Abstract
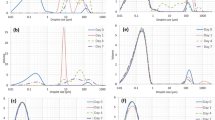
There is a continuous search for suitable emulsifiers of natural origin that can be used in food and pharmaceutical emulsions. Bambara groundnut is an important source of nutrient in many African communities with rich blend of high protein and carbohydrate composition which makes it a potential candidate as an emulsifier, and where it can serve additional nutritional role in such emulsions. The current study aimed at investigating the stability of Bambara groundnut-stabilized emulsions physicochemical changes. The stability of the emulsions increased significantly with the speed of homogenization (up to 15, 000 rpm beyond which the difference in stability was not significant). Compared to control (pH 7), emulsion stability decreased with acidity (about 80 % stability by Day-5 at pH 2) and alkalinity (90 % stability at pH 10 by Day 5) with corresponding increase in droplet size. Emulsion stability increased with increasing NaCl concentration (65 % stability at 2 % NaCl compared to 82 % stability at 10 % NaCl). Stability however decreased sharply with increasing concentration of vinegar (45 % stability at 10 % vinegar compared to 81 % stability at 2 % vinegar). The Bambara groundnut flour-stabilized emulsions were more stable (ordinarily and in the presence of the additives) than the Bambara groundnut starch-stabilized ones. Stability values in the Bambara groundnut flour emulsions, in most cases, double those for Bambara groundnut starch.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adebowale KO, Afolabi TA, Lawal OS (2002) Isolation, chemical modification and physicochemical characterisation of Bambarra groundnut (Voandzeia subterranean) starch and flour. Food Chem 78:305–311
Alakali JS, Irtwange SV, Mzer MT (2010) Quality evaluation of beef patties formulated with bambara groundnut (Vigna subterranean L.) seed flour. Meat Sci 85:215–223
Amarteifio JO, Sawula G, Gibbons MRD (1997) Comparison of four landraces of bambara groundnuts. Trop Sci 37:143–145
Aremu MO, Olaofe O, Akintayo TE (2006) A comparative study on the chemical and amino acid composition of some Nigerian under-utilized legume flours. Pak J Nutr 5(1):34–38
Aronson MP, Petko MF (1993) Highly concentrated water-in-oil emulsions: influence of electrolyte on their properties and stability. J Colloid Interface Sci 159(1):134–149
Chau CF, Cheung PC, Wong YS (1997) Functional properties of protein concentrates from three Chinese indigenous legume seeds. J Agric Food Chem 45(7):2500–2503
Chel-Guerrero L, Pérez-Flores V, Betancur-Ancona D, Davila-Ortiz G (2002) Functional properties of flours and protein isolates from Phaseolus lunatus and Canavalia ensiformis seeds. J Agric Food Chem 50(3):584–591
Dickinson E, Phillips GO, Williams PA (2009) Hydrocolloids and emulsion stability. Handbook of hydrocolloids, Woodhead Publishing, 23–49
Doku VE (1996). Problems and prospects for the improvement of bambara groundnut. In Proceedings of the International Bambara Groundnut Symposium, University of Nottingham, UK (pp. 19–27)
Dumay E, Lambert C, Funtenberger S, Cheftel JC (1996) Effects of high pressure on the physico-chemical characteristics of dairy creams and model oil/water emulsions. LWT Food Sci Technol 29(7):606–625
Floury J, Desrumaux A, Lardieres J (2000) Effect of high-pressure homogenization on droplet size distributions and rheological properties of model oil-in-water emulsions. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 1(2):127–134
Floury J, Desrumaux A, Axelos MA, Legrand J (2003) Effect of high-pressure homogenization on methylcellulose as food emulsifier. J Food Eng 58(3):227–238
Fortuny M, Oliveira CB, Melo RL, Nele M, Coutinho RC, Santos AF (2007) Effect of salinity, temperature, water content, and pH on the microwave demulsification of crude oil emulsions. Energy and Fuels 21(3):1358–1364
Gabriel EG, Jideani VA, Ikhu-Omoregbe DI (2013) Investigation of the emulsifying properties of Bambara groundnut flour and starch. Int J Agric Biosyst Sci Eng 7(11):508–516
