger tumor nodules than those injected with SMMC-7721 + NKD1. Mechanism studies demonstrated that NKD1 repressed HCC cell proliferation by inducing p53 expression. Taken together, our study revealed that NKD1 mRNA expression was downregulated in HCC tissues and correlated with a poor prognosis. NKD1 inhibited HCC cell proliferation by inducing p53 expression.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Park YY, Kim SB, Han HD, Sohn BH, Kim JH, Liang J, et al. Tat-activating regulatory DNA-binding protein regulates glycolysis in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating the platelet isoform of phosphofructokinase through microRNA 520. Hepatology. 2013;58:182–91.
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108.
Befeler AS, Di Bisceglie AM. Hepatocellular carcinoma: diagnosis and treatment. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:1609–19.
Van Raay TJ, Fortino NJ, Miller BW, Ma H, Lau G, Li C, et al. Naked1 antagonizes Wnt signaling by preventing nuclear accumulation of beta-catenin. PLoS One. 2011;6:e18650.
Larraguibel J, Weiss AR, Pasula DJ, Dhaliwal RS, Kondra R, Van Raay TJ. Wnt ligand-dependent activation of the negative feedback regulator Nkd1. Mol Biol Cell. 2015;26:2375–84.
Yan D, Wiesmann M, Rohan M, Chan V, Jefferson AB, Guo L, et al. Elevated expression of axin2 and hnkd mRNA provides evidence that Wnt/beta -catenin signaling is activated in human colon tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:14973–8.
Caldwell GM, Jones CE, Soon Y, Warrack R, Morton DG, Matthews GM. Reorganisation of Wnt-response pathways in colorectal tumorigenesis. Br J Cancer. 2008;98:1437–42.
Koch A, Waha A, Hartmann W, Hrychyk A, Schüller U, Waha A. Elevated expression of Wnt antagonists is a common event in hepatoblastomas. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:4295–304.
Cheng AS, Lau SS, Chen Y, Kondo Y, Li MS, Feng H, et al. EZH2-mediated concordant repression of Wnt antagonists promotes beta-catenin-dependent hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2011;71:4028–39.
Lv ZD, Zhang L, Liu XP, Jin LY, Dong Q, Li FN, et al. NKD1 down-regulation is associated with poor prognosis in breast invasive ductal carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8:4015–21.
Ahn S, Hwangbo W, Kim H, Kim CH. Naked cuticle drosophila 1 expression in histologic subtypes of small adenocarcinoma of the lung. Korean J Pathol. 2013;47:211–8.
Zhang S, Wang Y, Dai SD, Wang EH. Down-regulation of NKD1 increases the invasive potential of non-small-cell lung cancer and correlates with a poor prognosis. BMC Cancer. 2011;11:–186.
Zhang S, Li J, Yin ZY, Liu PG, Zhao WX, Xie CR, et al. Expression pattern and clinicopathologic significance of NKD1 in human primary hepatocellular carcinoma. APMIS. 2015;123:315–20.
Brooks CL, Gu W. Ubiquitination, phosphorylation and acetylation: the molecular basis for p53 regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2003;15:164–71.
Vousden KH, Lane DP. p53 in health and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:275–83.
Zhang S, Li J, Liu P, Xu J, Zhao W, Xie C, et al. Pygopus-2 promotes invasion and metastasis of hepatic carcinoma cell by decreasing E-cadherin expression. Oncotarget. 2015;6:11074–86.
Zhang S, Li J, He F, Wang XM. Abnormal nuclear expression of Pygopus-2 in human primary hepatocellular carcinoma correlates with a poor prognosis. Histopathology. 2015;67:176–84.
Ma Y, Zhu B, Liu X, Yu H, Yong L, Liu X, et al. Inhibition of oleandrin on the proliferation show and invasion of osteosarcoma cells in vitro by suppressing Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2015;34:115.
Wands JR, Kim M. WNT/β-catenin signaling and hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2014;60:452–4.
Koontongkaew S. The tumor microenvironment contribution to development, growth, invasion and metastasis of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. J Cancer. 2013;4:66–83.
Chung AS, Lee J, Ferrara N. Targeting the tumour vasculature: insights from physiological angiogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10:505–14.
Wei JC, Meng FD, Qu K, Wang ZX, QF W, Zhang LQ, et al. Sorafenib inhibits proliferation and invasion of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells via up-regulation of p53 and suppressing FoxM1. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015;36:241–51.
Zhao B, Zhao W, Wang Y, Xu Y, Xu J, Tang K, et al. Connexin32 regulates hepatoma cell metastasis and proliferation via the p53 and Akt pathways. Oncotarget. 2015;6:10116–33.
Guo J, Cagatay T, Zhou G, Chan CC, Blythe S, Suyama K, et al. Mutations in the human naked cuticle homolog NKD1 found in colorectal cancer alter Wnt/Dvl/beta-catenin signaling. PLoS One. 2009;4:e7982.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank Alfred Sze Lok Cheng and Yingying Lee (Chinese University of Hong Kong) for kindly providing the plasmid for NKD1. And we also appreciate all of the patients participated in this study. This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81401945 and No. 81472231), the Youth Project of Fujian provincial Health and Family Planning commission (NO. 2013-2-89), the Science and Technology Project of Xiamen, China (NO. 3502Z20164023) and the Medical Innovative Project of Fujian provincial Health and Family Planning commission (No. 2015-CXB-40).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
There is no conflict of interest between the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 41 kb)
Fig. S1
NKD1 expression was positively associated with HCC cell apoptosis. a Annexin V/PI analysis showed that NKD1 overexpression promoted HCC cell apoptosis and increased sensitivity to cis-platinum. b On the contrary, NKD1 knockdown inhibited HCC cell apoptosis and decreased resistance to cis-platinum. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01. Three independent experiments were performed (n = 3) (GIF 15 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Li, J. & Wang, X. NKD1 correlates with a poor prognosis and inhibits cell proliferation by inducing p53 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 37, 14059–14067 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5173-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5173-0