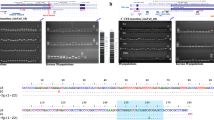
Abstract
The human genome has various genomic structural variations such as insertion/deletions between human individuals. These structural variations have led to genomic fluidity and rearrangements in individuals and populations. To investigate Korean-specific structural genomic variations, we performed next generation sequencing with 30× mean coverage from 27 Korean individuals using illumina-HiSeq 2000 platform. We collected a total of 119 deletion loci as transposable element-mediated Korean-specific deletion (KSD) candidates. Of the 119 loci, 35 were filtered out due to computational overlapping regions. A total of 78 loci were validated by PCR amplification with 27 Korean individuals and 80 human individuals from four different populations. We confirmed deletion breakpoints of the 78 loci using Sanger sequencing. We also investigated different deletion mechanisms based on sequencing alignment analysis. We found at least one KSD locus in 80 human individual panel. It has not been previously reported in human genomes. Here, for the first time, we report transposable element-mediated KSD study based on whole genome sequencing data of 27 Korean.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson KJ, Allen RL (2009) Regulation of T-cell immunity by leucocyte immunoglobulin-like receptors: innate immune receptors for self on antigen-presenting cells. Immunology 127:8–17
Baker MD, Birmingham EC (2001) Evidence for biased holliday junction cleavage and mismatch repair directed by junction cuts during double-strand-break repair in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol 21:3425–3435
Batzer MA, Deininger PL (2002) Alu repeats and human genomic diversity. Nat Rev Genet 3:370–379
Belancio VP, Deininger PL, Roy-Engel AM (2009) LINE dancing in the human genome: transposable elements and disease. Genome Med 1:97
Bennett EA, Coleman LE, Tsui C, Pittard WS, Devine SE (2004) Natural genetic variation caused by transposable elements in humans. Genetics 168:933–951
Boissinot S, Chevret P, Furano AV (2000) L1 (LINE-1) retrotransposon evolution and amplification in recent human history. Mol Biol Evol 17:915–928
Burwinkel B, Kilimann MW (1998) Unequal homologous recombination between LINE-1 elements as a mutational mechanism in human genetic disease. J Mol Biol 277:513–517
Callinan PA, Batzer MA (2006) Retrotransposable elements and human disease. Genome Dyn 1:104–115
Chen K, Wallis JW, McLellan MD, Larson DE, Kalicki JM, Pohl CS, McGrath SD, Wendl MC, Zhang Q, Locke DP et al (2009) BreakDancer: an algorithm for high-resolution mapping of genomic structural variation. Nat Methods 6:677–681
Cordaux R, Batzer MA (2009) The impact of retrotransposons on human genome evolution. Nat Rev Genet 10:691–703
Deininger PL, Batzer MA (1999) Alu repeats and human disease. Mol Genet Metab 67:183–193
Dridi S (2012) Alu mobile elements: from junk DNA to genomic gems. Scientifica 2012:545328
Genomes Project C, Abecasis GR, Altshuler D, Auton A, Brooks LD, Durbin RM, Gibbs RA, Hurles ME, McVean GA (2010) A map of human genome variation from population-scale sequencing. Nature 467:1061–1073
Genomes Project C, Abecasis GR, Auton A, Brooks LD, DePristo MA, Durbin RM, Handsaker RE, Kang HM, Marth GT, McVean GA (2012) An integrated map of genetic variation from 1,092 human genomes. Nature 491:56–65
Han JS (2010) Non-long terminal repeat (non-LTR) retrotransposons: mechanisms, recent developments, and unanswered questions. Mobile DNA 1:15
Han K, Lee J, Meyer TJ, Remedios P, Goodwin L, Batzer MA (2008) L1 recombination-associated deletions generate human genomic variation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:19366–19371
Han K, Lee J, Meyer TJ, Wang J, Sen SK, Srikanta D, Liang P, Batzer MA (2007) Alu recombination-mediated structural deletions in the chimpanzee genome. PLoS Genet 3:1939–1949
Hedges DJ, Deininger PL (2007) Inviting instability: transposable elements, double-strand breaks, and the maintenance of genome integrity. Mutat Res 616:46–59
Jackson SP (2002) Sensing and repairing DNA double-strand breaks. Carcinogenesis 23:687–696
