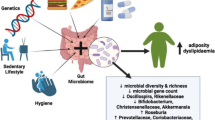
Abstract
Gut microbiota, its evolutive dynamics and influence on host through its protective, trophic and metabolic actions, has a key role in health and opens unique opportunities for the identification of new markers of the physiopathological state of each individual. Alterations in gut microbiota composition have been associated with plenty disorders. Of interest, the vast number of studies demonstrates the role of microbiota in obesity, a serious public health problem that has reached epidemic proportions in many developed and middle-income countries. The economic and health costs of this condition and its comorbidities such as fatty liver, insulin resistance/diabetes, or cardiovascular events are considerable. Therefore, every strategy designed to reduce obesity would imply important savings. Targeting microbiota, in order to restore/modulate the microbiota composition with antibiotics, probiotics, prebiotics, or even fecal transplants, is considered as a promising strategy for the development of new solutions for the treatment of obesity. However, there is still lot to do in this field in order to identify the exact composition of microbiota in “health” and the specific mechanisms that regulate the host-microbiotal crosstalk. In addition, it is important to note that changes not only in the gut microbiota profile (abundance) but also in its metabolism and functions need to be taken into account in the context of contribution in the physiopathology of obesity and related disorders.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2-AG:
-
2-Arachidonoylglycerol
- ACC:
-
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase
- AMP:
-
Adenosine monophosphate
- AMPK:
-
Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase
- AOX :
-
Alternative oxidase
- AP-1:
-
Activator protein 1
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- CB1R/CB2R:
-
Cannabinoid receptor 1/2
- Ccl2 :
-
Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2
- CD14:
-
CD14 molecule
- Cd36 :
-
CD36 molecule (thrombospondin receptor)
- Cd68 :
-
CD68 molecule
- CFU:
-
Colony-forming unit
- ChREBP:
-
Carbohydrate response element-binding protein
- Cpt1 :
-
Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1
- eCB:
-
Endocannabinoid system
- FAAH:
-
Fatty acid amide hydrolase
- Ffar2 :
-
Free fatty acid receptor 2
- FIAF:
-
Fasting-induced adipocyte factor
- FMT:
-
Fecal transplantation
- Gαi/Gαo/Gαq:
-
Guanine nucleotide-binding protein (G protein), alpha subunit i/o/q
- GLP-1/2:
-
Glucagon-like peptide 1/2
- GPRs:
-
G-protein-coupled receptors
- HDL:
-
High-density lipoprotein
- HFD:
-
High-fat diet
- HMP:
-
Human Microbiome Project
- IL-18:
-
Interleukin 18
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin 1β
- LPL:
-
Lipoprotein lipase
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- MD2:
-
Myeloid differentiation protein-2
- MetaHIT:
-
Metagenomics of the Human Intestinal Tract
- MyD88:
-
Myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88
- NAFLD:
-
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells
- NLRs:
-
Nuclear oligodimerization receptors
- NOD1/2:
-
Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing protein 1/2
- PGC-1:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1 alpha
- Ppara :
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha
- PYY:
-
Peptide YY
- SCFA:
-
Short chain fatty acids
- SREBP-1:
-
Sterol response element-binding protein type-1
- TG:
-
Triglyceride
- Th17 cell:
-
