Abstract
Backgrounds: Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic, inflammatory, and relapsing skin disorder that occurs due to a Th1/Th2 cytokine imbalance and an elevation of immunoglobulin E (IgE) levels. We investigated whether chlorin e6 (Ce6)-mediated photodynamic therapy (PDT), which is commonly used for the clinical treatment of several cancers and non-neoplastic skin disorders, has a therapeutic effect on AD.
Methods: β-hexosaminidase assay was performed in RBL-2H3 stimulated by DNP-BSA. Total IgE levels and serum cytokine levels were analyzed by ELISA assay. Eosinophils and mast cells were analyzed by hematoxylin- eosin stain and toluidine blue stain on ear of AD mouse model.
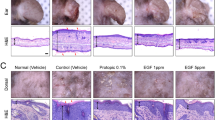
Results: Ce6-mediated PDT significantly reduced the secretion of β-hexosaminidase in DNP-BSA-stimulated RBL-2H3 cells. In a DNCB-induced AD-like mouse model, serum IFN-γ was found to be elevated in conjunction with reduced IL-4 following Ce6-mediated PDT. The DNCB-induced serum IgE level was also reduced following Ce6-mediated PDT. In addition, DNCB-induced infiltration of eosinophils and mast cells was decreased by Ce6-mediated PDT in the mouse ear.
Conclusion: Ce6-mediated PDT might be used as a potent therapeutics for AD via restoring Th1/Th2 balance and reducing over expressed immune cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yamanaka, K. & Mizutani, H. The role of cytokines/chemokines in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. Curr Probl Dermatol 41, 80–92 (2011).
Furue, M. et al. Atopic dermatitis: immune deviation, barrier dysfunction, IgE autoreactivity and new therapies. Allergol Int 66, 398–403 (2017).
Leung, D. Y., Boguniewicz, M., Howell, M. D., Nomura, I. & Hamid, Q. A. New insights into atopic dermatitis. J Clin Invest 113, 651–657 (2004).
Cooney, L. A., Towery, K., Endres, J. & Fox, D. A. Sensitivity and resistance to regulation by IL-4 during Th17 maturation. J Immunol 187, 4440–4450 (2011).
Lazarski, C. A., Ford, J., Katzman, S. D., Rosenberg, A. F. & Fowell, D. J. IL-4 attenuates Th1-associated chemokine expression and Th1 trafficking to inflamed tissues and limits pathogen clearance. PLoS One 8, e71949 (2013).
Poulsen, L. K. & Hummelshoj, L. Triggers of IgE class switching and allergy development. Ann Med 39, 440–456 (2007).
Kim, S. Y. et al. Transduced PEP-1-FK506BP ameliorates atopic dermatitis in NC/Nga mice. J Invest Dermatol 131, 1477–1485 (2011).
Kudo, C. Major side effects of systemic glucocorticoid. Nihon Rinsho 73, 317–321 (2015).
Dolmans, D. E., Fukumura, D. & Jain, R. K. Photodynamic therapy for cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 3, 380–387 (2003).
Agostinis, P. et al. Photodynamic therapy of cancer: an update. CA Cancer J Clin 61, 250–281 (2011).
Zhao, B. & He, Y. Y. Recent advances in the prevention and treatment of skin cancer using photodynamic therapy. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 10, 1797–1809 (2010).
Kim, M., Jung, H. Y. & Park, H. J. Topical PDT in the treatment of benign skin diseases: principles and new applications. Int J Mol Sci 16, 23259–23278 (2015).
Simone, C. B. 2nd et al. Photodynamic therapy for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Dis 4, 63–75 (2012).
Wachowska, M. et al. Aminolevulinic acid (ALA) as a prodrug in photodynamic therapy of cancer. Molecules 16, 4140–4164 (2011).
Jin, S., Ryu, A. R., Han, C. S. & Lee, M. Y. A comparison of the anti-bacterial and anti-inflammatory effect between two forms of chlorins. Toxicol Environ Health Sci 8, 271–276 (2016).
Jeon, Y. M. et al. Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy using chlorin e6 with halogen light for acne bacteria-induced inflammation. Life Sci 124, 56–63 (2015).
Wang, Y. Y., Ryu, A. R., Jin, S., Jeon, Y. M. & Lee, M. Y. Chlorin e6-mediated photodynamic therapy suppresses P. acnes-induced inflammatory response via NFkB and MAPKs signaling pathway. PLoS One 12, e0170599 (2017).
Ryu, A. R. & Lee, M. Y. Chlorin e6-mediated photodynamic therapy promotes collagen production and suppresses MMPs expression via modulating AP-1 signaling in P. acnes-stimulated HaCaT cells. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 20, 71–77 (2017).
Lee, J. K. et al. Perfluorooctane sulfonate exacerbates mast cell-mediated allergic inflammation by the release of histamine. Mol Cell Toxicol 14, 173–181 (2018).
Babu, K. S., Arshad, S. H. & Holgate, S. T. Anti-IgE treatment: an update. Allergy 56, 1121–1128 (2001).
Ciprandi, G. Serum IgE as biomarker for predicting allergen immunotherapy effectiveness. J Allergy Clin Immunol 139, 2029 (2017).
Herberth, G. et al. Reduced IFN-gamma-and enhanced IL-4-producing CD4+ cord blood T cells are associated with a higher risk for atopic dermatitis during the first 2 yr of life. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 21, 5–13 (2010).
Platts-Mills, T. A. The role of immunoglobulin E in allergy and asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 164, S1-S5 (2001).
Sanjuan, M. A., Sagar, D. & Kolbeck, R. Role of IgE in autoimmunity. J Allergy Clin Immunol 137, 1651–1661 (2016).
Brandt, E. B. & Sivaprasad, U. Th2 cytokines and atopic dermatitis. J Clin Cell Immunol 2, 110 (2011).
Lee, G. R. & Flavell, R. A. Transgenic mice which overproduce Th2 cytokines develop spontaneous atopic dermatitis and asthma. Int Immunol 16, 1155–1160 (2004).
Simon, D., Braathen, L. R. & Simon, H. U. Eosinophils and atopic dermatitis. Allergy 59, 561–570 (2004).
Esche, C., de Benedetto, A. & Beck, L. A. Keratinocytes in atopic dermatitis: inflammatory signals. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 4, 276–284 (2004).
Lebwohl, M. G. et al. Pathways to managing atopic dermatitis: consensus from the experts. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol 6, S2–S18 (2013).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Soonchunhyang University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
A-Reum Ryu & Mi-Young Lee declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Human and animal rights
The experimental procedure followed the actual law of animal protection that was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Soonchunhyang University, Korea.
Author’s contributions
A-Reum carried out the experiment and Mi-Young Lee supervised the project. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ryu, AR., Lee, MY. Ameliorative effect of chlorin e6-mediated photodynamic therapy on DNCB-induced atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in mice. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 15, 265–270 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-019-0030-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-019-0030-z