Abstract
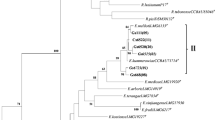
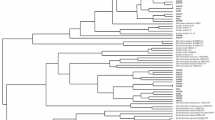
Forty rhizobial strains were isolated from root nodules of Medicago littoralis Rhode and Melilotus indicus (L.) harvested from the sandy soils of Touggourt’s oases in the Oued Righ Valley, Algerian Sahara. The isolates were studied for their cultural, biochemical and symbiotic effectiveness. All of them were fast-growing bacteria; utilized a wide range of carbon sources, produced abundant extracellular polysaccharides, tolerated high concentrations of NaCl (up to 2.5 %), grew at temperatures between 28 and 45 °C and at pH values between 4.5 and 9. The isolates were sensitive to the antibiotics kanamycin, tetracycline and rifampicin but showed resistance to neomycin and erythromycin. All the isolates induced the formation of effective nodules on their host plants. On the basis of the physiological, biochemical and symbiotic effectiveness, we selected six strains MD05, MD09, MD12, ML08, ML17 and ML22 for genotypic characterization. Phylogenetic analysis of the selected strains based on 16S ribosomal RNA gene showed that these strains of bacteria were affiliated to the Ensifer meliloti group.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelguerfi A, Ait Ouada M, Kies N, Si Ziani Y (1996) From autoecology to variability of medics in Algeria: synthesis trial of works realized at the National Agronomic Institute - El Harrach. Options Méditerr Sér A Mediterr Semin 18:39–52
Abdel-Salam MS, Ibrahim SA, Abd-El-Halim MM, Badawy FM, Abo-Aba SEM (2010) phenotypic characterization of indigenous Egyptian Rhizobial strains for abiotic stresses performance. J Am Sci 6(9):498–501
Amrani S, Nazhat-Ezzaman N, Tej Bhatnagar T, Argandonña M, Nieto JJ, Vargas C (2010) Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of rhizobia associated with Acacia saligna (Labill.) Wendl. In nurseries from Algeria. Syst Appl Microbiol 33:44–51
Badri Y, Zribi K, Badri M, Huguet T, van Berkum P, Aouani ME (2007) Comparison of rhizobia that nodulate Medicago laciniata and Medicago truncatula present in a single Tunisian arid soil. Can J Microbiol 53:277–283
Boukhatem ZF, Domergue O, Bekki A, Chahinez Merabet C, Sekkour S, Bouazza F, Duponnois R, de Lajudie P, Galiana A (2012) Symbiotic characterization and diversity of rhizobia associated with native and introduced acacias in arid and semi-arid regions in Algeria. FEMS Microbiol Ecol:1–14
Bouzar H, Jones JB, Bishop AL (1995) Simple Cultural Tests for Identification of Agrobacterium Biovars: Methods in Molecular Biology. In: Gartland KMA, Davey Humana Totowa MR (eds) Agrobacterium Protocols, vol 44. Inc Press, NJ, pp 9–13
Bromfield ESP, Tambong JT, Cloutier S, Prévost D, Laguerre G, van Berkum P, Tran-Thi TV, Assabgui R, Barran LR (2010) Ensifer, Phyllobacterium and Rhizobium species occupy nodules of Medicago sativa (alfalfa) and Melilotus alba (sweet clover) grown at a Canadian site without a history of cultivation. Microbiology 156:505–520
Bruning B, Rozema J (2012) Symbiotic nitrogen fixation in legumes: perspectives for saline agriculture. Environ Exp Bot 2587:1–10
Cacciari I, Di Mattia E, Quatrini P, Moscatelli MC, Grego S, Lippi D, De Paolis MR (2003) Réponses adaptatives des isolats de Rhizobium aux stress. In: Grouzis M, Le Floc’h E (eds) Un arbre au désert, Acacia raddiana. IRD, Paris, pp 183–200
Chaabena A, Abdelguerfi A (2007) Aperçu sur les cultures fourragères au sahara septentrional est. Annu Fac Sci Sci Ingé 1(2):13–20
Chaabena A, Laouar M, Guediri O, Benmoussa A, Abdelguerfi A (2011) Quelques populations sahariennes de luzerne pérenne (Medicago sativa L.) face à un stress hydrique. Rev Bio Res 1(2):36–48
Chafi MH, Bensoltane A (2009) Vicia faba (L), a source of organic and biological manure for the Algerian arid regions. World J Agric Sci 5(6):698–706
Chouaki S, Bessedik F, Chebouti A, Maamri F, Oumata S, Khaldoun S, Hamana M-F, Douzene M, Bellah F, Kheldoun A (2006) Deuxième rapport national sur l’état des ressources phytogénétiques. Institut national de la recherche agronomique d’Algérie (INRA) et l’Organisation des nations unies pour l’alimentation et l’agriculture (FAO), pp 9–10
Djedidi S, Yokoyama T, Ohkama-Ohtsu N, Chandra-Prasad-Risal C, Abdelly C, Hitoshi-Sekimoto H (2011) Stress tolerance and symbiotic and phylogenic features of root nodule bacteria associated with Medicago species in different bioclimatic regions of Tunisia. Microbes Environ 26(1):36–45. doi:10.1264/jsme2.ME10138
