Abstract
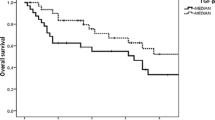
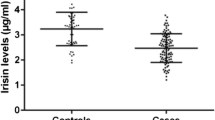
Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and its primary binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) play an important role in cellular proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis in many tumors, including breast cancer (BC). The objective of this study was to determine the clinical significance of the serum levels of IGF-1 and IGFBP-3 in BC patients. A total of 96 patients with a pathologically confirmed diagnosis of BC were enrolled into this study. Serum IGF-1 and IGFBP-3 levels were determined by the solid-phase sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) methods. Age- and sex-matched 30 healthy controls were included in the analysis. The median age of diagnosis was 48 years (range: 29–80). Thirty-seven (39 %) consisted of metastatic disease. No significant difference in baseline serum was found in both IGF-1 and IGFBP-3 levels between BC patients and healthy controls (p = 0.92 and p = 0.26, respectively). None of the prognostic parameters analyzed was correlated significantly with the serum assay concentrations. Likewise, no correlations were also found between these serum concentrations and response to chemotherapy. No significant correlation was found between serum IGF-1 and IGFBP-3 levels in BC patients (r s = 0.048, p = 0.66).The patients with elevated serum IGF-1 levels had favorable in survival than those with lower levels (p = 0.05). However, serum IGFBP-3 concentrations were found no prognostic role for outcome (p = 0.35). In conclusion, elevated serum IGF-1 level is afavorable prognostic factor for overall survival in BC patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Renehan AG, Zwahlen M, Minder C, O'Dwyer ST, Shalet SM, Egger M. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF binding protein-3, and cancer risk: systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Lancet. 2004;363:1346–53.
Key TJ, Appleby PN, Reeves GK, Roddam AW. Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1), IGF binding protein 3 (IGFBP3), and breast cancer risk: pooled individual data analysis of 17 prospective studies. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:530–42.
Rinaldi S, Peeters PH, Berrino F, Dossus L, Biessy C, Olsen A, et al. IGF-1, IGFBP-3 and breast cancer risk in women: the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer And Nutrition (EPIC). Endocrine Rel Cancer. 2006;13:593–605.
Al-Delaimy WK, Flatt SW, Natarajan L, Laughlin GA, Rock CL, Gold EB, et al. IGF1 and risk of additional breast cancer in the WHEL study. Endocrine Rel Cancer. 2011;18:235–44.
Holdaway IM, Mason BH, Lethaby AE, Singh V, Harvey VJ, Thompson PI, et al. Serum insulin-like growth factor-1 and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 following chemotherapy for advanced breast cancer. ANZ J Surg. 2003;73:905–8.
Hankinson SE, Willett WC, Colditz GA, Hunter DJ. Circulating concentrations of insulin-like growth factor-1 and risk of breast cancer. Lancet. 1998;351:1393–6.
Goodwin PJ, Ennis M, Pritchard KI, Trudeau ME, Koo J, Madarnas Y, Hartwick W, Hoffman B, Hood N. Fasting ınsulin and outcome in early-stage breast cancer: results of a prospective cohort study. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20: 42–51
Pasanisi P, Venturelli E, Morelli D, Fontana L, Secreto G, Berrino F. Serum insulin-like growth factor-1 and platelet-derived growth factor as biomarkers of breast cancer prognosis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2008;17:1719–22.
Vadgama JV, Wu Y, Datta G, Khan H, Chillar R. Plasma insulin-like growth factor-1 and serum IGF-binding protein 3 can be associated with the progression of breast cancer, and predict the risk of recurrence and the probability of survival in African-American and Hispanic women. Oncology. 1999;57:330–40.
Hartog H, Boezen HM, de Jong MM, Schaapveld M, Wesseling J, van der Graaf WTA. Prognostic value of insulin-like growth factor 1 and insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 blood levels in breast cancer. Breast. 2013;22:1155–60.
Oh Y. IGF-independent regulation of breast cancer growth by IGF binding proteins. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1998;47:283–93.
Figueroa JA, Jackson JG, McGuire WL, Krywicki RF, Yee D. Expression of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in human breast cancer correlates with estrogen receptor status. J Cell Biochem. 1993;52:196–205.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tas, F., Karabulut, S., Bilgin, E. et al. Clinical significance of serum insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) in patients with breast cancer. Tumor Biol. 35, 9303–9309 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2224-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2224-2