Abstract
The interaction between cancer and its microenvironment is crucial for survival and development of cancerous cells. Tumor microenvironment is usually under hypoxia, which promotes tumor aggressiveness like growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis. How cancer cells respond to hypoxia and the resultant impact on tumorigenesis are not yet fully explored. Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been attracting more and more attention since their functions in regulating gene expression at chromatic, transcriptional, and posttranscriptional levels were found. lncRNAs are dysregulated in cancer and act as oncogenes or tumor suppressors. Moreover, emerging evidence has been provided that the expression of lncRNAs changes with the stimulus of hypoxia and they in turn produce a significant influence on the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF), the most common transcription regulator in response to hypoxia. In this review, we discuss the recent findings of hypoxia-responsive lncRNAs and summarize their interaction with hypoxia to further understand their roles in cancer growth, metabolism, angiogenesis, and metastasis and their potential for cancer diagnosis and treatment.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lodish H, Berk A, Zipursky SL et al. (2000) Tumor cells and the onset of cancer; Molecular cell biology, ed4. New York, W. H. Freeman
Wels J, Kaplan RN, Rafii S, Lyden D. Migratory neighbors and distant invaders: tumor-associated niche cells. Genes Dev. 2008;22:559–74.
Harris AL. Hypoxia—a key regulatory factor in tumour growth. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:38–47.
Quail DF, Joyce JA. Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat Med. 2013;19:1423–37.
Prensner JR, Chinnaiyan AM. The emergence of lncRNAs in cancer biology. Cancer discovery. 2011;1:391–407.
Autuoro JM, Pirnie SP, Carmichael GG. Long noncoding RNAs in imprinting and x chromosome inactivation. Biomolecules. 2014;4:76–100.
Kornienko AE, Guenzl PM, Barlow DP, Pauler FM. Gene regulation by the act of long non-coding RNA transcription. BMC Biol. 2013;11:59.
Yoon JH, Abdelmohsen K, Gorospe M. Posttranscriptional gene regulation by long noncoding RNA. J Mol Biol. 2013;425:3723–30.
Shi X, Sun M, Liu H, Yao Y, Song Y. Long non-coding RNAs: a new frontier in the study of human diseases. Cancer Lett. 2013;339:159–66.
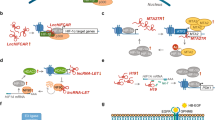
Xue M, Li X, Li Z, Chen W. Urothelial carcinoma associated 1 is a hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha-targeted long noncoding RNA that enhances hypoxic bladder cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Oncogene. 2014;35:6901–12.
Matouk IJ, Raveh E, Abu-lail R, Mezan S, Gilon M, Gershtain E, et al. Oncofetal h19 RNA promotes tumor metastasis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1843;2014:1414–26.
Fish JE, Matouk CC, Yeboah E, Bevan SC, Khan M, Patil K, et al. Hypoxia-inducible expression of a natural cis-antisense transcript inhibits endothelial nitric-oxide synthase. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:15652–66.
Shen XH, Qi P, Du X. Long non-coding RNAs in cancer invasion and metastasis. Modern pathology: an official journal of the United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology, Inc, 2015;28:4–13.
Gomez-Maldonado L, Tiana M, Roche O, Prado-Cabrero A, Jensen L, Fernandez-Barral A, et al. EFNA3 long noncoding RNAs induced by hypoxia promote metastatic dissemination. Oncogene. 2014;34(20):2609–200.
Zhou C, Ye L, Jiang C, Bai J, Chi Y, Zhang H: Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR, a hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha activated driver of malignancy, enhances hypoxic cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer. Tumour biology: the journal of the International Society for Oncodevelopmental Biology and Medicine 2015 (in press)
Choudhry H, Schodel J, Oikonomopoulos S, Camps C, Grampp S, Harris AL, et al. Extensive regulation of the non-coding transcriptome by hypoxia: role of HIF in releasing paused RNAPOL2. EMBO Rep. 2014;15:70–6.
Choudhry H, Albukhari A, Morotti M, Hider S, Moralli D, Smythies J, Schodel J, Green CM, Camps C, Buffa F, Ratcliffe P, Ragoussis J, Harris AL, Mole DR: Tumor hypoxia induces nuclear paraspeckle formation through HIF-2alpha dependent transcriptional activation of NEAT1 leading to cancer cell survival. Oncogene. 2015;34:4482–90.
Wu MZ, Tsai YP, Yang MH, Huang CH, Chang SY, Chang CC, et al. Interplay between HDAC3 and WDR5 is essential for hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Mol Cell. 2011;43:811–22.
Yang F, Huo XS, Yuan SX, Zhang L, Zhou WP, Wang F, et al. Repression of the long noncoding RNA-LET by histone deacetylase 3 contributes to hypoxia-mediated metastasis. Mol Cell. 2013;49:1083–96.