Lander ES, Linton LM, Birren B, Nusbaum C, Zody MC, Baldwin J, Devon K, Dewar K, Doyle M, FitzHugh W et al (2001) Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 409:860–921
Lee H-E, Eo J, Kim H-S (2014) Composition and evolutionary importance of transposable elements in humans and primates. Genes Genomics 37:135–140
Li L, Bray PF (1993) Homologous recombination among three intragene alu sequences causes an inversion-deletion resulting in the hereditary bleeding disorder glanzmann thrombasthenia. Am J Hum Genet 53:140–149
Li M, Wu Y, Chen G, Yang Y, Zhou D, Zhang Z, Zhang D, Chen Y, Lu Z, He L et al (2011) Deletion of the late cornified envelope genes LCE3C and LCE3B is associated with psoriasis in a Chinese population. J Invest Dermatol 131:1639–1643
Marchini J, Howie B (2010) Genotype imputation for genome-wide association studies. Nat Rev Genet 11:499–511
Matejcic M, Li D, Prescott NJ, Lewis CM, Mathew CG, Parker MI (2011) Association of a deletion of GSTT2B with an altered risk of oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma in a South African population: a case-control study. PLoS One 6:e29366
Miller CA, Hampton O, Coarfa C, Milosavljevic A (2011) ReadDepth: a parallel R package for detecting copy number alterations from short sequencing reads. PLoS One 6:e16327
Mills RE, Bennett EA, Iskow RC, Devine SE (2007) Which transposable elements are active in the human genome? Trends Genet 23:183–191
Mullaney JM, Mills RE, Pittard WS, Devine SE (2010) Small insertions and deletions (INDELs) in human genomes. Hum Mol Genet 19:R131–R136
Munoz-Lopez M, Garcia-Perez JL (2010) DNA transposons: nature and applications in genomics. Curr Genomics 11:115–128
Ostertag EM, Kazazian HH Jr (2001) Biology of mammalian L1 retrotransposons. Annu Rev Genet 35:501–538
Pearson TA, Manolio TA (2008) How to interpret a genome-wide association study. JAMA 299:1335–1344
Pousi B, Hautala T, Heikkinen J, Pajunen L, Kivirikko KI, Myllyla R (1994) Alu–Alu recombination results in a duplication of seven exons in the lysyl hydroxylase gene in a patient with the type VI variant of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 55:899–906
Price AL, Eskin E, Pevzner PA (2004) Whole-genome analysis of Alu repeat elements reveals complex evolutionary history. Genome Res 14:2245–2252
Rajput MK (2014) Retrotransposons: the intrinsic genomic evolutionist. Genes Genomics 37:113–123
Riveira-Munoz E, He SM, Escaramis G, Stuart PE, Huffmeier U, Lee C, Kirby B, Oka A, Giardina E, Liao W et al (2011) Meta-analysis confirms the LCE3C_LCE3B deletion as a risk factor for psoriasis in several ethnic groups and finds interaction with HLA-Cw6. J Invest Dermatol 131:1105–1109
Sen SK, Han K, Wang J, Lee J, Wang H, Callinan PA, Dyer M, Cordaux R, Liang P, Batzer MA (2006) Human genomic deletions mediated by recombination between Alu elements. Am J Hum Genet 79:41–53
Shrivastav M, De Haro LP, Nickoloff JA (2008) Regulation of DNA double-strand break repair pathway choice. Cell Res 18:134–147
Tan KL, Board PG (1996) Purification and characterization of a recombinant human Theta-class glutathione transferase (GSTT2-2). Biochem J 315(Pt 3):727–732
Torkar M, Haude A, Milne S, Beck S, Trowsdale J, Wilson MJ (2000) Arrangement of the ILT gene cluster: a common null allele of the ILT6 gene results from a 6.7-kbp deletion. Eur J Immunol 30:3655–3662
Wisniewski A, Wagner M, Nowak I, Bilinska M, Pokryszko-Dragan A, Jasek M, Kusnierczyk P (2013) 6.7 kbp deletion in LILRA3 (ILT6) gene is associated with later onset of the multiple sclerosis in a Polish population. Hum Immunol 74:353–357
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests exists in this paper.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all participants, and this research was approved by the institutional review boards of TheragenEtex Bio Institute.
Additional information
Jungsu Ha and Wooseok Lee have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ha, J., Lee, W., Mun, S. et al. Identification of transposable element-mediated deletions in 27 Korean individuals based on whole genome sequencing data. Genes Genom 38, 179–192 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-015-0370-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-015-0370-6