Abstract
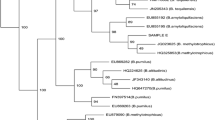
Bacillus pumilus was isolated from surface-sterilized tissues of the medicinal plant Ocimum sanctum. Scanning electron microscopic (SEM) imaging confirmed the presence of a rod shaped bacterium within the plant tissues. The bacterium was identified as B. pumilus by biochemical analyses and 16S rRNA gene sequencing. In vitro analyses indicate that the isolated strain of B. pumilus was endowed with multiple plant growth promotion (PGP) traits such as phosphate solubilization and the production of indole acetic acid (IAA), siderophore and hydrogen cyanide (HCN). Phosphate solubilization (37.3 μg ml−1) and IAA production (36.7 μg ml−1) by the isolate was found to reach a maximum after 60 h of incubation. Siderophore mediated iron sequestration by B. pumilus may confer a competitive advantage to the host with respect to pathogen inhibition. Siderophore produced by the isolate was found to be of a trihydroxamate type with hexadentate nature. The B. pumilus isolate also exhibited cellulolytic, proteolytic and chitinolytic activity. Cell free supernatant, culture filtrates of the isolate were found to suppress the growth of fungal phytopathogens. The culture filtrate retained its antifungal activity even after exposure to heat. In addition to PGP, the isolate exhibited probiotic properties such as acid tolerance (pH2), bile salt tolerance (2 %), auto-aggregation, antibiotic resistance and the absence of haemolytic activity. These finding suggest the possibility of utilizing this endophytic strain of B. pumilus as a bioinoculant to enhance plant growth and also as a probiotic.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahire JJ, Patil KP, Chaudari BL, Chincholkar SB (2011) A potenetial probiotic culture ST2 produces siderophore 2,3-dihydroxybenzoylserine under intestinal conditions. Food Chem 127:387–393
Baakza A, Dave BP, Dube HC (2004) Chemical nature, ligand denticity and quantification of fungal siderophores. Indian J Exp Biol 42:96–105
Babu TG, Nithyanand C, Babu NKC, Pandian SK (2009) Evaluation of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide as a potential short-term preservative agent for stripped goat skin. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:901–907
Bakker AW, Shipper B (1987) Microbial cyanide production in the rhizosphere in relation to potato yield reduction and Pseudomonas sp. mediated plant growth stimulation. Soil Biol Biochem 19:451–457
Boris S, Suárez JE, Barbés C (1997) Characterization of the aggregation promoting factor from Lactobacillus gasseri, a vaginal isolate. J Appl Microbiol 83:413–420
Brenner DJ, Krieg NR, Staley JT (2005) The Proteobacteria. In: George GM (ed) Bergey’s manual of systematic Bacteriology, vol. II. Springer pub, New York, pp 491–545
Del Re B, Sgorbati B, Miglioli M, Palenzona D (2000) Adhesion, autoaggregation and hydrophobicity of 13 strains of Bifidobacterium longum. Lett Appl Microbiol 31:438–442
Dileep Kumar BS, Dube HC (1992) Seed bacterization with a Pseudomonas for enhanced plant growth, yield and disease control. Soil Biol Biochem 24:539–542
Dutta S, Kundu S, Chakraborty MR, Ojha S, Chakrabarti J, Chatterjee NC (2006) Production and optimization of Fe(III) specific ligand, the siderophore of soil inhabiting and wood rotting fungi as deterrent to plant pathogens, Acta Phytopathol. Entomol Hungarica 41:237–248
Erkkila S, Petaja E (2000) Screening of commercial meat starter cultures at low pin the presence of bile salts for potential probiotic use. J Meat Sci 55:297–300
FAO/WHO (2002) Guidelines for the evaluation of probiotics in food. Report of a joint FAO/WHO working group on drafting guidelines for the evaluation of probioticsin food, London
Forchetti G, Masciarelli O, Alemano S, Alvarez D, Abdala G (2007) Endophytic bacteria in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.): isolation, characterization, and production of jasmonates and abscisic acid in culture medium. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76:1145–1152
Gaur AC (1990) Physiological functions of phosphate solubilizing micro-organisms. In: Gaur AC (ed) Phosphate solubilizing microorganisms as biofertilizers. Omega Scientific, New Delhi, pp 16–72
Geetha R, Falguni S, Anjana JD, Archana G (2008) Enhanced growth and nodulation of pigeon pea by co-inoculation of Bacillus strains with Rhizobium sp. Biores Technol 99:4544–4550
González FI, Guerrero CA, Quijano G (2011) The benefits of probiotics on human health. J Microbial Biochem Technol S1:003. doi:10.4172/1948-5948.S1-003
Gray EJ, Smith DL (2005) Intracellular and extracellular PGPR: Commonalities and distinctions in the plant-bacterium signaling processes. Soil Biol Biochem 37:395–412
Hontzeasa N, Zoidakisb GBR, Abu-Omarc MM (2004) Expression and characterization of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase from the rhizobacterium Pseudomonas putida UW4: A key enzyme in bacterial plant growth promotion. Biochim Biophys Acta 703:11–19
Hurek BR, Hurek T (2011) Living inside plants: Bacterial endophytes. Curr Opin Plant Biol 14:1–9
Jalal MAF, Helm D (1990) Isolation and spectroscopic identification of fungal siderophores. In: Winklemann G (ed) Handbook of microbial iron chelates. CRC Press, Bacon Raton, pp 235–269
Jha PN, Kumar A (2007) Endophytic colonization of Typha australis by a plant growth-promoting bacterium Klebsiella oxytoca strain. J Appl Microbiol 103:1311–1320