Galazka VB, Dickinson E, Ledward DA (1999) Emulsifying behaviour of 11S globulin (Vicia faba) in mixtures with sulphated polysaccharides: comparison of thermal and high-pressure treatments. Food Hydrocoll 13(5):425–435
Guzey D, Kim HJ, McClements DJ (2004) Factors influencing the production of o/w emulsions stabilized by β-lactoglobulin–pectin membranes. Food Hydrocoll 18:967–975
Makri E, Papalamprou E, Doxastakis G (2005) Study of functional properties of seed storage proteins from indigenous European legume crops (lupin, pea, broad bean) in admixture with polysaccharides. Food Hydrocoll 19(3):583–594
Martini S, Tippetts M (2008) Effect of processing conditions on the crystallization behavior and destabilization kinetics of oil-in-water emulsions. J Am Oil Chem Soc 85(2):119–128
McClements DJ (2005) Food emulsions: principles, practice, and techniques. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Mengual O, Meunier G, Cayré I, Puech K, Snabre P (1999a) TURBISCAN MA 2000: multiple light scattering measurements for concentrated emulsion and suspension instability analysis. Talanta 50(2):445–456
Mengual O, Meunier G, Cayre I, Puech K, Snabre P (1999b) Characterisation of instability of concentrated dispersions by a new optical analyzer: the Turbiscan MA 1000. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 152:111–123
Mirhosseini H, Tan CP, Hamid NSA, Yosuf S (2008) Effect of Arabic gum, xanthan gum and orange oil contents on ζ- potential, conductivity, stability, size index and pH of orange beverage emulsion. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 315:47–56
Mpotokwane SM, Gaditlhatlhelwe E, Sebaka A, Jideani VA (2008) Physical properties of bambara groundnuts from Botswana. J Food Eng 89:93–98
Narayana K, Narasinga Rao MS (1982) Functional properties of raw and heat processed winged bean (Psophocarpus tetragonolobus) flour. J Food Sci 47(5):1534–1538
Neumann HJ, Paczynska-Lahme B (1996) Stability and demulsification of petroleum emulsions. In Interfaces, Surfactants and Colloids in Engineering, Steinkopff pp. 101–104
Rachie KO, Roberts LM (1974) Grain legumes in the lowland tropics. Adv Agron 26:127–132
Ramanatham G, Ran LH, Urs LN (1978) Emulsification properties of groundnut protein. J Food Sci 43(4):1270–1273
Sathe SK, Deshpande SS, Salunkhe DK (1982) Functional properties of lupin seed (Lupinus mutabilis) proteins and protein concentrates. J Food Sci 47(2):491–497
Taha EI, Samy AM, Kassem AA, Khan MA (2005) Response surface methodology for the development of self-nanoemulsified drug delivery system (SNEDDS) of all-trans-retinol acetate. Pharm Dev Technol 10(3):363–370
Tornberg E, Hermansson AM (1977) Functional characterization of protein stabilized emulsions: effect of processing. J Food Sci 42(2):468–472
Walstra P (1993) Principle of emulsion formation. Chem Eng Sci 48:333–349
Wang B, Li D, Wang LJ, Adhikari B, Shi J (2010) Ability of flaxseed and soybean protein concentrates to stabilize oil-in-water emulsions. J Food Eng 100:417–426
White DA, Fisk ID, Mitchell JR, Wolf B, Hill SE, Gray DA (2008) Sunflower-seed oil body emulsions: rheology and stability assessment of a natural emulsion. Food Hydrocoll 22:1224–1232
Yang F, Liu S, Xu J, Lan Q, Wei F, Sun D (2006) Pickering emulsions stabilized solely by layered double hydroxides particles: the effect of salt on emulsion formation and stability. J Colloid Interface Sci 302(1):159–169
Yang F, Niu Q, Lan Q, Sun D (2007) Effect of dispersion pH on the formation and stability of Pickering emulsions stabilized by layered double hydroxides particles. J Colloid Interface Sci 306(2):285–295
Yu J, Ahmedna M, Goktepe I (2007) Peanut protein concentrate: production and functional properties as affected by processing. Food Chem 103(1):121–129
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fasinu, E.G., Ikhu-Omoregbe, D.I.O. & Jideani, V.A. Influence of selected physicochemical factors on the stability of emulsions stabilized by Bambara groundnut flour and starch. J Food Sci Technol 52, 7048–7058 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-1818-z
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-1818-z