Djennane A (1990) Les systèmes agricoles oasiens: constat de situation des zones sud des oasis algériennes. Options Méditerr Sér A Mediterr Semin 11:29–32
Drevon JJ, Abdelly C, Amarger N, Aouani EA, Aurag J, Jebara M, Gherbi H, Liuch C, Payre H, Schump O, Sifi B, Trabelsi M (2004) FABAMED interdisciplinary strategy to improve symbiotic nitrogen fixation of legumes in the Mediterranean basin. In: Serraj R (ed) Symbiotic nitrogen fixation prospects for enhanced application in tropical agriculture. Oxford and IBH Publishing, New Delhi, pp 223–232
Elbanna K, Elbadry M, Gamal-Eldin H (2009) Genotypic and phenotypic characterization of rhizobia that nodulate snap bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) in Egyptian soils. Syst Appl Microbiol 32(7):522–530
Elboutahiri N, Thami-Alami I, Udupa SM (2010) Phenotypic and genetic diversity in Sinorhizobium meliloti and S. medicae from drought and salt affected regions of Morocco. BMC Microbiol 10(15):1–13
Ferry M, Toutain M (1990) Concurrence et complémentarité des espèces végétales dans les oasis. Options Méditerr Sér A Mediterr Semin 11:261–270
Fitouri Dhane S, Ben Jeddi F, Zribi K, Rezgui S, Mhamdi R (2012) Effet de l’inoculation par une souche osmotolerante de Rhizobium sullae sur la croissance et la production en proteine du sulla (Sulla coronarium L.) sous déficit hydrique. J Appl Biosci 51:3642–3651
Gnat S, Wójcik M, Wdowiak-Wróbel S, Kalita M, Ptaszyńska A, Małek W (2014) Phenotypic characterization of Astragalus glycyphyllos symbionts and their phylogeny based on the 16S rDNA sequences and RFLP of 16S rRNA gene. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 105:1033–1048. doi:10.1007/s10482-014-0163-y
Hartmann AM, Rodiguez-Navarro DN, Temprano Vera F, Cleyet-Marel J-C, Priny G, Fernández-López M, Toro N, Moënne-Loccoz Y (2006) Nodulating Symbiotic Bacteria and Soil Quality. In: Bloem J, Hopkins D W, Benedetti A (eds) Microbiological methods for assessing soil quality. pp 231–234
Janati A (1990) Les cultures fourragères dans les oasis. Options Méditérr A1:165–167
Jebara M, Drevon JJ, Aouani ME (2001) Effects of hydroponic culture system and NaCl on interactions between common bean lines and native rhizobia from Tunisian soils. Agronomy 21:601–605
Jordan DC (1984) Rhizobiaceae. In: Krieg N R, Holt J G (Eds) Bergey’s Manual of systematic bacteriology. The Williams and Wilkins Baltimore, pp 234–242
Kersters K, Hinz KH, Hertle A, Segers P, Lievens A, Siegmann O, De Ley J (1984) Bordetella avium sp. Nov., Isolated from the respiratory tracts of Turkeys and other birds. Int J Syst Bacteriol 34(1):56–70
Koull K, Kherraze MH, Lakhdari K, Benzaoui T, Helimi S, Laouissat MS, Kherfi Y, Bougafla A, Mimouni F, Lakhdari K, Mezrag M, Benazzouz MT (2013) Eaux d’irrigation et salinisation des sols des perimetres irrigues dans la vallee de l’oued righ. J Alg Rég Arid 12:97–102
Le Houérou HN (1975) Problèmes et potentialités des terres arides de l’Afrique du Nord. Options Méditerr Sér A Mediterr Semin 26:17–32
Maâtallah J, Berraho EB, Muñoz S, Sanjuan J, Lluch C (2002) Phenotypic and molecular characterization of chickpea rhizobia isolated from different areas of morocco. J Appl Microbiol 93:531–540
Merabet C, Martens M, Mahdhi M, Zakhia F, Sy A, Le Roux C, Domergue O, Coopman R, Bekki A, Mars M, Willems A, de Lajudie P (2010) Multilocus sequence analysis of root nodule isolates from Lotus arabicus (Senegal), Lotus creticus, Argyrolobium uniflorum and Medicago sativa (Tunisia) and description of Ensifer numidicus sp. nov. and Ensifer garamanticus sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:664–674
Messar EM (1996) Le secteur phœnicicole algérien. Options méditerranéennes CIHEM and Estación Phoenix, 24
Mnasri B, Aouani ME, Mhamdi R (2007a) Nodulation and growth of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) under water deficiency. Soil Biol Biochem 39:1744–1750
Mnasri B, Mrabet M, Laguerre G, Aouani ME, Mhamdi R (2007b) Salt-tolerant rhizobia isolated from a Tunisian oasis that are highly effective for symbiotic N2-fixation with Phaseolus vulgaris constitute a novel biovar (bv. mediterranense) of Sinorhizobium meliloti. Arch Microbiol 187(1):79–85. doi:10.1007/s00203-006-0173-x
