Abstract
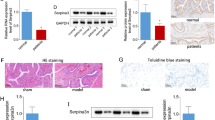
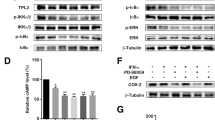
Phospholipase Cε (PLCε) is a multifunctional enzyme implicated in inflammatory functions. There are limited data, however, on how PLCε can alter inflammatory cytokine by affecting downstream pathways. Recent studies suggest that inflammation is likely to have an important role in transitional cell carcinoma of bladder (TCCB) and cancer disease progression. Here, we showed that PLCε and p-STAT3 expression were both elevated in TCCB tissues compared to adjacent tissues, and the increase of PLCε level was associated with the increase of p-STAT3 level. Then, knockdown of PLCε using adenovirus-shPLCε significantly decreased inflammatory cytokine (IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β) expression and inflammation-associated gene (TLR4, MyD88, p-STAT3) expression. Furthermore, we demonstrated that PLCε knockdown blocked LPS-induced inflammatory cytokine and p-STAT3 expression. Additionally, we found that combined treatment of STAT3 inhibitor S3I-201 with adenovirus-shPLCε exhibited synergistic inhibitory effects on expression of p-STAT3. Our results suggested that STAT3 phosphorylation is involved in PLCε-mediated inflammatory cytokine release. Our research is of potential importance in drug development programs using PLCε as a therapeutic target for TCCB.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rhee SG. Regulation of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C. Annu Rev Biochem. 2001;70:281–312.
Ada-Nguema AS, Xenias H, Hofman JM, Wiggins CH, Sheetz MP, Keely PJ. The small GTPase R-Ras regulates organization of actin and drives membrane protrusions through the activity of PLCepsilon. J Cell Sci. 2006;119:1307–19.
Edamatsu H, Satoh T, Kataoka T. Ras and Rap1 activation of PLCepsilon lipase activity. Method Enzymol. 2006;407:99–107.
Wing MR, Snyder JT, Sondek J, Harden TK. Direct activation of phospholipase C-epsilon by Rho. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:41253–8.
Li M, Edamatsu H, Kitazawa R, Kitazawa S, Kataoka T. Phospholipase Cepsilon promotes intestinal tumorigenesis of Apc(Min/+) mice through augmentation of inflammation and angiogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 2009;30:1424–32.
Harada Y, Edamatsu H, Kataoka T. PLCε cooperates with the NF-κB pathway to augment TNFα-stimulated CCL2/MCP1 expression in human keratinocyte. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;414:106–11.
Oka M, Edamatsu H, Kunisada M, Hu L, Takenaka N, Sakaguchi M, et al. Phospholipase Cε has a crucial role in ultraviolet B-induced neutrophil-associated skin inflammation by regulating the expression of CXCL1/KC. Lab Invest. 2011;91:711–8.
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9–29.
Zhang Y, Yan L, Zhao Y, Ou L, Wu X, Luo C. Knockdown of phospholipase C-epsilon by short-hairpin RNA-mediated gene silencing induces apoptosis in human bladder cancer cell lines. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2013;28(3):233–9.
Ling Y, Chunli L, Xiaohou W, Qiaoling Z. Involvement of the PLCε/PKCα pathway in human BIU-87 bladder cancer cell proliferation. Cell Biol Int. 2011;35(10):1031–6.
Du HF, Ou LP, Yang X, Song XD, Fan YR, Tan B, et al. A new PKCα/β/TBX3/E-cadherin pathway is involved in PLCε-regulated invasion and migration in human bladder cancer cells. Cell Signal. 2014;26:580–93.
Janeway Jr CA, Medzhitov R. Innate immune recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002;20:197–216.
LaRue H, Ayari C, Bergeron A, Fradet Y. Toll-like receptors in urothelial cells—targets for cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Urol. 2013;10:537–45.
Kim HM, Park BS, Kim JI, Kim SE, Lee J, Oh SC, et al. Crystal structure of the TLR4-MD-2 complex with bound endotoxin antagonist Eritoran. Cell. 2007;130:906–17.
Park BS, Song DH, Kim HM, Choi BS, Lee H, Lee JO. The structural basis of lipopolysaccharide recognition by the TLR4-MD-2 complex. Nature. 2009;458:1191–5.
Lu YC, Yeh WC, Ohashi PS. LPS/TLR4 signal transduction pathway. Cytokine+. 2008;42:145–51.
Qian Y, Deng J, Xie H, Geng L, Zhou L, Wang Y, et al. Regulation of TLR4-induced IL-6 response in bladder cancer cells by opposing actions of MAPK and PI3K signaling. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2009;135:379–86.
Ferguson SD, Srinivasan VM, Heimberger AB. The role of STAT3 in tumor-mediated immune suppression. J Neurooncol. 2015;22.