Kohler J, Hernandez JA, Caravaca F, Roldan A (2009) Induction of antioxidant enzymes is involved in the greater effectiveness of a PGPR versus AM fungi with respect to increasing the tolerance of lettuce to severe salt stress. Environ Exp Bot 65:245–252
Krohn K, Michel A, Florke U, Aust HJ, Drager S, Schulz B (1994) Palmarumycins CP1–CP4 from Coniothyrium palmarum: isolation, structure elucidation and biological activity. Liebigs Annalen Der Chemie 1093–1097
Leroux P, Chapeland F, Desbrosses D, Gredt M (2002) Patterns of cross-resistance to fungicide in Botryotinia fuckeliana (Botrytis cinerea) isolates from French vineyards. Crop Prot 18:687–692
Liu X, Jia J, Atkinson S, Camara M, Gao K, Li H, Cao J (2010) Biocontrol potential of an endophytic Serratia sp. G3 and its mode of action. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 26:1465–1471
Matzanke BF (1990) Structure, coordination and function of microbial iron. In: Winklemann G (ed) Handbook of microbial iron Chelates. CRC Press, Bacon Raton, p 15
Miller KI, Qing C, Sze DMY, Roufogalis BD, Neilan BA (2012) Culturable Endophytes of Medicinal Plants and the Genetic Basis for their Bioactivity. doi:10.1007/s00248-012-0044-8
Nimnoi P, Pongsilp N, Lumyong S (2010) Endophytic actinomycetes isolated from Aquilaria crassna Pierre ex Lec and screening of plant growth promoters production. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 26:193–203
Oehrle NW, Karr DB, Kremer RJ, Emerich DW (2000) Enhanced attachment of Bradyrhizobium japonicum to soybean through reduced root colonization of internally seed borne microorganisms. Can J Microbiol 46:600–606
Patten CL, Glick BR (2002) Role of Pseudomonas putida indole acetic acid in development of the host plant root system. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:3795–3801
Payne SN (1994) Detection, isolation and characterization of siderophores. Method Enzymol 235:329–344
Prakash P, Gupta N (2005) Therapeutic uses of Ocimum sanctum Linn (tulsi) with a note on eugenol and its pharmacological actions: A short review. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 49:125–131
Puente ME, Li CY, Bashan Y (2009) Endophytic bacteria in cacti seeds can improve the development of cactus seedlings. Environ Exp Bot 66:402–408
Sanders ME (2003) Probiotics: Considerations for human health. Nutr Rev 61:91–99
Schallmey M, Singh A, Ward O (2004) Development of use of Bacillus species for industrial production. Can J Microbiol 50:1–17
Schwyn B, Neilands JB (1987) Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal Biochem 160:47–56
Sieber TN, Grunig CHR (2006) Biodiversity of fungal root-endophyte communities and populations, in particular of the dark septate endophyte Phialocephala fortinii s.1. In: Schulz BJE, Boyle CHJC, Sieber TN (eds) Microbial root endophytes. Springer, Berlin, pp 107–132
Strobel G, Daisy B (2003) Bioprospecting for microbial endophytes and their natural products. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 67:491–502
Tejera N, Ortega E, Rodes R, Lluch C (2006) Nitrogen compounds in the apoplastic sap of sugarcane stem: Some implications in the association with endophytes. J Plant Physiol 163:80–85
Tejesvi MV, Pirttila AM (2011) Potential of tree endophytes as sources for new drug compounds. In: Pirttila AM, Frank AC (eds) Endophytes of forest trees: Biology and applications. Forestry Sciences, Finland, pp 295–311
Tiwari R, Kalra A, Darokar MP, Chandra M, Aggarwal N, Singh AK, Khanuja SPS (2010) Endophytic bacteria from Ocimum sanctum and their yield enhancing capabilities. Curr Microbiol 60:167–171
Tiwari S, Singh P, Tiwari R, Meena KK, Yandigeri M, Singh DP, Arora DK (2011) Salt-tolerant rhizobacteria-mediated induced tolerance in wheat (Triticum aestivum) and chemical diversity in rhizosphere enhance plant growth. Biol Fertil Soils doi. doi:10.1007/s00374-011-0598-5
Wang H, Peixia J, Yuan L, Zhiyong R, Ruibo J, Xin-Hui X, Kai L, Dong W (2009) Optimization of culture conditions for violacein production by a new strain of Duganella sp. B2. Biochem Eng J 44:119–124
Winkelmann G (2002) Microbial siderophore-mediated transport. Biochem Soc Transac 30:691–696
Zhao GZ, Li J, Qin S, Huang HY, Zhu WY, Xu LH, Li WJ (2010) Streptomyces artemisiae sp. nov., isolated from surface-sterilized tissue of Artemisia annua L. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:27–32
Zahin M, Hasan S, Aqil F, Khan MSA, Husain F, Ahmad I (2010) Screening of certain medicinal plants from India for their anti-quorum sensing activity. Indian J Exp Biol 48:1219–1224
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Thiagarajar college management for providing all the necessary infrastructure facilities. Authors acknowledge the financial support from University Grants Commission (UGC) under Rajiv Gandhi National Fellowship and Maulana Azad National Fellowship programme. Assistance extended by Central Electrochemical Research Institute (CECRI), Karaikudi for SEM analysis is acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murugappan, R., Begum, S.B. & Roobia, R.R. Symbiotic influence of endophytic Bacillus pumilus on growth promotion and probiotic potential of the medicinal plant Ocimum sanctum . Symbiosis 60, 91–99 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-013-0244-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-013-0244-0