Abstract
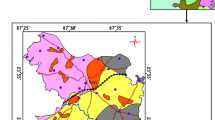
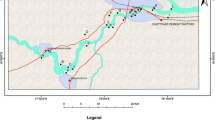
This study presents the usefulness of multivariate statistical techniques, such as correlation matrix, cluster analysis, and factor analysis to evaluate their usefulness to classify the groundwater samples and to identify geochemical processes controlling groundwater geochemistry of the southern Bam, SE Iran. Hydrogeochemical analysis has been conducted on 24 spring locations to portray volcanic and sedimentary hydrogeological system. Based on the hydrochemistry, the groundwater was classified into five types: Ca–Mg–HCO3 (29.16 %), Ca–Mg–SO4–Cl (29.16 %), Na–Cl (20.83 %), Ca–SO4 (16.67 %) and Mg–Na–HCO3–Cl (4.18 %). Nearly 20.83 % of samples have arsenic concentrations above WHO permissible value (10 µg/L) for drinking waters with maximum concentration of aqueous arsenic up to 13.9 mg/L. Result showed that the chemical composition of ground water in district is controlled by the natural weathering processes. Among the chemical weathering processes, silicate weathering was dominant.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alavi M (1994) Tectonic of the Zagros orogenic belt of Iran: new data and interpretations. Tectonophysics 229:211–238
Baker MC, Brown PJ, Griffiths PS, Talley KL, Davies RG, Turner WS (1978) Geology map of Nagisan 1:100000 sheets. Geol Surv Iran
Beiranvand Pour A, Hashim M (2012) Identifying areas of high economic-potential copper mineralization using ASTER data in the Urumieh-Dokhtar Volcanic Belt, Iran. Adv Sp Res 49:753–769
Belkhiri L, Boudoukha A, Mouni L, Baouz T (2010) Application of multivariate statistical methods and inverse geochemical modeling for characterization of groundwater—a case study: ain Azel plain (Algeria). Geoderma 159:390–398
Berberian F, Muir ID, Pankhurst RJ, Berberian M (1982) Late Cretaceous and early Miocene Andean type plutonic activity in northern Makran and central Iran. J Geo Soci London 139:605–614
Cloutier V, Lefebvre R, Therrien R, Savard MM (2008) Multivariate statistical analysis of geochemical data as indicative of the hydrogeochemical evolution of groundwater in a sedimentary rock aquifer system. J Hydrol 353:294–313
Guler C, Thyne GD, Mccray JE, Turner AK (2002) Evaluation of graphical and multivariate statistical methods for classification of water chemistry data. Hydrogeol J 10:455–474
Halim MA, Majumder RK, Nessa SA, Hiroshiro Y, Uddin MJ, Shimada J, Jinno K (2009) Hydrogeochemistry and arsenic contamination of groundwater in the Ganges Delta Plain, Bangladesh. J Hazard Mater 164:1335–1345
Hem JD (1985) Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water, 3rd edn. USGS Water-supply paper, USA p 2254
Hoang TH, Bang S, Kim KW, Nguyen MH, Dang DM (2010) Arsenic in groundwater and sediment in the Mekong River delta, Vietnam. Environ Pollu 1–11
Kumar M, Kumari K, Singh UK, Ramanathan AL (2009) Hydrogeochemical processes in the groundwater environment of Muktsar, Punjab: conventional graphical and multivariate statistical approach. Environ Geo 57:873–884
Pazand K (2014) Geochemical and hydrogeochemical evolution of groundwater in Ferdows area, northeast of Iran. Environ Earth Sci 71:685–695
Pazand K, Fereidoni Sarvestani J (2013) Hydrogeochemical investigation in an arid region of Iran (Tabas, Central Iran). Environ Earth Sci 70:743–752
Pazand K, Hezarkhani A (2013) Hydrogeochemical processes and chemical characteristics around Sahand Mountain, NW Iran. Appl Water Sci 3:479–489
Pazand K, Pazand K (2013) Hydrogeochemical investigation using multivariate analytical methods in Esfadan basin, eastern Iran. Environ Earth Sci. doi:10.1007/s12665-013-2967-x
Regard V, Bellier O, Thomas JC, Abbassi MR, Mercier J, Shabanian E, Feghhi K, Soleymani S (2004) Accommodation of Arabia-Eurasia convergence in the Zagros-Makran transfer zone, SE Iran: a transition between collision and subduction through a young deforming system. Tectonics 23(4):24
Reghunath R, Murthy TRS, Raghavan BR (2002) The utility of multivariate statistical techniques in hydrogeochemical studies: an example from Karnataka, India. Water Res 36:2437–2442
Salifu A, Petrusevski B, Ghebremichael K, Buamah R, Amy G (2012) Multivariate statistical analysis for fluoride occurrence in groundwater in the Northern region of Ghana. J Contam Hydrol 140:34–44
Shafiei B, Haschke M, Shahabpour J (2009) Recycling of orogenic arc crust triggers porphyry Cu mineralization in Kerman Cenozoic arc rocks, southeastern Iran. Miner Depos 44:265–283
Sun LH (2013) Statistical analysis of hydrochemistry of groundwater and its implications for water source identification: a case study. Arab J Geosci. doi:10.1007/s12517-013-1061-8
Suvedha M, Gurugnanam B, Suganya M, Vasudevan S (2009) Multivariate Statistical Analysis of Geochemical Data of Groundwater in Veeranam Catchment Area, Tamil Nadu. J Geo Soc India 74:573–578
WHO (2004) Guidline for drinking water quality. In: Recommendations, vol 1, 3rd edn. World Health Organization, Geneva
Woocay A, Walton J (2008) Multivariate analyses of water chemistry: surface and ground water interactions. Gr Water 45:437–449
Yidana SM, Ophori D, Yakubo BB (2008) A multivariate statistical analysis of surface water chemistry data—the Ankobra Basin, Ghana. J Environ Manag 86:80–87
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pazand, K., Javanshir, A.R. Application of multivariate statistical techniques in hydrogeochemical evolution of groundwater in a igneous rock and sedimentary aquifer system: a case study of the southern Bam, SE Iran. Carbonates Evaporites 31, 9–16 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-015-0234-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-015-0234-9