Abstract
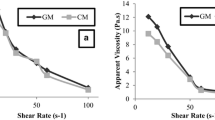
Melon seed milk (MSM) powder was produced by aiming to get alternative vegetable milk from crushed Kırkağaç (Cucumis melo subsp. melo cv. Kırkağaç) and Çeşme (C. melo subsp. melo cv. Çeşme) type melon seeds. MSM was converted to powder form via spray dryer at inlet air temperature of 150 °C, air flow rate of 473 l · h−1, aspiration ratio of 24 m3 · h−1and feed flow rate of 8 ml · min−1 in order to extend the shelf life and usage area. The moisture content and water activity of samples changed in range of 2.1 to 2.4 % and 0.260 to 0.310, respectively. Bulk densities and the tapped densities of powders were ranged from 340 to 360 kg · m−3 and 730 and 740 kg · m−3. MSM powders showed poor flow behavior as determined from Carr Index. The particle densities of powders ranged between and 1069 kg · m−3. Wettability time of powders was found as 7 s. The Bingham model was the best model fitted to rheological data of MSM beverages. Sensory evaluation test results showed that, the beverage obtained from reconstituted Kırkağaç powder achieved the highest score by panelists.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aidoo H, Sakyi-Dawson E, Tano-Debrah K, Saalia FK (2010) Development and characterization of dehydrated peanut–cowpea milk powder for use as a dairy milk substitute in chocolate manufacture. Food Res Int 43:79–85. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2009.08.018
Akubor PI (1998) Physicochemical and sensory characteristics of melon seed milk. J Food Sci Technol 35:93–97
Akubor PI, Ogbadu RL (2003) Effects of processing methods on the quality and acceptability of melon milk. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 58:1–6. doi:10.1023/A:1024063105507
Akubor PI, Achi OK, Offonry SU (2002) Influence of storage on chemical, microbial and consumer acceptability of a milk-like product made from melon seeds. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 57(2):91–196. doi:10.1023/A:1015249906416
AOAC (2005) In: Horwitz W, Latimer G (eds) Official Methods of Analysis, 18th edn. AOAC International, Gaithersburg
Bae KE, Lee SJ (2008) Microencapsulation of avocado oil by spray drying using whey protein and maltodextrin. J Microencapsul 25(8):549–560. doi:10.1080/02652040802075682
Barbosa-Canovas GV, Ortega-Rivas E, Juliano P, Yan H (2005) Food powders: physical properties, processing, and functionality. Kluwer Academic/Plenu, New York
Belewu MA, Belewu KY (2007) Comparative physico-chemical evaluation of tiger-nut, soybean and coconut milk sources. Int J Agric Biol 5:785–787, 1560-8530/2007/09-5-785-787
Cano-Chauca M, Stringheta PC, Ramos AM, Cal-Vidal J (2005) Effect of the carriers on the microstructure of mango powder spray drying and its functional characterization. Innov Food Sci Emerg 6:420–428. doi:10.1016/j.ifset.2005.05.003
Carr RL (1965) Evaluating flow properties of solids. Chem Eng 72:163–168
De Mello LSM, Bora SP, Narain N (2001) Fatty and amino acids composition of melon (Cucumis melo Var. saccharinus) seeds. J Food Compos Anal 14:69–74. doi:10.1006/jfca.2000.0952
Deboni TM, Bündchen M, Junior CV, Hotza D, Piletti R, Quadri MGN (2013) Effect of the processing steps on cactus juice production. Food Bioprocess Technol 7(4):990–1000. doi:10.1007/s11947-013-1098-4
Deswal A, Deora NS, Mishra HN (2014) Effect of concentration and temperature on the rheological properties of oat milk. Food Bioprocess Technol 7(8):2451–2459. doi:10.1007/s11947-014-1332-8
Diarra K, Nong ZG, Jie C (2005) Peanut milk and peanut milk based products production: a review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 45:405–423. doi:10.1080/10408390590967685
FAO (2015) Food and Agriculture Organization/WHO (World Health Organization), http://faostat3.fao.org/browse/Q/QL/E. Accessed 04 Dec 2015
Fazaeli M, Emam-Djomeh Z, Ashtari AK, Omid M (2012) Effect of spray drying conditions and feed composition on the physical properties of black mulberry juice powder. Food Bioprocess Technol 90:667–675. doi:10.1016/j.fbp.2012.04.006
Fitzpatrick JJ, Iqbal T, Delaney C, Twomey T, Keogh MK (2004) Effect of powder properties and storage conditions on the flowability of milk powders with different fat contents. J Food Eng 64(4):435–444. doi:10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2003.11.011