Bromberg JF, Wrzeszczynska MH, Devgan G, Zhao Y, Pestell RG, Albanese C, et al. STAT3 as an oncogene. Cell. 1999;98:295–303.
Kishimoto T. IL-6: from its discovery to clinical applications. Int Immunol. 2010;22:347–52.
Yu H, Pardoll D, Jove R. STATs in cancer inflammation and immunity: a leading role for STAT3. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:798–809.
Lee H, Deng J, Kujawski M, Yang C, Liu Y, Herrmann A, et al. STAT3-induced S1PR1 expression is crucial for persistent STAT3 activation in tumors. Nat Med. 2010;16:1421–8.
Samavati L, Rastogi R, Du W, Hüttemann M, Fite A, Franchi L. STAT3 tyrosine phosphorylation is critical for interleukin 1 beta and interleukin-6 production in response to lipopolysaccharide and live bacteria. Mol Immunol. 2009;46:1867–77.
Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 2006;124:783–801.
Szajnik M, Szczepanski MJ, Czystowska M, Elishaev E, Mandapathil M, Nowak-Markwitz E, et al. TLR4 signaling induced by lipopolysaccharide or paclitaxel regulates tumor survival and chemoresistance in ovarian cancer. Oncogene. 2009;28:4353–63.
Hua D, Liu MY, Cheng ZD, Qin XJ, Zhang HM, Chen Y, et al. Small interfering RNA-directed targeting of Toll-like receptor 4 inhibits human prostate cancer cell invasion, survival, and tumorigenicity. Mol Immunol. 2009;46:2876–84.
Szczepanski MJ, Czystowska M, Szajnik M, Harasymczuk M, Boyiadzis M, Kruk-Zagajewska A, et al. Triggering of Toll-like receptor 4 expressed on human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma promotes tumor development and protects the tumor from immune attack. Cancer Res. 2009;69:3105–13.
Ying H, Da L, Yu-xiu S, Yu X, Li-xia L, Li-mei X, et al. TLR4 mediates MAPK–STAT3 axis activation in bladder epithelial cells. Inflammation. 2013;36:1064–74.
Ikuta S, Edamatsu H, Li M, Hu L, Kataoka T. Crucial role of phospholipase C epsilon in skin inflammation induced by tumor-promoting phorbol ester. Cancer Res. 2008;68:64–72.
Hu L, Edamatsu H, Takenaka N, Ikuta S, Kataoka T. Crucial role of phospholipase Cepsilon in induction of local skin inflammatory reactions in the elicitation stage of allergic contact hypersensitivity. J Immunol. 2010;184:993–1002.
Dusaban SS, Purcell NH, Rockenstein E, Masliah E, Cho MK, Smrcka AV, et al. Phospholipase Cε links G protein-coupled receptor activation to inflammatory astrocytic responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110:3609–14.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–74.
Grivennikov SI, Greten FR, Karin M. Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell. 2010;140:883–99.
Cai T, Nesi G, Boddi V, Mazzoli S, Dal Canto M, Bartoletti R. Prognostic role of the tumor-associated tissue inflammatory reaction in transitional bladder cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2006;16:329–34.
Michaud DS. Chronic inflammation and bladder cancer. Urol Oncol. 2007;25:260–8.
Kagan JC, Su T, Horng T, Chow A, Akira S, Medzhitov R. TRAM couples endocytosis of Toll-like receptor 4 to the induction of interferon-beta. Nat Immunol. 2008;9:361–8.
Tanimura N, Saitoh S, Matsumoto F, Akashi-Takamura S, Miyake K. Roles for LPS-dependent interaction and relocation of TLR4 and TRAM in TRIF-signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;368:94–9.
Zanoni I, Ostuni R, Marek LR, Barresi S, Barbalat R, Barton GM, et al. CD14 controls the LPS-induced endocytosis of Toll-like receptor 4. Cell. 2011;147:868–80.
Nagano T, Edamatsu H, Kobayashi K, Takenaka N, Yamamoto M, Sasaki N, et al. Phospholipase cε, an effector of ras and rap small GTPases, is required for airway inflammatory response in a mouse model of bronchial asthma. PLoS One. 2014;9, e108373.
Jarnicki A, Putoczki T, Ernst M. STAT3: linking inflammation to epithelial cancer-more than a “gut” feeling? Cell Div. 2010;5:14.
Garner JM, Fan M, Yang CH, Du Z, Sims M, Davidoff AM, et al. Constitutive activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and nuclear factor κB signaling in glioblastoma cancer stem cells regulates the Notch pathway. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:26167–76.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81072086) and Scientific and Technological Research Program of Chongqing Municipal Education Committee of China (Grant No. KJ110305).
Conflict of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xue Yang and Liping Ou contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Ou, L., Tang, M. et al. Knockdown of PLCε inhibits inflammatory cytokine release via STAT3 phosphorylation in human bladder cancer cells. Tumor Biol. 36, 9723–9732 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3712-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3712-8