Abstract
Background
A microRNA (miRNA) is a small non-coding RNA (ncRNA) approximately 20 nucleotides long and it affects gene expression through mRNA cleavage or translational repression. Horses (Equus caballus) have been domesticated and bred to enhance their speed for racing. It has been studied extensively with genetic diversity, origins and evolution.
Objectives
We examined expression patterns of miR-221-3p and its target gene CDKN1C in various horse tissues.
Methods
We used bioinformatic tools to examine target gene, seed region and evolutionary conservation of miR-221-3p. The expression patterns of miR-221-3p and its target gene CDKN1C were analyzed by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR).
Results
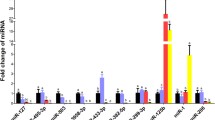
Among eight tissues of horse, miR-221-3p was highly expressed in cerebellum and spleen. On the other hand, only medulla was highly expressed in CDKN1C gene.
Conclusion
Our study provides expression data of miR-221-3p and CDKN1C gene in horse and suggests the fundamental information for future studies in relation to functional importance.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn K, Bae JH, Nam KH, Lee CE, Park KD, Lee HK, Cho BW, Kim HS (2011) Identification of reference genes for normalization of gene expression in thoroughbred and Jeju native horse (Jeju pony) tissues. Genes Genomics 33:245–250
Aigner A (2011) MicroRNAs (miRNAs) in cancer invasion and metastasis: therapeutic approaches based on metastasis-related miRNAs. J Mol Med 89:445–457
Ambros V (2004) The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431:350–355
Baker DL, Powers JG, Ransom JI, McCann BE, Oehler MW, Bruemmer JE, Galloway NL, Eckery DC, Nett TM (2018) Reimmunization increases contraceptive effectiveness of gonadotropin-releasing hormone vaccine (GonaCon-Equine) in free-ranging horses (Equus caballus): limitations and side effects. PLoS ONE 13:7 e0201570
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Bartel DP (2009) MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136:215–233
Bauer A, Hiemesch T, Jagannathan V, Neuditschko M, Bachmann I, Rieder S, Mikko S, Penedo MC, Tarasova N, Vitková M et al (2017) A nonsense variant in the ST14 gene in Akhal-Teke horses with naked foal syndrome. G3 7:1315–1321
Bueno MJ, Malumbres M (2011) MicroRNAs and the cell cycle. Biochim Biophys Acta 1812:592–601
Cappelli K, Capomaccio S, Viglino A, Silvestrelli M, Beccati F, Moscati L, Chiaradia E (2018) Circulating miRNAs as putative biomarkers of exercise adaptation in endurance horses. Front Physiol 9:429–439
Chen Y, Zeng L, Wang Y, Tolleson WH, Knox B, Chen S, Ren Z, Guo L, Mei N, Qian F et al (2017) The expression, induction and pharmacological activity of CYP1A2 are post-transcriptionally regulated by microRNA hsa-miR-132-5p. Biochem Pharmacol 145:178–191
de Yébenes VG, Ramiro AR (2010) MicroRNA activity in B lymphocytes. Methods Mol Biol 667:177–192
Deng L, Lei Q, Wang Y, Wang Z, Xie G, Zhong X, Wang Y, Chen N, Qiu Y, Pu T et al (2017) Downregulation of miR-221-3p and upregulation of its target gene PARP1 are prognostic biomarkers for triple negative breast cancer patients and associated with poor prognosis. Oncotarget 8:108712–108725
Fornari F, Gramantieri L, Ferracin M, Veronese A, Sabbioni S, Calin GA, Grazi GL, Giovannini C, Croce CM, Bolondi L et al (2008) MiR-221 controls CDKN1C/p57 and CDKN1B/p27 expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 27:5651–5661
Galardi S, Mercatelli N, Giorda E, Massalini S, Frajese GV, Ciafrè SA, Farace MG (2007) miR-221 and miR-222 expression affects the proliferation potential of human prostate carcinoma cell lines by targeting p27Kip1. J Biol Chem 282:23716–23724
Gim JA, Kim HS (2017) Identification and expression of Equine MER-derived miRNAs. Mol Cells 40:262–270
Iliff BW, Riazuddin SA, Gottsch JD (2012) A single-base substitution in the seed region of miR-184 causes EDICT syndrome. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 53:348–353
Janečka JE, Davis BW, Ghosh S, Paria N, Das PJ, Orlando L, Schubert M, Nielsen MK, Stout TAE, Brashear W et al (2018) Horse Y chromosome assembly displays unique evolutionary features and putative stallion fertility genes. Nat Commun 9:1–15
Jo A, Lee HE, Kim HS (2017a) Genomic analysis of miR-21-3p and expression pattern with target gene in olive flounder. Genomics Inform 15:98–107