Goula AM, Adamopoulos KG (2008) Effect of maltodextrin addition during spray drying of tomato pulp in dehumidified air: I. Drying kinetics and product recovery. Dry Technol 26:714–725. doi:10.1080/07373930802046369
Heyman MB (2006) Lactose intolerance in infants, children, and adolescents. Pediatrics 118(3):1279–1286. doi:10.1542/peds.2006-1721
Horne DS (2011) Viscosity of milk and its concentrates. In: Dickinson E, Walstra P (eds) Food colloids and polymers: Stability and mechanical properties. Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge, pp 260–266
Jinapong N, Suphantharika M, Jammong P (2008) Production of instant soymilk powders by ultrafiltration, spray drying and fluidized bed agglomeration. J Food Eng 84:194–205. doi:10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2007.04.032
Karakaya S, Kavas A, Nehir-El S, Gündüç N, Akdoğan L (1995) Nutritive value of a melon seed beverage. Food Chem 52:139–141. doi:10.1016/0308-8146(94)P4193-J
Klinkesorn U, Sophanodora P, Chinachoti P, Decker EA, Mcclements DJ (2006) Characterization of spray-dried tuna oil emulsified in two-layered interfacial membranes prepared using electrostatic layer-by-layer deposition. Food Res Int 39:449–457. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2005.09.008
Koç M, Koç B, Sakin-Yılmazer M, Kaymak-Ertekin F, Susyal G, Bağdatlıoğlu N (2011) Physicochemical characterization and oxidative stability of microencapsulated egg powder by spray drying. Dry Technol 29(7):780–788. doi:10.1080/07373937.2010.538820
Koç B, Sakin-Yılmazer M, Kaymak-Ertekin F, Balkır P (2014) Physical properties of yoghurt powder produced by spray drying. J Food Sci Technol Mys 51(7):1377–1383. doi:10.1007/s13197-012-0653-8
Koç M, Zungur A, Güngör Ö, Yalçın B, Selek İ, Kaymak-Ertekin F, Ötleş S (2015) Microencapsulation of extra virgin olive oil by spray drying: effect of wall materials composition, process conditions and emulsification method on microencapsulation efficiency, particle size and oxidative stability of microcapsules. Food Bioprocess Technol 8:301–318. doi:10.1007/s11947-014-1404-9
Kowalska J, Lenart A (2005) The influence of ingredients distribution on properties of agglomerated cocoa products. J Food Eng 68(2):155–161. doi:10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2004.05.028
Martinelli L, Gabas AL, Telis-Romero J (2007) Thermodynamic and quality properties of lemon juice powder as affected by maltodextrin and arabic gum. Dry Technol 25:2035–2045. doi:10.1080/07373930701728836
Rao MA (2007) Application of rheology to fluid food handling and processing. In: Barbosa-Cànovas GV (ed) Rheology of Fluid and Semisolid Foods, Food Engineering Series. Springer, New York, pp 427–469, ISBN: 978-0-387-70929-1
Rao VNM, Hamann DD, Humphries EG (1975) Flow behavior of sweet potato puree and its relation to mouthfeel quality. J Texture Stud 6(2):197–209. doi:10.1111/j.1745-4603.1975.tb01248.x
Sakın-Yılmazer M, Koç B, Balkır P, Kaymak-Ertekin F (2014) Rheological behaviour of reconstituted yoghurt powder-an optimization study. Powder Technol 266(15):433–439. doi:10.1016/j.powtec.2014.06.060
Samaram S, Mirhosseini H, Tan CP, Ghazali HM (2014) Ultrasound-assisted extraction and solvent extraction of papaya seed oil: crystallization and thermal behavior, saturation degree, color and oxidative stability. Ind Crop Prod 52:702–708. doi:10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.11.047
Sanful RE (2009) Production and sensory evaluation of tigernut beverages. Pak J Nutr 8(5):688–690. doi:10.3923/pjn.2009.688.690
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Highlights:
• This study offers a different perspective for food wastes and by-products
• Melon seed milk was converted to powder form without any additives
• The limited shelf life of melon seed milk was extended by producing powder form
• Melon seed milk powder was able to consume by vegans and lactose-intolerant people
• In this study, melon seed was shown to be a new source for plant derived milk
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zungur Bastıoğlu, A., Tomruk, D., Koç, M. et al. Spray dried melon seed milk powder: physical, rheological and sensory properties. J Food Sci Technol 53, 2396–2404 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-016-2214-z
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-016-2214-z