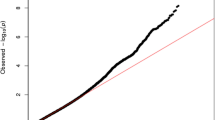
Abstract
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is characterized by a progressive loss of kidney function over a period of months or years. It is estimated that about 7.2 % of adults over the age of 30 have CKD worldwide. Although one of the major risk factors of CKD is family history, the heritability of CKD is not fully understood. It is also known that the diabetic condition is highly influential on the onset of CKD. To understand the genetic bases of CKD that remain unidentified, we performed genetic association analyses for kidney function-related traits such as blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and albumin in subjects stratified by diabetic status. In the discovery stage of the study, we used genome-wide scan data and clinical data in about 8800 subjects from the Korean Association Resource (KARE) project. Health2 study data comprising about 1800 subjects were used for the replication stage. Our two stage association analyses demonstrated that the LOC105374266 locus (rs9820070) showed strong evidence of association with BUN (P = 8.47 × 10−14) in nondiabetic normal subjects (n = ~4300). To extend our knowledge of the genetic determinants influencing kidney function, we also analyzed the association between kidney function-related traits and microRNA related variants. For this analysis, miRNA related SNPs were selected from KARE and Health2 cohort genotype data. Our study suggests the potential relevance of miRNA to the kidney function (miR-518b for BUN; miR-146a and miR-1295a for albumin) in Korean populations.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberti KG, Zimmet PZ (1998) Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabet Med 15:539–553
Ardekani AM, Naeini MM (2010) The role of MicroRNAs in human diseases. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol 2:161–179
Barnes EA, Porter LA, Lenormand JL, Dellinger RW, Donoghue DJ (2003) Human Spy1 promotes survival of mammalian cells following DNA damage. Cancer Res 63:3701–3707
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Biros E, Golledge J (2008) Meta-analysis of whole-genome linkage scans for intracranial aneurysm. Neurosci Lett 431:31–35
Boger CA, Gorski M, Li M, Hoffmann MM, Huang C, Yang Q, Teumer A, Krane V, O’Seaghdha CM, Kutalik Z et al (2011) Association of eGFR-related loci identified by GWAS with incident CKD and ESRD. PLoS Genet 7:e1002292
Chambers JC, Zhang W, Lord GM, van der Harst P, Lawlor DA, Sehmi JS, Gale DP, Wass MN, Ahmadi KR et al (2010) Genetic loci influencing kidney function and chronic kidney disease. Nat Genet 42:373–375
Chen K, Song F, Calin GA, Wei Q, Hao X, Zhang W (2008) Polymorphisms in microRNA targets: a gold mine for molecular epidemiology. Carcinogenesis 29:1306–1311
Cho YS, Go MJ, Kim YJ, Heo JY, Oh JH, Ban HJ, Yoon D, Lee MH, Kim DJ, Park M et al (2009) A large-scale genome-wide association study of Asian populations uncovers genetic factors influencing eight quantitative traits. Nat Genet 41:527–534
DCCT/EDIC, Jacobson AM, Musen G, Ryan CM, Silvers N, Cleary P, Waberski B, Burwood A, Weinger K, Bayless M et al (2007) Long-term effect of diabetes and its treatment on cognitive function. N Engl J Med 356:1842–1852
Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN, Sonenberg N (2008) Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet 9:102–114
Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, Shenmen CM, Grouse LH, Schuler G, Klein SL, Old S, Rasooly R, Good P et al (2004) The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the mammalian gene collection (MGC). Genome Res 14:2121–2127
Gunjaca G, Boban M, Pehlic M, Zemunik T, Budimir D, Kolcic I, Lauc G, Rudan I, Polasek O (2010) Predictive value of 8 genetic loci for serum uric acid concentration. Croat Med J 51:23–31
Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, Matthews DR, Neil HA (2008) 10-year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 359:1577–1589
Ichii O, Otsuka S, Sasaki N, Namiki Y, Hashimoto Y, Kon Y (2012) Altered expression of microRNA miR-146a correlates with the development of chronic renal inflammation. Kidney Int 81:280–292
Jha V, Garcia-Garcia G, Iseki K, Li Z, Naicker S, Plattner B, Saran R, Wang AY, Yang CW (2013) Chronic kidney disease: global dimension and perspectives. Lancet 382:260–272
Jin Y, Lee CG (2013) Single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with MicroRNA regulation. Biomolecules 3:287–302
Kim YJ, Go MJ, Hu C, Hong CB, Kim YK, Lee JY, Hwang JY, Oh JH, Kim DJ, Kim NH et al (2011) Large-scale genome-wide association studies in East Asians identify new genetic loci influencing metabolic traits. Nat Genet 43:990–995
Kottgen A, Glazer NL, Dehghan A, Hwang SJ, Katz R, Li M, Yang Q, Gudnason V, Launer LJ, Harris TB et al (2009) Multiple loci associated with indices of renal function and chronic kidney disease. Nat Genet 41:712–717
Kottgen A, Pattaro C, Boger CA, Fuchsberger C, Olden M, Glazer NL, Parsa A, Gao X, Yang Q, Smith AV et al (2010) New loci associated with kidney function and chronic kidney disease. Nat Genet 42:376–384