McCarty G, Loeb DM. Hypoxia-sensitive epigenetic regulation of an antisense-oriented lncRNA controls wt1 expression in myeloid leukemia cells. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0119837.
Wang KC, Chang HY. Molecular mechanisms of long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell. 2011;43:904–14.
He Y, Vogelstein B, Velculescu VE, Papadopoulos N, Kinzler KW. The antisense transcriptomes of human cells. Science. 2008;322:1855–7.
Villegas VE, Zaphiropoulos PG. Neighboring gene regulation by antisense long non-coding RNAs. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16:3251–66.
Bertozzi D, Iurlaro R, Sordet O, Marinello J, Zaffaroni N, Capranico G. Characterization of novel antisense HIF-1alpha transcripts in human cancers. Cell Cycle. 2011;10:3189–97. Georgetown, Tex.
Wang Y, Yao J, Meng H, Yu Z, Wang Z, Yuan X, et al. A novel long non-coding RNA, hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha promoter upstream transcript, functions as an inhibitor of osteosarcoma stem cells in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 2015;11:2534–40.
Sun YW, Chen YF, Li J, Huo YM, Liu DJ, Hua R, et al. A novel long non-coding RNA ENST00000480739 suppresses tumour cell invasion by regulating OS-9 and HIF-1alpha in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2014;111:2131–41.
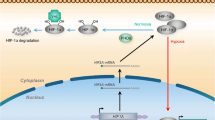
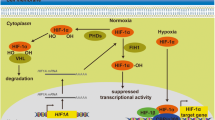
Baek JH, Mahon PC, Oh J, Kelly B, Krishnamachary B, Pearson M, et al. Os-9 interacts with hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha and prolyl hydroxylases to promote oxygen-dependent degradation of HIF-1alpha. Mol Cell. 2005;17:503–12.
Wong BW, Kuchnio A, Bruning U, Carmeliet P. Emerging novel functions of the oxygen-sensing prolyl hydroxylase domain enzymes. Trends Biochem Sci. 2013;38:3–11.
Zhu Z, Gao X, He Y, Zhao H, Yu Q, Jiang D, et al. An insertion/deletion polymorphism within RERT-lncRNA modulates hepatocellular carcinoma risk. Cancer Res. 2012;72:6163–72.
Yang F, Zhang H, Mei Y, Wu M. Reciprocal regulation of HIF-1alpha and lincRNA-p21 modulates the Warburg effect. Mol Cell. 2014;53:88–100.
Ma MZ, Kong X, Weng MZ, Zhang MD, Qin YY, Gong W, et al. Long non-coding RNA-LET is a positive prognostic factor and exhibits tumor-suppressive activity in gallbladder cancer. Mol Carcinog. 2014;54(11):1397–406.
Takahashi K, Yan IK, Haga H, Patel T. Modulation of hypoxia-signaling pathways by extracellular linc-ror. J Cell Sci. 2014;127:1585–94.
Xu Q, Liu LZ, Qian X, Chen Q, Jiang Y, Li D, et al. Mir-145 directly targets p70s6k1 in cancer cells to inhibit tumor growth and angiogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:761–74.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100:57–70.
Ferdin J, Nishida N, Wu X, Nicoloso MS, Shah MY, Devlin C, et al. HINCUTS in cancer: hypoxia-induced noncoding ultraconserved transcripts. Cell Death Differ. 2013;20:1675–87.
Nolte D, Muller U. Human o-GlcNAc transferase (OGT): genomic structure, analysis of splice variants, fine mapping in xq13.1. Mammalian genome: official journal of the International Mammalian Genome Society. 2002;13:62–4.
Kreppel LK, Blomberg MA, Hart GW. Dynamic glycosylation of nuclear and cytosolic proteins. Cloning and characterization of a unique o-GlcNAc transferase with multiple tetratricopeptide repeats. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:9308–15.
Lowe SW, Lin AW. Apoptosis in cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2000;21:485–95.
Goldar S, Khaniani MS, Derakhshan SM, Baradaran B. Molecular mechanisms of apoptosis and roles in cancer development and treatment. Asian Pacific journal of cancer prevention: APJCP. 2015;16:2129–44.
Soussi T. The p53 tumor suppressor gene: from molecular biology to clinical investigation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000;910:121–37. discussion 137–129.
Matouk IJ, DeGroot N, Mezan S, Ayesh S, Abu-lail R, Hochberg A, et al. The h19 non-coding RNA is essential for human tumor growth. PLoS One. 2007;2:e845.
Matouk IJ, Mezan S, Mizrahi A, Ohana P, Abu-Lail R, Fellig Y, et al. The oncofetal h19 RNA connection: hypoxia, p53 and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1803;2010:443–51.