T helper 17 cell
- TLRs:
-
Toll-like receptors
- TMAO:
-
Trimethylamine N-oxide
- Tregs:
-
Regulatory T cells
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
- ZO-1:
-
Zonula occludens protein-1
References
Abdallah Ismail N, Ragab SH, Abd Elbaky A, Shoeib AR, Alhosary Y, Fekry D (2011) Frequency of Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes in gut microbiota in obese and normal weight Egyptian children and adults. Arch Med Sci 7:501–507
Ali AA, Velasquez MT, Hansen CT, Mohamed AI, Bhathena SJ (2005) Modulation of carbohydrate metabolism and peptide hormones by soybean isoflavones and probiotics in obesity and diabetes. J Nutr Biochem 16:693–699
An HM, Park SY, Lee Do K, Kim JR, Cha MK, Lee SW, Lim HT, Kim KJ, Ha NJ (2011) Antiobesity and lipid-lowering effects of Bifidobacterium spp. in high fat diet-induced obese rats. Lipids Health Dis 10:116
Anderson JL, Edney RJ, Whelan K (2012) Systematic review: faecal microbiota transplantation in the management of inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 36:503–516
Angelakis E, Merhej V, Raoult D (2013) Related actions of probiotics and antibiotics on gut microbiota and weight modification. Lancet Infect Dis 13:889–899
Arumugam M, Raes J, Pelletier E, Le Paslier D, Yamada T, Mende DR, Fernandes GR, Tap J, Bruls T, Batto JM, Bertalan M, Borruel N, Casellas F, Fernandez L, Gautier L, Hansen T, Hattori M, Hayashi T, Kleerebezem M, Kurokawa K, Leclerc M, Levenez F, Manichanh C, Nielsen HB, Nielsen T, Pons N, Poulain J, Qin J, Sicheritz-Ponten T, Tims S, Torrents D, Ugarte E, Zoetendal EG, Wang J, Guarner F, Pedersen O, de Vos WM, Brunak S, Dore J, Antolin M, Artiguenave F, Blottiere HM, Almeida M, Brechot C, Cara C, Chervaux C, Cultrone A, Delorme C, Denariaz G, Dervyn R, Foerstner KU, Friss C, van de Guchte M, Guedon E, Haimet F, Huber W, van Hylckama-Vlieg J, Jamet A, Juste C, Kaci G, Knol J, Lakhdari O, Layec S, Le Roux K, Maguin E, Merieux A, Melo Minardi R, M’Rini C, Muller J, Oozeer R, Parkhill J, Renault P, Rescigno M, Sanchez N, Sunagawa S, Torrejon A, Turner K, Vandemeulebrouck G, Varela E, Winogradsky Y, Zeller G, Weissenbach J, Ehrlich SD, Bork P (2011) Enterotypes of the human gut microbiome. Nature 473:174–180
Azad MB, Konya T, Maughan H, Guttman DS, Field CJ, Chari RS, Sears MR, Becker AB, Scott JA, Kozyrskyj AL (2013) Gut microbiota of healthy Canadian infants: profiles by mode of delivery and infant diet at 4 months. Cmaj 185:385–394
Backhed F, Ding H, Wang T, Hooper LV, Koh GY, Nagy A, Semenkovich CF, Gordon JI (2004) The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:15718–15723
Backhed F, Ley RE, Sonnenburg JL, Peterson DA, Gordon JI (2005) Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine. Science 307:1915–1920
Backhed F, Manchester JK, Semenkovich CF, Gordon JI (2007) Mechanisms underlying the resistance to diet-induced obesity in germ-free mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:979–984
Bailey MT (2011) Influence of stressor-induced nervous system activation on the intestinal microbiota and the importance for immunomodulation. Adv Exp Med Biol 817:255–276
Bellahcene M, O'Dowd JF, Wargent ET, Zaibi MS, Hislop DC, Ngala RA, Smith DM, Cawthorne MA, Stocker CJ, Arch JR (2013) Male mice that lack the G-protein-coupled receptor GPR41 have low energy expenditure and increased body fat content. Br J Nutr 109:1755–1764
Bervoets L, Van Hoorenbeeck K, Kortleven I, Van Noten C, Hens N, Vael C, Goossens H, Desager KN, Vankerckhoven V (2013) Differences in gut microbiota composition between obese and lean children: a cross-sectional study. Gut Pathog 5:10
