Abstract
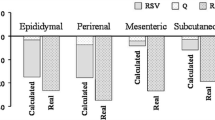
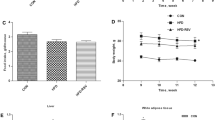
Liver steatosis is characterized by an abnormal accumulation of triacylglycerols in this organ. This metabolic disorder is closely associated with obesity. In the present study, we aimed to analyse the effect of a combination of resveratrol and quercetin on liver steatosis in an animal model of dietetic obesity, and to compare it with one induced by the administration of each polyphenol separately. Rats were divided into four dietary groups of nine animals each and fed a high-fat, high-sucrose diet: an untreated control group and three groups treated either with resveratrol (RSV; 15 mg/kg/day), with quercetin (Q; 30 mg/kg/day), or with both (RSV + Q; 15 mg resveratrol/kg/day and 30 mg quercetin/kg/day) for 6 weeks. Liver weight and triacylglycerol content decreased only in the RSV + Q group. A significant reduction in acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity was observed in RSV and RSV + Q groups, without changes in fatty acid synthase activity. A significant increase in carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1a activity was observed only in rats treated with the combination of resveratrol and quercetin, suggesting increased fatty acid oxidation. Citrate synthase, a marker of mitochondrial density, remained unchanged in all groups. No significant changes were observed in the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα), nuclear respiratory factor 1 (NRF-1) and transcription factor A mitochondrial (TFAM). In conclusion, resveratrol and quercetin together, combining two doses which were shown to be ineffective singly, is an interesting tool to prevent liver steatosis associated with high-fat high-sucrose feeding. The delipidating effect seems to be mediated by increased fatty acid oxidation not associated with increased mitochondriogenesis, and by reduced de novo lipogenesis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams LA, Lymp JF, St Sauver J, Sanderson SO, Lindor KD, Feldstein A, Angulo P (2005) The natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a population-based cohort study. Gastroenterology 129:113–121
Aguirre L, Portillo MP, Hijona E, Bujanda L (2014) Effects of resveratrol and other polyphenols in hepatic steatosis. World J Gastroenterol 20:7366–7380
Alberdi G, Macarulla MT, Portillo MP, Rodríguez VM (2014) Resveratrol does not increase body fat loss induced by energy restriction. J Physiol Biochem 70:639–646
Alberdi G, Rodríguez VM, Macarulla MT, Miranda J, Churruca I, Portillo MP (2013) Hepatic lipid metabolic pathways modified by resveratrol in rats fed an obesogenic diet. Nutrition 29:562–567
Arias N, Macarulla MT, Aguirre L, Martínez-Castaño MG, Portillo MP (2014) Quercetin can reduce insulin resistance without decreasing adipose tissue and skeletal muscle fat accumulation. Genes Nutr 9:361
Berlanga A, Guiu-Jurado E, Porras JA, Auguet T (2014) Molecular pathways in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Exp Gastroenterol 7:221–239
Bieber LL, Abraham T, Helmrath T (1972) A rapid spectrophotometric assay for carnitine palmitoyltransferase. Anal Biochem 50:509–518
Boehm O, Zur B, Koch A, Tran N, Freyenhagen R, Hartmann M, Zacharowski K (2007) Clinical chemistry reference database for Wistar rats and C57/BL6 mice. Biol Chem 388:547–554
Bradamante S, Barenghi L, Villa A (2004) Cardiovascular protective effects of resveratrol. Cardiovasc Drug Rev 22:169–188
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Bujanda L, Hijona E, Larzabal M, Beraza M, Aldazabal P, García-Urkia N, Sarasqueta C, Cosme A, Irastorza B, González A, Arenas JI Jr (2008) Resveratrol inhibits nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in rats. BMC Gastroenterol 8:40
Castaño D, Larequi E, Belza I, Astudillo AM, Martínez-Ansó E, Balsinde J, Argemi J, Aragon T, Moreno-Aliaga MJ, Muntane J, Prieto J, Bustos M (2014) Cardiotrophin-1 eliminates hepatic steatosis in obese mice by mechanisms involving AMPK activation. J Hepatol 60:1017–1025
Cucciolla V, Borriello A, Oliva A, Galletti P, Zappia V, Della Ragione F (2007) Resveratrol: from basic science to the clinic. Cell Cycle 6:2495–2510
Folch J, Lees M, Sloane Stanley GH (1957) A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem 226:497–509
Gómez-Zorita S, Fernández-Quintela A, Macarulla MT, Aguirre L, Hijona E, Bujanda L, Milagro F, Martínez JA, Portillo MP (2012) Resveratrol attenuates steatosis in obese Zucker rats by decreasing fatty acid availability and reducing oxidative stress. Br J Nutr 107:202–210
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−delta delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Macarulla MT, Alberdi G, Gómez S, Tueros I, Bald C, Rodríguez VM, Martínez JA, Portillo MP (2009) Effects of different doses of resveratrol on body fat and serum parameters in rats fed a hypercaloric diet. J Physiol Biochem 65:369–376
Macarulla MT, Medina C, De Diego MA, Chávarri M, Zulet MA, Martínez JA, Nöel-Suberville C, Higueret P, Portillo MP (2001) Effects of the whole seed and a protein isolate of faba bean (Vicia faba) on the cholesterol metabolism of hypercholesterolaemic rats. Br J Nutr 85:607–614
Miranda J, Fernández-Quintela A, Churruca I, Rodríguez VM, Simón E, Portillo MP (2009) Hepatomegaly induced by trans-10, cis-12 conjugated linoleic acid in adult hamsters fed an atherogenic diet is not associated with steatosis. J Am Coll Nutr 28:43–49
Panchal SK, Poudyal H, Brown L (2012) Quercetin ameliorates cardiovascular, hepatic, and metabolic changes in diet-induced metabolic syndrome in rats. J Nutr 142:1026–1032
Poulsen MM, Larsen JØ, Hamilton-Dutoit S, Clasen BF, Jessen N, Paulsen SK, Kjær TN, Richelsen B, Pedersen SB (2012) Resveratrol up-regulates hepatic uncoupling protein 2 and prevents development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in rats fed a high-fat diet. Nutr Res 32:701–708
Shang J, Chen LL, Xiao FX, Sun H, Ding HC, Xiao H (2008) Resveratrol improves non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Acta Pharmacol Sin 29:698–706
Somerset SM, Johannot L (2008) Dietary flavonoid sources in Australian adults. Nutr Cancer 60:442–449
Srere PA (1969) Citrate synthase. Methods Enzymol 13:3–11
Zabala A, Churruca I, Macarulla MT, Rodríguez VM, Fernández-Quintela A, Martínez JA, Portillo MP (2004) The trans-10, cis-12 isomer of conjugated linoleic acid reduces hepatic triacylglycerol content without affecting lipogenic enzymes in hamsters. Br J Nutr 92:383–389
Zhang L, Song H, Ge Y, Ji G, Yao Z (2015) Temporal relationship between diet-induced steatosis and onset of insulin/leptin resistance in male Wistar rats. PLoS One 10:e0117008
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad (AGL2011-27406-ALI), Instituto de Salud Carlos III (CIBERobn), Government of the Basque Country (IT-572-13) and University of the Basque Country (UPV/EHU) (ELDUNANOTEK UFI11/32). N. Arias is a recipient of a doctoral fellowship from the Basque Country Government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arias, N., Macarulla, M.T., Aguirre, L. et al. Liver delipidating effect of a combination of resveratrol and quercetin in rats fed an obesogenic diet. J Physiol Biochem 71, 569–576 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-015-0403-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-015-0403-2