Rossi MN, Antonangeli F. LncRNAs: new players in apoptosis control. International journal of cell biology. 2014;2014:473857.
Maddika S, Ande SR, Panigrahi S, Paranjothy T, Weglarczyk K, Zuse A, et al. Cell survival, cell death and cell cycle pathways are interconnected: implications for cancer therapy. Drug resistance updates : reviews and commentaries in antimicrobial and anticancer chemotherapy. 2007;10:13–29.
Warburg O. On the origin of cancer cells. Science. 1956;123:309–14.
Bartrons R, Caro J. Hypoxia, glucose metabolism and the Warburg’s effect. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2007;39:223–9.
Zeng W, Liu P, Pan W, Singh SR, Wei Y. Hypoxia and hypoxia inducible factors in tumor metabolism. Cancer Lett. 2015;356:263–7.
Bikfalvi A. Angiogenesis and invasion in cancer. Handb Clin Neurol. 2012;104:35–43.
Raghunand N, Gatenby RA, Gillies RJ. Microenvironmental and cellular consequences of altered blood flow in tumours. Br J Radiol. 2003;76 Spec No 1:S11–22.
Carmeliet P, Jain RK. Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature. 2000;407:249–57.
Chen L, Endler A, Shibasaki F. Hypoxia and angiogenesis: regulation of hypoxia-inducible factors via novel binding factors. Exp Mol Med. 2009;41:849–57.
Mizukami Y, Kohgo Y, Chung DC. Hypoxia inducible factor-1 independent pathways in tumor angiogenesis. Clinical cancer research: an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2007;13:5670–4.
Ji P, Diederichs S, Wang W, Boing S, Metzger R, Schneider PM, et al. MALAT-1, a novel noncoding RNA, and thymosin beta4 predict metastasis and survival in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene. 2003;22:8031–41.
Michalik KM, You X, Manavski Y, Doddaballapur A, Zornig M, Braun T, et al. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 regulates endothelial cell function and vessel growth. Circ Res. 2014;114:1389–97.
Weigelt B, Peterse JL, Veer LJ v ’t. Breast cancer metastasis: markers and models. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:591–602.
Wang Y, Liu X, Zhang H, Sun L, Zhou Y, Jin H, et al. Hypoxia-inducible lncRNA-ak058003 promotes gastric cancer metastasis by targeting gamma-synuclein. Neoplasia. 2014;16:1094–106.
Van Roosbroeck K, Pollet J, Calin GA. MiRNAs and long noncoding RNAs as biomarkers in human diseases. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2013;13:183–204.
Yan X, Hu Z, Feng Y, Hu X, Yuan J, Zhao SD, et al. Comprehensive genomic characterization of long non-coding RNAs across human cancers. Cancer Cell. 2015;28:529–40.
Vaupel P. Hypoxia and aggressive tumor phenotype: implications for therapy and prognosis. Oncologist. 2008;13 Suppl 3:21–6.
Zhang Q, Su M, Lu G, Wang J. The complexity of bladder cancer: long noncoding RNAs are on the stage. Mol Cancer. 2013;12:101.
Zheng Q, Wu F, Dai WY, Zheng DC, Zheng C, Ye H, Zhou B, Chen JJ, Chen P: Aberrant expression of UCA1 in gastric cancer and its clinical significance. Clinical & translational oncology: official publication of the Federation of Spanish Oncology Societies and of the National Cancer Institute of Mexico. Clin Transl Oncol. 2015;17:640–6.
Hughes JM, Legnini I, Salvatori B, Masciarelli S, Marchioni M, Fazi F, et al. C/EBPalpha-p30 protein induces expression of the oncogenic long non-coding RNA UCA1 in acute myeloid leukemia. Oncotarget. 2015;6(21):18534–44.
Zhou X, Yin C, Dang Y, Ye F, Zhang G. Identification of the long non-coding RNA h19 in plasma as a novel biomarker for diagnosis of gastric cancer. Sci Rep. 2015;5:11516.
Li CH, Chen Y. Targeting long non-coding RNAs in cancers: progress and prospects. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013;45:1895–910.
Qi P, Du X. The long non-coding RNAs, a new cancer diagnostic and therapeutic gold mine. Modern pathology: an official journal of the United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology, Inc. 2013;26:155–65.
Smaldone MC, Davies BJ. Bc-819, a plasmid comprising the h19 gene regulatory sequences and diphtheria toxin a, for the potential targeted therapy of cancers. Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2010;12:607–16.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 81372713, 81402048).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, J., Xu, J., Wang, X. et al. Influence of the interaction between long noncoding RNAs and hypoxia on tumorigenesis. Tumor Biol. 37, 1379–1385 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4457-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4457-0