Bindels LB, Dewulf EM, Delzenne NM (2013) GPR43/FFA2: physiopathological relevance and therapeutic prospects. Trends Pharmacol Sci 34:226–232
Brenchley JM, Douek DC (2012) Microbial translocation across the GI tract. Annu Rev Immunol 30:149–173
Burcelin R, Serino M, Chabo C, Garidou L, Pomie C, Courtney M, Amar J, Bouloumie A (2013) Metagenome and metabolism: the tissue microbiota hypothesis. Diabetes Obes Metab 15(Suppl 3):61–70
Cani PD, Amar J, Iglesias MA, Poggi M, Knauf C, Bastelica D, Neyrinck AM, Fava F, Tuohy KM, Chabo C, Waget A, Delmee E, Cousin B, Sulpice T, Chamontin B, Ferrieres J, Tanti JF, Gibson GR, Casteilla L, Delzenne NM, Alessi MC, Burcelin R (2007) Metabolic endotoxemia initiates obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes 56:1761–1772
Cani PD, Bibiloni R, Knauf C, Waget A, Neyrinck AM, Delzenne NM, Burcelin R (2008) Changes in gut microbiota control metabolic endotoxemia-induced inflammation in high-fat diet-induced obesity and diabetes in mice. Diabetes 57:1470–1481
Cani PD, Delzenne NM (2012) Involvement of the gut microbiota in the development of low grade inflammation associated with obesity: focus on this neglected partner. Acta Gastroenterol Belg 73:267–269
Cani PD, Hoste S, Guiot Y, Delzenne NM (2007) Dietary non-digestible carbohydrates promote L-cell differentiation in the proximal colon of rats. Br J Nutr 98:32–37
Cani PD, Neyrinck AM, Fava F, Knauf C, Burcelin RG, Tuohy KM, Gibson GR, Delzenne NM (2007) Selective increases of bifidobacteria in gut microflora improve high-fat-diet-induced diabetes in mice through a mechanism associated with endotoxaemia. Diabetologia 50:2374–2383
Cani PD, Possemiers S, Van de Wiele T, Guiot Y, Everard A, Rottier O, Geurts L, Naslain D, Neyrinck A, Lambert DM, Muccioli GG, Delzenne NM (2009) Changes in gut microbiota control inflammation in obese mice through a mechanism involving GLP-2-driven improvement of gut permeability. Gut 58:1091–1103
Cederroth CR, Vinciguerra M, Gjinovci A, Kuhne F, Klein M, Cederroth M, Caille D, Suter M, Neumann D, James RW, Doerge DR, Wallimann T, Meda P, Foti M, Rohner-Jeanrenaud F, Vassalli JD, Nef S (2008) Dietary phytoestrogens activate AMP-activated protein kinase with improvement in lipid and glucose metabolism. Diabetes 57:1176–1185
Chen Z, Guo L, Zhang Y, Walzem RL, Pendergast JS, Printz RL, Morris LC, Matafonova E, Stien X, Kang L, Coulon D, McGuinness OP, Niswender KD, Davies SS (2014) Incorporation of therapeutically modified bacteria into gut microbiota inhibits obesity. J Clin Invest 124:3391–3406
de La Serre CB, Ellis CL, Lee J, Hartman AL, Rutledge JC, Raybould HE (2010) Propensity to high-fat diet-induced obesity in rats is associated with changes in the gut microbiota and gut inflammation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 299:G440–G448
DiGiulio DB, Romero R, Amogan HP, Kusanovic JP, Bik EM, Gotsch F, Kim CJ, Erez O, Edwin S, Relman DA (2008) Microbial prevalence, diversity and abundance in amniotic fluid during preterm labor: a molecular and culture-based investigation. PLoS One 3:e3056
Duncan SH, Lobley GE, Holtrop G, Ince J, Johnstone AM, Louis P, Flint HJ (2008) Human colonic microbiota associated with diet, obesity and weight loss. Int J Obes (Lond) 32:1720–1724
Evans CC, LePard KJ, Kwak JW, Stancukas MC, Laskowski S, Dougherty J, Moulton L, Glawe A, Wang Y, Leone V, Antonopoulos DA, Smith D, Chang EB, Ciancio MJ (2014) Exercise prevents weight gain and alters the gut microbiota in a mouse model of high fat diet-induced obesity. PLoS One 9:e92193
