Abstract
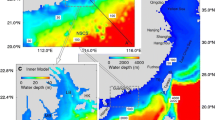
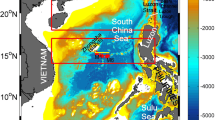
In this study, we develop a variable-grid global ocean general circulation model (OGCM) with a fine grid (1/6)° covering the area from 20°S–50°N and from 99°–150°E, and use the model to investigate the isopycnal surface circulation in the South China Sea (SCS). The simulated results show four layer structures in vertical: the surface and subsurface circulation of the SCS are characterized by the monsoon driven circulation, with basin-scaled cyclonic gyre in winter and anti-cyclonic gyre in summer. The intermediate layer circulation is opposite to the upper layer, showing anti-cyclonic gyre in winter but cyclonic gyre in summer. The circulation in the deep layer is much weaker in spring and summer, with the maximum velocity speed below 0.6 cm/s. In fall and winter, the SCS deep layer circulation shows strong east boundary current along the west coast of Philippine with the velocity speed at 1.5 m/s, which flows southward in fall and northward in winter. The results have also revealed a fourlayer vertical structure of water exchange through the Luzon Strait. The dynamics of the intermediate and deep circulation are attributed to the monsoon driving and the Luzon Strait transport forcing.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cai Shuqun, Gan Zijun, Su Jilan, et al. 2002. Three-dimensional baroclinic numerical simulation of the South China sea circulation's seasonal characteristics II. Middle and deep circulation. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 20(1): 9–15
Chen C T A, Huang M H. 1996. A mid-depth front separating the South China Sea water and the Philippine sea water. Journal of Oceanography, 52(1): 17–25
Chu P C, Edmons N L, Fan Chenwu. 1999. Dynamical mechanisms for the South China Sea seasonal circulation and thermohaline variabilities. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 29(11): 2971–2989
Chu P C, Li Rongfeng. 2000. South China Sea isopycnal-surface circulation. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 30(9): 2419–2438
Fang Guohong, Fang Wendong, Fang Yue, et al. 1998. A survey of studies on the South China Sea upper ocean circulation. Acta Oceanographica Taiwanica, 37(1): 1–16
Fang Guohong, Susanto R D, Soesilo I, et al. 2005. A note on the South China Sea shallow interocean circulation. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 22(6): 946–954
Fang Guohong, Susanto R D, Wirasantosa S, et al. 2010. Volume, heat, and freshwater transports from the South China Sea to Indonesian seas in the boreal winter of 2007–2008. Journal of Geophysical Research, 115(C12), doi: 10.1029/2010JC006225
Fang Guohong, Wang Yonggang, Wei Zexun, et al. 2009. Interocean circulation and heat and freshwater budgets of the South China Sea based on a numerical model. Dynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans, 47(1–3): 55–72
Fang Guohong, Wei Zexun, Fang Yue, et al. 2002a. Mean sea surface heights of the South and East China Seas from ocean circulation model and geodetic leveling. Chinese Science Bulletin, 47(4): 326–329
Fang Guohong, Wei Zexun, Chio B H, et al. 2003. Interbasin freshwater, heat and salt transport through the boundaries of the East and South China Seas from a variable-grid global ocean circulation model. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 46(2): 149–161
Fang Wendong, Fang Guohong, Shi Ping, et al. 2002b. Seasonal structures of upper layer circulation in the southern South China Sea from in situ observations. Journal of Geophysical Research, 107(C11): 23-1–12
Gan Jianping, Li H, Curchitser E N, et al. 2006. Modeling South China Sea circulation: Response to seasonal forcing regimes. Journal of Geophysical Research, 111(C6), doi: 10.1029/2005JC003298
Gordon A L, Huber B A, Metzger E J, et al. 2012. South China Sea throughflow impact on the Indonesian throughflow. Geophysical Research Letters, 39: L11602, doi: 10.1029/2012GL052021