Liu CT, Garnaas MK, Tin A, Kottgen A, Franceschini N, Peralta CA, de Boer IH, Lu X, Atkinson E, Ding J et al (2011) Genetic association for renal traits among participants of African ancestry reveals new loci for renal function. PLoS Genet 7:e1002264
Lyman JL (1986) Blood urea nitrogen and creatinine. Emerg Med Clin North Am 4:223–233
Meuth VM, Massy ZA, Metzinger L (2014) miR-126 and miR-223 as biomarkers of vascular damage in the course of chronic kidney disease. RNA & Dis 1:e347
Okada Y, Sim X, Go MJ, Wu JY, Gu D, Takeuchi F, Takahashi A, Maeda S, Tsunoda T et al (2012) Meta-analysis identifies multiple loci associated with kidney function-related traits in east Asian populations. Nat Genet 44:904–909
Pattaro C, Kottgen A, Teumer A, Garnaas M, Boger CA, Fuchsberger C, Olden M, Chen MH, Tin A, Taliun D et al (2012) Genome-wide association and functional follow-up reveals new loci for kidney function. PLoS Genet 8:e1002584
Porter LA, Dellinger RW, Tynan JA, Barnes EA, Kong M, Lenormand JL, Donoghue DJ (2002) Human Speedy: a novel cell cycle regulator that enhances proliferation through activation of Cdk2. J Cell Biol 157:357–366
Richardson K, Lai CQ, Parnell LD, Lee YC, Ordovas JM (2011) A genome-wide survey for SNPs altering microRNA seed sites identifies functional candidates in GWAS. BMC Genom 12:504
Saunders MA, Liang H, Li WH (2007) Human polymorphism at microRNAs and microRNA target sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:3300–3305
Schena FP, Serino G, Sallustio F (2014) MicroRNAs in kidney diseases: new promising biomarkers for diagnosis and monitoring. Nephrol Dial Transplant 29:755–763
Smith KA, Hayward RA (2011) Performance measurement in chronic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 22:225–234
Sohn SH, Jun HK, Kim CS, Kim KN, Chung SM, Shin SW, Ryu JJ, Kim MK (2006) Biological responses in osteoblast-like cell line according to thin layer hydroxyapatite coatings on anodized titanium. J Oral Rehabil 33:898–911
Sung H, Jeon S, Lee KM, Han S, Song M, Choi JY, Park SK, Yoo KY, Noh DY, Ahn SH et al (2012) Common genetic polymorphisms of microRNA biogenesis pathway genes and breast cancer survival. BMC Cancer 12:195
Takeuchi F, Katsuya T, Chakrewarthy S, Yamamoto K, Fujioka A, Serizawa M, Fujisawa T, Nakashima E, Ohnaka K, Ikegami H et al (2010) Common variants at the GCK, GCKR, G6PC2-ABCB11 and MTNR1B loci are associated with fasting glucose in two Asian populations. Diabetologia 53:299–308
Wang TT, Chen YJ, Sun LL, Zhang SJ, Zhou ZY, Qiao H (2015) Affection of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in miR-27a, miR-124a, and miR-146a on susceptibility to type 2 diabetes mellitus in Chinese Han people. Chin Med J (Engl) 128:533–539
Willer CJ, Li Y, Abecasis GR (2010) METAL: fast and efficient meta-analysis of genomewide association scans. Bioinformatics 26:2190–2191
Zhang M, Zhou S, Zhang L, Zhang J, Cai H, Zhu J, Huang C, Wang J (2012) miR-518b is down-regulated, and involved in cell proliferation and invasion by targeting Rap1b in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. FEBS Lett 586:3508–3521
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) Grant funded by the Korea government (MEST) (2012M3A9D1054534) and Hallym University Research Fund 2012 (HRF-201203-008). This study obtained biospecimens and data from the Korean Genome Analysis Project (4845-301), the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (4851-302), and Korea Biobank Project (4851-307, KBP-2015-029), which were supported by the Korea Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical statement
In this study, genetic and epidemiological data were provided by the Korea Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Republic of Korea. This study was approved by the Hallym University Institutional Review Board (HIRB-2015-028).
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
13258_2016_411_MOESM1_ESM.xlsx
Supplementary material 1. The list of SNPs identified in human microRNAs. A total of 612 SNPs in human pre-miRNAs were selected from a microRNA-related SNP database (http://www.bioguo.org/miRNASNP/) (XLSX 48 kb)
13258_2016_411_MOESM2_ESM.xlsx
Supplementary material 2. The list of SNPs identified in the 1 kb flanking region of human microRNAs. A total of 18,442 SNPs in human miRNA flanks (1 kb) were selected from a microRNA-related SNP database (http://www.bioguo.org/miRNASNP/) (XLSX 839 kb)
13258_2016_411_MOESM3_ESM.docx
Supplementary material 3. Genetic variants associated with BUN or blood albumin that were identified from previous studies. The allele that increased BUN or that decreased blood albumin was defined as the reference allele (RA) and is indicated on the basis of the forward strand of NCBI Build 36. The effect size of RA on natural log-transformed values of BUN or non-transformed values of albumin concentration. EA, East Asians; na, not available (DOCX 19 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, J., Koh, I. & Cho, Y.S. Identification of genetic loci stratified by diabetic status and microRNA related SNPs influencing kidney function in Korean populations. Genes Genom 38, 601–609 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-016-0411-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-016-0411-9