Everard A, Geurts L, Caesar R, Van Hul M, Matamoros S, Duparc T, Denis RG, Cochez P, Pierard F, Castel J, Bindels LB, Plovier H, Robine S, Muccioli GG, Renauld JC, Dumoutier L, Delzenne NM, Luquet S, Backhed F, Cani PD (2014) Intestinal epithelial MyD88 is a sensor switching host metabolism towards obesity according to nutritional status. Nat Commun 5:5648
Everard A, Lazarevic V, Derrien M, Girard M, Muccioli GG, Neyrinck AM, Possemiers S, Van Holle A, Francois P, de Vos WM, Delzenne NM, Schrenzel J, Cani PD (2011) Responses of gut microbiota and glucose and lipid metabolism to prebiotics in genetic obese and diet-induced leptin-resistant mice. Diabetes 60:2775–2786
Fernandes J, Su W, Rahat-Rozenbloom S, Wolever TM, Comelli EM (2014) Adiposity, gut microbiota and faecal short chain fatty acids are linked in adult humans. Nutr Diabetes 4:e121
Finucane MM, Sharpton TJ, Laurent TJ, Pollard KS (2014) A taxonomic signature of obesity in the microbiome? Getting to the guts of the matter. PLoS One 9:e84689
Foolad N, Armstrong AW (2014) Prebiotics and probiotics: the prevention and reduction in severity of atopic dermatitis in children. Benef Microbes 5:151–160
Fujimura KE, Slusher NA, Cabana MD, Lynch SV (2010) Role of the gut microbiota in defining human health. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 8:435–454
Furet JP, Kong LC, Tap J, Poitou C, Basdevant A, Bouillot JL, Mariat D, Corthier G, Dore J, Henegar C, Rizkalla S, Clement K (2010) Differential adaptation of human gut microbiota to bariatric surgery-induced weight loss: links with metabolic and low-grade inflammation markers. Diabetes 59:3049–3057
Geuking MB, Cahenzli J, Lawson MA, Ng DC, Slack E, Hapfelmeier S, McCoy KD, Macpherson AJ (2011) Intestinal bacterial colonization induces mutualistic regulatory T cell responses. Immunity 34:794–806
Gill SR, Pop M, Deboy RT, Eckburg PB, Turnbaugh PJ, Samuel BS, Gordon JI, Relman DA, Fraser-Liggett CM, Nelson KE (2006) Metagenomic analysis of the human distal gut microbiome. Science 312:1355–1359
Gordon JI, Hooper LV, McNevin MS, Wong M, Bry L (1997) Epithelial cell growth and differentiation. III. Promoting diversity in the intestine: conversations between the microflora, epithelium, and diffuse GALT. Am J Physiol 273:G565–G570
Guarner F, Malagelada JR (2003) Gut flora in health and disease. Lancet 361:512–519
Guilloteau P, Martin L, Eeckhaut V, Ducatelle R, Zabielski R, Van Immerseel F (2010) From the gut to the peripheral tissues: the multiple effects of butyrate. Nutr Res Rev 23:366–384
Harris K, Kassis A, Major G, Chou CJ (2012) Is the gut microbiota a new factor contributing to obesity and its metabolic disorders? J Obes 2012:879151
Hoskin-Parr L, Teyhan A, Blocker A, Henderson AJ (2013) Antibiotic exposure in the first two years of life and development of asthma and other allergic diseases by 7.5 yr: a dose-dependent relationship. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 24:762–771
Hossain P, Kawar B, El Nahas M (2007) Obesity and diabetes in the developing world—a growing challenge. N Engl J Med 356:213–215
http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/ (WHO: obesity and overweight. World Health Organization. Archived from the original on December 18, 2008. Retrieved November 29, 2014)
Ianiro G, Bibbo S, Gasbarrini A, Cammarota G (2014) Therapeutic modulation of gut microbiota: current clinical applications and future perspectives. Curr Drug Targets 15:762–770