Murugesan S, Manoharan C, Vijayakumar R, Panneerselvam A (2010) Isolation and characterization of Agrobacterium rhizogenes from the root nodules of some leguminous plants. Int J Microbiol Res 1(3):92–96
Palma F, Tejera NA, Lluch C (2013) Nodule carbohydrate metabolism and polyols involvement in the response of Medicago Sativa to salt stress. Environ Exp Bot 85:43–49
Priefer UB, Aurag J, Boesten B, Bouhmouch I, Defezy R, Filali-Mltouf A, Miklis M, Moawad H, Mouhsin B, Prell J, Schlüter A, Senatore B (2001) Characterization of Phaseolus symbionts isolated from Mediterranean soils and analysis of genetic factors related to pH tolerance. J Biotechnol 91:223–236
Rejii M, Mahdhi M, Domínguez-Núñez JA, Mars M (2014) the phenotypic, phylogenetic and symbiotic characterization of rhizobia nodulating Lotus sp. in Tunisian arid soils. Ann Microbiol 64:355–362. doi:10.1007/s13213-013-0670-5
Riou C (1990) Bioclimatologie des oasis. Options Méditerr Sér A Mediterr Semin 11:207–208
Rome S, Fernandez MP, Brunel B, Normand P, Cleyet-Marel J-C (1996) Sinorhizobium medicae sp. nov., isolated from annual Medicago spp. Int J Syst Bacteriol 46(4):972–980
Serraj R, Adu-Gyamfi J, Rupela O P, Drevon J J (2004) Symbiotic Nitrogen Fixation: Prospects for Enhanced Application in Tropical Agriculture. In: Serraj R (ed) International Crops Research Institue for the Semi-Arid Tropics. Oxford and IBH Publishing, pp 67–97
Shamseldin A, Moawad H, Abd El-Rahim WM, Sadowsky MJ (2013) Near-full length sequencing of 16S rDNA and RFLP indicates that Rhizobium etli is the dominant species nodulating Egyptian winter Berseem clover (Trifolium alexandrinum L.). Syst Appl Microbiol. doi:10.1016/j.syapm.2013.08.002
Shetta ND, Al-Shaharani TS, Abdel-Aal M (2011) Identification and characterization of Rhizobium associated with woody legume trees grown under Saudi Arabia condition. Am J Agric Environ Sci 10(3):410–418
Somasegaran P, Hoben HG (1985) Methods in Legume Rhizobium Technology. United States Agency for International Development (USAID), pp 69–70
Tabouche N, Achour S (2004) Etude de la qualité des eaux souterraines de la région orientale du sahara septentrional algérien. Larhyss J 03:99–113
Thami-Alami I, Elboutahiri N, Udupa SM (2010) Variability in natural population of Sinorhizobium meliloti in Morocco. Options Méditerr Sér A Mediterr Semin 92:265–269
Toutain G (1974) Conservation des sols en palmeraies sahariennes et bordières au Sahara. Options Méditerr Sér A Mediterr Semin 25:65–69
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16S Ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173:697–703
Yan AM, Wang ET, Kan FL, Tan ZY, Sui XH, Reinhold-Hurek B, Chen WX (2000) Sinorhizobium meliloti associated with Medicago sativa and Melilotus spp. In arid saline soils in Xinjiang, China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:1887–1891
Zahran HH (1997) Diversity, adaptation and activity of the bacterial flora in saline environments. Biol Fertil Soils 25:211–223
Zahran HH (1999) Rhizobium-legume symbiosis and nitrogen fixation under severe conditions and in an arid climate. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63(4):968–989
Zahran HH (2001) Rhizobia from wild legumes: diversity, taxonomy, ecology, nitrogen fixation and biotechnology. J Biotechnol 91:143–153
Zakhia F, Jeder H, Domergue O, Willems A, Cleyet-Marel J-C, Gillis M, Dreyfus B, de Lajudie P (2004) Characterisation of wild legume nodulating bacteria (LNB) in the infra-arid zone of Tunisia. Syst Appl Microbiol 27:380–395
Zhang X, Harper R, Karsist M, Lindstrom K (1991) Diversity of rhizobium bacteria isolated from the root nodules of leguminous trees. Int J Syst Bacteriol 41(1):104–113
Zribi K, Jeidi N, Mhamdi R, Aouani ME, Huguet T (2004) Diversité génétique et polymorphisme symbiotique de Sinorhizobium meliloti nodulant Medicago truncatula en sols tunisiens des régions arides. Options Méditerr Sér A Mediterr Semin 62:149–152
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baba Arbi, S., Chekireb, D., Quatrini, P. et al. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of root nodules rhizobia of Medicago littoralis Rhode and Melilotus indicus (L.) All. growing in the Oasis of Touggourt, Oued Righ Valley, in the Algerian Sahara. Symbiosis 66, 75–87 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-015-0336-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-015-0336-0