Hellerman S, Rosenstein M. 1983. Normal monthly wind stress over the world ocean with error estimates. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 13(7): 1093–1104
Ho C R, Zheng Quanan, Soong Y S, et al. 2000. Seasonal variability of sea surface height in the South China Sea observed with TOPEX/Poseidon altimeter data. Journal of Geophysical Research, 105(C6): 13981–13990
Hu Jianyu, Kawamura H, Hong Huasheng, et al. 2000. A review on the currents in the South China Sea: Seasonal circulation, South China Sea warm current and Kuroshio intrusion. Journal of Oceangraphy, 56(6): 607–624
Isobe A, Namba T. 2001. The circulation in the upper and intermediate layers of the South China Sea. Journal of Oceangraphy, 57(1): 93–104
Lan Jian, Zhang Ningning, Wang Yu. 2013. On the dynamics of the South China Sea deep circulation. Journal of Geophysical Research, 118(3): 1206–1210
Levitus S, Boyer T P. 1994. World Ocean Atlas 1994. Volume 4. Temperature. Washington D C: US Gov Printing Office, 117
Lin M, Fang Guohong. 1991. Data set of water depth and chart datum at stanard latitues and longitudes of the China Seas (Bohai, Yellow and East China Sea Part) (in Chinese). Qingdao: Institute of Oceanography, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 144
Liu Qinyu, Kaneko A, Su Jilan. 2008a. Recent progress in studies of the South China Sea circulation. Journal of Oceanography, 64(5): 753–762
Liu Yonggang, Weisberg R H, Yuan Yaochu. 2008b. Patterns of upper layer circulation variability in the South China Sea from satellite altimetry using the self-organizing map. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 27(Suppl): 129–144
Liu Zhengyu, Yang Haijun, Liu Qinyu. 2001. Regional dynamics of seasonal variability in the South China Sea. Journal of physical oceanography, 31(1): 272–284
Metzger E J, Hurlburt H E. 1996. Coupled dynamics of the south China sea, the Sulu sea, and the Pacific ocean. Journal of Geophysical Research, 101(C5): 12331–12352
Pacanowski R C. 1996. MOM 2 Documentation User's Guide and Reference Manual. GFDL Ocean Tech Report, No.32, Princeton: Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory/NOAA, 1–329
Qu Tangdong. 2000. Upper-Layer Circulation in the South China Sea. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 30(6): 1450–1460
Qu Tangdong, Du Yan, Meyers G, et al. 2005. Connecting the tropical Pacific with Indian Ocean through South China Sea. Geophysical Research Letters, 32(24), doi: 10.1029/2005GL024698
Qu Tangdong, Du Yan, Sasaki H. 2006a. South China Sea throughflow: A heat and freshwater conveyor. Geophysical Research Letters, 33(23), doi: 10.1029/2006GL028350
Qu Tangdong, Girton J B, Whitehead J A. 2006b. Deepwater overflow through Luzon strait. Journal of Geophysical Research, 111(C1), doi: 10.1029/2005JC003139
Qu Tangdong, Mitsudera H, Yamagata T. 2000. Intrusion of the North Pacific waters into the South China Sea. Journal of Geophysical Research, 105(C3): 6415–6424
Qu Tangdong, Song Y T, Yamagata T. 2009. An introduction to the South China Sea throughflow: Its dynamics, variability, and application for climate. Dynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans, 47(1–3): 3–14
Reid J L. 1965. Intermediate waters of the Pacific Ocean. Johns Hopkins Oceanographic Studies, 2: 1–85
Shaw P T, Chao S Y. 1994. Surface circulation in the South China Sea. Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 41(11–12): 1663–1683
Shaw P T, Chao S Y, Fu L L. 1999. Sea surface height variations in the South China Sea from satellite altimetry. Oceanologica Acta, 22(1): 1–17
Shi Maochong, Chen Changsheng, Xu Qichun, et al. 2002. The role of Qiongzhou strait in the seasonal variation of the South China Sea circulation. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 32(1): 103–121
Stockdale T, Anderson D, Devey M, et al. 1993. Intercomparison of Tropical Pacific Ocean GCMs. WCRP79, WMO/TD-545, Geneva: World Meterological Organization, 99
Tian Jiwei, Qu Tangdong. 2012. Advances in research on the deep South China Sea circulation. Chinese Science Bulletin, 57(24): 3115–3120