Jo A, Im J, Lee HE, Jang D, Nam GH, Mishra A, Kim WJ, Kim W, Cha HJ, Kim HS (2017b) Evolutionary conservation and expression of miR-10a-3p in olive flounder and rock bream. Gene 628:16–23
Jo A, Lee HE, Kim HS (2018) Identification and expression analysis of a novel miRNA derived from ERV-E1 LTR in Equus caballus. Gene 687:238–245
Kim HA, Kim MC, Kim NY, Ryu DY, Lee HS, Kim Y (2018) Integrated analysis of microRNA and mRNA expressions in peripheral blood leukocytes of Warmblood horses before and after exercise. J Vet Sci 19:99–106
Lee S, Hwang S, Yu HJ, Oh D, Choi YJ, Kim MC, Kim Y, Ryu DY (2016) Expression of microRNAs in horse plasma and their characteristic nucleotide composition. PLoS ONE 11:e0146374
Malumbres M, Barbacid M (2001) To cycle or not to cycle: a critical decision in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 1:222–231
Mißbach S, Aleksic D, Blaschke L, Hassemer T, Lee KJ, Mansfeld M, Hänske J, Handler J, Kammerer R (2018) Alternative splicing after gene duplication drives CEACAM1-paralog diversification in the horse. BMC Evol Biol 18:32–44
Padilha FGF, El-Jaick KB, de Castro L, Moreira ADS, Ferreira AMR (2018) Effect of selection for eventing on the MSTN gene in Brazilian sport horses. J Equine Sci 29:21–24
Pircs K, Petri R, Jakobsson J (2018) Crosstalk between microRNAs and autophagy in adult neurogenesis: implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Brain Plast 3:195–203
Ropka-Molik K, Stefaniuk-Szmukier M, Piórkowska K, Szmatoła T, Bugno-Poniewierska M (2018) Molecular characterization of the apoptosis-related SH3RF1 and SH3RF2 genes and their association with exercise performance in Arabian horses. BMC Vet Res 14:237–243
Schurink A, da Silva VH, Velie BD, Dibbits BW, Crooijmans RPMA, FranÒ«ois L, Janssens S, Stinckens A, Blott S, Buys N et al (2018) Copy number variations in Friesian horses and genetic risk factors for insect bite hypersensitivity. BMC Genet 19:49–61
Shao N, Ma G, Zhang J, Zhu W (2018) miR-221-5p enhances cell proliferation and metastasis through post-transcriptional regulation of SOCS1 in human prostate cancer. BMC Urol 18:14–22
Sherr CJ, Roberts JM (1999) CDK inhibitors: positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes Dev 13:1501–1512
Shukla GC, Singh J, Barik S (2011) MicroRNAs: processing, maturation, target recognition and regulatory functions. Mol Cell Pharmacol 3:83–92
Sun K, Wang W, Zeng JJ, Wu CT, Lei ST, Li GX (2011) MicroRNA-221 inhibits CDKN1C/p57 expression in human colorectal carcinoma. Acta Pharmacol Sin 32:375–384
Valberg SJ, Henry ML, Perumbakkam S, Gardner KL, Finno CJ (2018) An E321G MYH1 mutation is strongly associated with nonexertional rhabdomyolysis in Quarter horses. J Vet Intern Med 32:1718–1725
Wei WF, Zhou CF, Wu XG, He LN, Wu LF, Chen XJ, Yan RM, Zhong M, Yu YH, Liang L et al (2017) MicroRNA-221-3p, a TWIST2 target, promotes cervical cancer metastasis by directly targeting THBS2. Cell Death Dis 8:1–13
Wu Q, Ren X, Zhang Y, Fu X, Li Y, Peng Y, Xiao Q, Li T, Ouyang C, Hu Y et al (2018) MiR-221-3p targets ARF4 and inhibits the proliferation and migration of epithelial ovarian cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 497:1162–1170
Wurz K, Garcia RL, Goff BA, Mitchell PS, Lee JH, Tewari M, Swisher EM (2010) MiR-221 and miR-222 alterations in sporadic ovarian carcinoma: relationship to CDKN1B, CDKN1C and overall survival. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 49:577–584
Xue Y, Wei Z, Ding H, Wang Q, Zhou Z, Zheng S, Zhang Y, Hou D, Liu Y, Zen K et al (2015) MicroRNA-19b/221/222 induces endothelial cell dysfunction via suppression of PGC-1α in the progression of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 241:671–681
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from the Ministry of Education, Republic of Korea (NRF-2015R1D1A1A01056650).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
The animal protocol and sample extraction method in this study were reviewed by the Pusan National University-Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (PNU-IACUC) for the ethical procedures and scientific care (approval number PNU-2013-0411).
Research involving human participants
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, SW., Jo, A., Im, J. et al. Expression analysis of miR-221-3p and its target genes in horses. Genes Genom 41, 459–465 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-018-00778-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-018-00778-3