Abstract
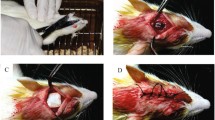
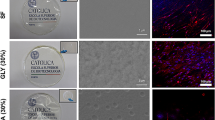
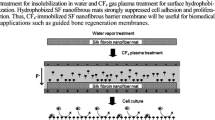
Biocompatible barrier membranes with both hydrophobic and hydrophilic surface properties provide critical backup for guided regeneration at localized bone defects without soft tissue invasion. As a surface modified functional barrier, saturated fluorocarbon (CF4)-immobilized nanofibrous silk fibroin (SF) membranes were fabricated by electrospinning for a fibrous non-woven mat, water vapor treatment for insolubilization, and followed by CF4 gas plasma treatment for top surface hydrophobization. Plasma-treated SF nanofiber membranes maintained a non-woven mat structure without shrinkage and deformation in a five-month biodegradation test. From in vivo rabbit cranium perforation model, nanofibrous SF membranes prevented soft tissue invasion and facilitated volumetric bone regeneration compared with the control groups. New bone ingrowth in bone defects at 4 and 8 weeks after surgery was visualized by trichrome staining. Medical application of fluorocarbon-immobilized nanofibrous SF barrier membranes could be one of the practical approaches for guided bone regeneration.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. M. Min, L. Jeong, K. Y. Lee, and W. H. Park, Macromol. Biosci., 6, 285 (2006).
L. Jeong, K. Y. Lee, J. W. Liu, and W. H. Park, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 38, 140 (2006).
C. Zaharia, M. R. Tudora, P. O. Stanescu, E. Vasile, and C. Cincu, J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater., 14, 163 (2012).
B. M. Min, G. Lee, S. H. Kim, Y. S. Nam, T. S. Lee, and W. H. Park, Biomaterials, 25, 1289 (2004).
K. E. Park, S. Y. Jung, S. J. Lee, B. M. Min, and W. H. Park, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 38, 165 (2006).
J. P. Chen, S. H. Chen, and G. J. Lai, Nanoscale Res. Lett., 7, 1 (2012).
K. Yamada, Y. Tsuboi, and A. Itaya, Thin Solid Films, 440, 208 (2003).
E.-U. Lee, D.-J. Kim, H.-C. Lim, J.-S. Lee, U.-W. Jung, and S.-H. Choi, Biomater. Res., 19, 50 (2015).
J.-Y. Park, C. Yang, I.-H. Jung, H.-C. Lim, J.-S. Lee, U.-W. Jung, Y.-K. Seo, J.-K. Park, and S.-H. Choi, Biomater. Res., 19, 57 (2015).
C.-H. Chung, Y.-K. Kim, J.-S. Lee, U.-W. Jung, E.-K. Pang, and S.-H. Choi, Biomater. Res., 19, 164 (2015).
J.-Y. Park, I.-H. Jung, Y.-K. Kim, H.-C. Lim, J.-S. Lee, U.-W. Jung, and S.-H. Choi, Biomater. Res., 19, 154 (2015).
K. Naresh, R. B. Ramesh, and B. Utpal, Mater. Lett., 63, 2466 (2009).
G. H. Altman, F. Diaz, C. Jakuba, T. Calabro, R. L. Horan, J. Chen, H. Lu, J. Richmond, and D. L. Kaplan, Biomaterials, 24, 401 (2003).
G. E. Wnek, M. E. Carr, D. G. Simpson, and G. L. Bowlin, Nano Lett., 3, 213 (2003).
H. Fong, I. Chun, and D. H. Reneker, Polymer, 40, 4585 (1999).
X. M. Mo, C. Y. Xu, M. Kotaki, and S. Ramakrishna, Biomaterials, 25, 1883 (2004).
O. H. Kwon, I. S. Lee, Y.-G. Ko, W. Meng, K. H. Jung, I.-K. Kang, and Y. Ito, Biomed. Mater., 2, S52 (2007).
H. Yoshimoto, Y. M. Shin, H. Terai, and J. P. Vacanti, Biomaterials, 24, 2077 (2003).
Y. Iriyama, T. Yasuda, D. L. Cho, and H. Yasuda, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 39, 249 (1990).
M. Shimosaki, N. Hayashi, S. Ihara, S. Satoh, and C. Yamabe, Vacuum, 73, 573 (2004).
O. Kylián, M. Petr, A. Serov, P. Solar, O. Polonskyi, J. Hanuš, A. Choukourov, and H. Biederman, Vacuum, 100, 57 (2014).
M. Lee, Y.-G. Ko, J. B. Lee, W. H. Park, D. Cho, and O. H. Kwon, Macromol. Res., 22, 746 (2014).
P. P. Spicer, J. D. Kretlow, S. Young, J. A. Jansen, F. K. Kasper, and A. G. Mikos, Nat. Protoc., 7, 1918 (2012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The image from this article is used as the cover image of the Volume 24, Issue 9.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ko, YG., Lee, M., Park, W.H. et al. Guiding bone regeneration using hydrophobized silk fibroin nanofiber membranes. Macromol. Res. 24, 824–828 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-016-4109-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-016-4109-2