Tian Jiwei, Yang Qingxuan, Liang Xinfeng, et al. 2006. Observation of Luzon Strait transport. Geophysical Research Letters, 33(19), doi: 10.1029/2006GL026272
Tian Jiwei, Yang Qingxuan, Zhao Wei. 2009. Enhanced diapycnal mixing in the South China Sea. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 39(12): 3191–3203
Tsuchiya M. 1968. Upper waters of the intertropical Pacific Ocean. Johns Hopkins Oceanographic Studies, 4: 1–50
Wang Guihua, Chen Dake, Su Jilan. 2006a. Generation and life cycle of the dipole in the South China Sea summer circulation. Journal of Geophysical Research, 111(C6), doi: 10.1029/ 2005JC003314
Wang Guihua, Huang Ruixin, Su Jilan, et al. 2012. The effects of thermohaline circulation on wind-driven circulation in the South China Sea. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 42(12): 2283–2296
Wang Guihua, Ling Zhen, Wang Chunzai. 2009. Influence of tropical cyclones on seasonal ocean circulation in the South China Sea. Journal of Geophysical Research, 114(C10), doi:10.1029/2009JC005302
Wang Guihua, Xie Shangping, Qu Tangdong, et al. 2011. Deep South China Sea circulation. Geophysical Research Letters, 38(5), doi: 10.1029/2010GL046626
Wang Yonggang, Fang Guohong, Wei Zexun, et al. 2006b. Interannual variation of the South China Sea circulation and its relation to El Niño, as seen from a variable grid global ocean model. Journal of Geophysical Research, 111(C11), doi:10.1029/2005JC003269
Wei Zexun, Fang Guohong, Choi B H, et al. 2003. Sea surface height and transport stream function of the South China Sea from a variable-grid global ocean circulation model. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 46(2): 139–148
Wu C R, Shaw P T, Chao S Y. 1998. Seasonal and interannual variations in the velocity field of the South China Sea. Journal of Oceanography, 54(4): 361–372
Wyrtki K. 1961. Physical oceanography of the southeast Asian waters, scientific results of marine investigations of the South China Sea and Gulf of Thailand. Naga Report, 2: 195
Xie Qiang, Xiao Jingen, Wang Dongxiao, et al. 2013. Analysis of deeplayer and bottom circulations in the South China Sea based on eight quasi-global ocean model outputs. Chinese Sience Bulletin, 58(32): 4000–4011
Xu Danya, Malanotte-Rizzoli P. 2013. The seasonal variation of the upper layers of the South China Sea (SCS) circulation and the Indonesian through flow (ITF): An ocean model study. Dynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans, 63: 103–130
Xue Huijie, Chai Fei, Pettigrew N, et al. 2004. Kuroshio intrusion and the circulation in the South China Sea. Journal of Geophysical Research, 109(C2), doi: 10.1029/2002JC001724
Yaremchuk M, McCreary J P, Yu Zuojun, et al. 2009. The South China Sea Throughflow Retrieved from Climatological Data. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 39(3): 753–767
Yu Zuojun, Shen S, McCreary J P, et al. 2007. South China Sea throughflow as evidenced by satellite images and numerical experiments. Geophysical Research Letters, 34(1), doi: 10.1029/2006GL028103
Yuan Dongliang. 2002. A numerical study of the South China Sea deep circulation and its relation to the Luzon Strait transport. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 21(2): 187–202
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: The National High Technology Research and Development Program (863 Program) of China under contract No. 2013AA09A506; the National Natural Science Foundation of China-Shandong Joint Fund for Marine Science Research Centers under contract No. U1406404; the National Basic Research Program (973 Program) of China under contract No. 2011CB956000; the National Natural Science Foundation of China under contract No. 40476016.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Z., Fang, G., Xu, T. et al. Seasonal variability of the isopycnal surface circulation in the South China Sea derived from a variable-grid global ocean circulation model. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 35, 11–20 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-016-0791-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-016-0791-3