Inoue D, Tsujimoto G, Kimura I (2014) Regulation of energy homeostasis by GPR41. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 5:81
Jorth P, Turner KH, Gumus P, Nizam N, Buduneli N, Whiteley M (2014) Metatranscriptomics of the human oral microbiome during health and disease. MBio 5:e01012–e01014
Kamada N, Chen GY, Inohara N, Nunez G (2013) Control of pathogens and pathobionts by the gut microbiota. Nat Immunol 14:685–690
Kamada N, Nunez G (2013) Role of the gut microbiota in the development and function of lymphoid cells. J Immunol 190:1389–1395
Kim DH, Jung EA, Sohng IS, Han JA, Kim TH, Han MJ (1998) Intestinal bacterial metabolism of flavonoids and its relation to some biological activities. Arch Pharm Res 21:17–23
Lee CY, Abizaid A (2014) The gut-brain-axis as a target to treat stress-induced obesity. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 5:117
Ley RE, Backhed F, Turnbaugh P, Lozupone CA, Knight RD, Gordon JI (2005) Obesity alters gut microbial ecology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:11070–11075
Ley RE, Turnbaugh PJ, Klein S, Gordon JI (2006) Microbial ecology: human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 444:1022–1023
Liou AP, Paziuk M, Luevano JM Jr, Machineni S, Turnbaugh PJ, Kaplan LM (2013) Conserved shifts in the gut microbiota due to gastric bypass reduce host weight and adiposity. Sci Transl Med 5:178ra141
Lozupone CA, Stombaugh JI, Gordon JI, Jansson JK, Knight R (2012) Diversity, stability and resilience of the human gut microbiota. Nature 489:220–230
Lyte M (2013) Microbial endocrinology in the microbiome-gut-brain axis: how bacterial production and utilization of neurochemicals influence behavior. PLoS Pathog 9:e1003726
Mackie RI, Sghir A, Gaskins HR (1999) Developmental microbial ecology of the neonatal gastrointestinal tract. Am J Clin Nutr 69:1035S–1045S
Manach C, Donovan JL (2004) Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of dietary flavonoids in humans. Free Radic Res 38:771–785
Martinez JA, Parra MD, Santos JL, Moreno-Aliaga MJ, Marti A, Martinez-Gonzalez MA (2008) Genotype-dependent response to energy-restricted diets in obese subjects: towards personalized nutrition. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 17(Suppl 1):119–122
Martinez I, Wallace G, Zhang C, Legge R, Benson AK, Carr TP, Moriyama EN, Walter J (2009) Diet-induced metabolic improvements in a hamster model of hypercholesterolemia are strongly linked to alterations of the gut microbiota. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:4175–4184
Matsumoto M, Kibe R, Ooga T, Aiba Y, Sawaki E, Koga Y, Benno Y (2013) Cerebral low-molecular metabolites influenced by intestinal microbiota: a pilot study. Front Syst Neurosci 7:9
Mesonero JE, Latorre E, Mendoza C, Matheus N, Alcalde AI (2012) Papel del sistema serotoninérgico en la fisiopatología intestinal. Gaceta de Ciencias Veterinarias 15:72–79
Morgan XC, Segata N, Huttenhower C (2013) Biodiversity and functional genomics in the human microbiome. Trends Genet 29:51–58
Munyaka PM, Khafipour E, Ghia JE (2014) External influence of early childhood establishment of gut microbiota and subsequent health implications. Front Pediatr 2:109
Nadal I, Santacruz A, Marcos A, Warnberg J, Garagorri JM, Moreno LA, Martin-Matillas M, Campoy C, Marti A, Moleres A, Delgado M, Veiga OL, Garcia-Fuentes M, Redondo CG, Sanz Y (2009) Shifts in clostridia, bacteroides and immunoglobulin-coating fecal bacteria associated with weight loss in obese adolescents. Int J Obes (Lond) 33:758–767
