Abstract
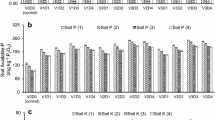
Organic agriculture is gaining a gradual momentum across the world for improving nutritional quality of food, restoring soil health, generating rural economy, and creating better environmental conditions. Organic agriculture can foster sustainability in subhumid tropical soils low in organic carbon. Nutrient use efficiency of basal soil application of vermicompost is very low. Thus, this study was aimed to test whether nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) and crop yield can be enhanced by split application of vermicompost. There is no published information on split application of vermicompost (VC) in rainfed rice. An experiment with rice (cv. Pankaj) was conducted on loam soil in Giridih, India, during 2008 and 2009. Vermicompost, a rich source of readily available nutrients, has high microbial activity and contains growth hormones. Study comprises one of three split applications of vermicompost at different growth stages of rice (i.e., maximum tillering, panicle initiation, and flower). Split application of vermicompost resulted higher yield parameters such as panicles (294 m−2), filled grains per panicle (138), and total spikelets per panicle (142), grain yield (3.91 t ha−1), and NUE, but only if vermicompost was applied at two or three doses. Higher availability of nitrogen (N) in soil with split applications coincides with higher NUE, and thus, split application not promoted N losses. Split application of vermicompost enhances the sustainability of rice cropping system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banik P, Sharma RC (2009) Effect of organic and inorganic sources of nutrients on the winter crops-rice based cropping systems in sub-humid tropics of India. Arch Agron Soil Sci 55:285–294
Bejbaruha R, Sharma RC, Banik P (2009) Direct and residual effect of organic and inorganic source of nutrients on rice based cropping systems in sub-humid tropics of India. J Sustain Agric 33:674–689
Bezbaruha R, Sharma RC, Banik P (2011) Effect of nutrient management and planting geometry on productivity of hybrid rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars. Am J Plant Sci 2:297–302
Bhandari AL, Ladha JK, Pathak H, Padre AT, Dawe D, Gupta RK (2002) Yield and soil nutrient changes in a long-term rice-wheat rotation in India. Soil Sci Soc Am J 66:162–170
Bhattacharyya R, Sachdev MS, Uppal KS, Narayanaswamy G, Datta SP, Singh AK (2006) Effect of nitrogen N 15-labeled urea application alone and in combination with FYM and green manure on yield and nitrogen use efficiency by rice. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 54:500–504
Cochran WG, Cox GM (1992) Experimental designs. Wiley, New York
Dobermann A, Fairhurst TH (2000) Rice: nutrient disorders and nutrient management. Potash and Phosphate Institute of Canada (PPIC) and IRRI, Norcross.
Dobermann A, Dawe D, Roetter RP, Cassman KG (2000) Reversal of rice yield decline in a long-continuous cropping experiment. Agron J 92:633–643
Edwards CA (1998) Breakdown of animal, vegetable and industrial organic wastes by earthworms. In: Edwards CA (ed) Earthworm ecology. CRC, Boca Raton, pp 292–300
Gandhi M, Sangwan V, Kapoor KK, Dilbaghi N (1997) Composting of household wastes with and without earthworms. Environ Ecol 15:432–434
Gastal F, Lemaire G (2002) N uptake distribution in crops: an agronomical and ecophysiological perspective. J Exp Bot 53:789–799
Jackson ML (1973) Soil chemical analysis. Prentice-Hall of India, New Delhi
Jadhav AD, Talashilkar SC, Pawar AG (1997) Influence of the conjunctive use of FYM, vermicompost and urea on growth and nutrient uptake in rice. J Maharashtra Agric Univ 22:249–250
Kale RD, Mallesh BG, Bano K, Bagyaraj DJ (1992) Influence of vermicompost application on the available macro-nutrients and selected microbial population in a paddy field. Soil Biol Biochem 24:1317–1320
Keeney DR, Bremner TM (1966) Exchangeable NH4, NO3 and NO2 by direct distillation method. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 30:577–582
Manivannan R, Sriramachandrasekharan MV (2009) Effect of organic sources and urea on N transformation and lowland rice grown in clay loam soil. Res J Agric Biol Sci 5:1104–1109
Murali A, Ramasamy P, Mohammad AM (2007) Impact of post panicle initiation nutrient management on the yield of rice. Res J Agric Biol Sci 3:638–641
Myint AK, Yamakawar T, Kajihara T, Myint KKM, Zenmyo T (2010) Nitrogen dynamics in a paddy field fertilized with mineral and organic nitrogen sources. American-Eurasian J Agric Environ Sci 7:221–231
Nielson RL (1985) Presence of plant growth substances in earthworm demonstrated by paper chromatography and went pea test. Nature 208:1113–1114
Peng S, Buresh RJ, Huang J, Zhong X, Zou Y, Yang J, Wang G, Liu Y, Hu R, Tang Q, Cui K, Zhong F, Dobermann A (2010) Improving nitrogen fertilization in rice by site-specific N management—a review. Agron Sustain Dev 30:649–656
Perez CM, Juliano BO, Liboo SP, Alcantara JM, Cassman KG (1996) Effects of late nitrogen fertilizer application on head rice yield, protein content, and grain quality of rice. Cereal Chem 73:556–560
San-oh Y, Kondo M, Ookawa T, Hirasawa T (2008) Ecophysiological analysis on effect of planting patter on biomass production and grain yield in rice. JARQ 42:79–89
Sreenivas C, Muralidhar S, Rao MS (2000) Vermicompost, a viable component of IPNSS in nitrogen nutrition of ridge gourd. Ann Agric Res 21:108–113
Tandon HLS (1992) Fertilizers and their integration with organics and bio-fertilizers. In: Tandon HLS (ed) Fertilizers, organic manures, recyclable wastes and bio-fertilizers, (p 32–36). Fertiliser Development Consultation Organisation, New Delhi
Vaarst M (2010) Organic farming as a development strategy: who are interested and who are not? J Sustain Develop 3:38–50
Walkley A, Black IA (1934) An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci 37:29–38
Westerman RL, Kurtz LT (1974) Isotopic and non isotopic estimation of fertilizer nitrogen uptake by Sudangrass in field experiments. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 38:107–109
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bejbaruah, R., Sharma, R.C. & Banik, P. Split application of vermicompost to rice (Oryza sativa L.): its effect on productivity, yield components, and N dynamics. Org. Agr. 3, 123–128 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13165-013-0049-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13165-013-0049-8