Naito E, Yoshida Y, Makino K, Kounoshi Y, Kunihiro S, Takahashi R, Matsuzaki T, Miyazaki K, Ishikawa F (2011) Beneficial effect of oral administration of Lactobacillus casei strain Shirota on insulin resistance in diet-induced obesity mice. J Appl Microbiol 110:650–657
Ottman N, Smidt H, de Vos WM, Belzer C (2012) The function of our microbiota: who is out there and what do they do? Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2:104
Panda S, El khader I, Casellas F, Lopez Vivancos J, Garcia Cors M, Santiago A, Cuenca S, Guarner F, Manichanh C (2014) Short-term effect of antibiotics on human gut microbiota. PLoS One 9:e95476
Paolella G, Mandato C, Pierri L, Poeta M, Di Stasi M, Vajro P (2014) Gut-liver axis and probiotics: their role in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 20:15518–15531
Pathak R, Enuh HA, Patel A (2013) Treatment of relapsing Clostridium difficile infection using fecal microbiota transplantation. Clin Exp Gastroenterol 2014:1–6
Poggi M, Bastelica D, Gual P, Iglesias MA, Gremeaux T, Knauf C, Peiretti F, Verdier M, Juhan-Vague I, Tanti JF, Burcelin R, Alessi MC (2007) C3H/HeJ mice carrying a toll-like receptor 4 mutation are protected against the development of insulin resistance in white adipose tissue in response to a high-fat diet. Diabetologia 50:1267–1276
Puigserver P, Spiegelman BM (2003) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1 alpha (PGC-1 alpha): transcriptional coactivator and metabolic regulator. Endocr Rev 24:78–90
Purchiaroni F, Tortora A, Gabrielli M, Bertucci F, Gigante G, Ianiro G, Ojetti V, Scarpellini E, Gasbarrini A (2013) The role of intestinal microbiota and the immune system. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 17:323–333
Quigley EM (2013) Gut bacteria in health and disease. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y) 9:560–569
Raoult D, Henrissat B (2014) Are stool samples suitable for studying the link between gut microbiota and obesity? Eur J Epidemiol 29:307–309
Rautava S, Luoto R, Salminen S, Isolauri E (2012) Microbial contact during pregnancy, intestinal colonization and human disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 9:565–576
Robles-Alonso V, Guarner F (2013) Progress in the knowledge of the intestinal human microbiota. Nutr Hosp 28:553–557
Salazar N, Arboleya S, Valdes L, Stanton C, Ross P, Ruiz L, Gueimonde M, de Los Reyes-Gavilan CG (2014) The human intestinal microbiome at extreme ages of life. Dietary intervention as a way to counteract alterations. Front Genet 5:406
Santacruz A, Marcos A, Warnberg J, Marti A, Martin-Matillas M, Campoy C, Moreno LA, Veiga O, Redondo-Figuero C, Garagorri JM, Azcona C, Delgado M, Garcia-Fuentes M, Collado MC, Sanz Y (2009) Interplay between weight loss and gut microbiota composition in overweight adolescents. Obesity (Silver Spring) 17:1906–1915
Scalbert A, Williamson G (2000) Dietary intake and bioavailability of polyphenols. J Nutr 130:2073S–2085S
Setchell KD, Lawson AM, Borriello SP, Harkness R, Gordon H, Morgan DM, Kirk DN, Adlercreatz H, Anderson LC, Axelson M (1981) Lignan formation in man—microbial involvement and possible roles in relation to cancer. Lancet 2:4–7
Shen J, Obin MS, Zhao L (2013) The gut microbiota, obesity and insulin resistance. Mol Aspects Med 34:39–58
Shu Z, Ma J, Tuerhong D, Yang C, Upur H (2013) How intestinal bacteria can promote HIV replication. AIDS Rev 15:32–37
Smith PM, Howitt MR, Panikov N, Michaud M, Gallini CA, Bohlooly YM, Glickman JN, Garrett WS (2013) The microbial metabolites, short-chain fatty acids, regulate colonic Treg cell homeostasis. Science 341:569–573
Smits LP, Bouter KE, de Vos WM, Borody TJ, Nieuwdorp M (2013) Therapeutic potential of fecal microbiota transplantation. Gastroenterology 145:946–953
Sridharan GV, Choi K, Klemashevich C, Wu C, Prabakaran D, Pan LB, Steinmeyer S, Mueller C, Yousofshahi M, Alaniz RC, Lee K, Jayaraman A (2014) Prediction and quantification of bioactive microbiota metabolites in the mouse gut. Nat Commun 5:5492
Tsukumo DM, Carvalho BM, Carvalho-Filho MA, Saad MJ (2009) Translational research into gut microbiota: new horizons in obesity treatment. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol 53:139–144
Turnbaugh PJ, Ley RE, Mahowald MA, Magrini V, Mardis ER, Gordon JI (2006) An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 444:1027–1031
Udayappan SD, Hartstra AV, Dallinga-Thie GM, Nieuwdorp M (2014) Intestinal microbiota and faecal transplantation as treatment modality for insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Exp Immunol 177:24–29
Ursell LK, Clemente JC, Rideout JR, Gevers D, Caporaso JG, Knight R (2012) The interpersonal and intrapersonal diversity of human-associated microbiota in key body sites. J Allergy Clin Immunol 129:1204–1208
Verdam FJ, Fuentes S, de Jonge C, Zoetendal EG, Erbil R, Greve JW, Buurman WA, de Vos WM, Rensen SS (2013) Human intestinal microbiota composition is associated with local and systemic inflammation in obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring) 21:E607–E615
Vijay-Kumar M, Aitken JD, Carvalho FA, Cullender TC, Mwangi S, Srinivasan S, Sitaraman SV, Knight R, Ley RE, Gewirtz AT (2010) Metabolic syndrome and altered gut microbiota in mice lacking Toll-like receptor 5. Science 328:228–231
Vrieze A, Van Nood E, Holleman F, Salojarvi J, Kootte RS, Bartelsman JF, Dallinga-Thie GM, Ackermans MT, Serlie MJ, Oozeer R, Derrien M, Druesne A, Van Hylckama Vlieg JE, Bloks VW, Groen AK, Heilig HG, Zoetendal EG, Stroes ES, de Vos WM, Hoekstra JB, Nieuwdorp M (2012) Transfer of intestinal microbiota from lean donors increases insulin sensitivity in individuals with metabolic syndrome. Gastroenterology 143(913–916):e917
Wang B, Mao YK, Diorio C, Pasyk M, Wu RY, Bienenstock J, Kunze WA (2010) Luminal administration ex vivo of a live Lactobacillus species moderates mouse jejunal motility within minutes. Faseb J 24:4078–4088
Wilson ID, Nicholson JK (2009) The role of gut microbiota in drug response. Curr Pharm Des 15:1519–1523
Zaibi MS, Stocker CJ, O'Dowd J, Davies A, Bellahcene M, Cawthorne MA, Brown AJ, Smith DM, Arch JR (2010) Roles of GPR41 and GPR43 in leptin secretory responses of murine adipocytes to short chain fatty acids. FEBS Lett 584:2381–2386
Zhang H, DiBaise JK, Zuccolo A, Kudrna D, Braidotti M, Yu Y, Parameswaran P, Crowell MD, Wing R, Rittmann BE, Krajmalnik-Brown R (2009) Human gut microbiota in obesity and after gastric bypass. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:2365–2370
Zhao J, Murray S, Lipuma JJ (2014) Modeling the impact of antibiotic exposure on human microbiota. Sci Rep 4:4345
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Ref-Bio (POLYFrEsNOL project) and by Fundación Rioja Salud, Spain. MJ Villanueva-Millán was supported by a predoctoral grant from Consejería de Industria, Innovación y Empleo (La Rioja Government).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Villanueva-Millán, M.J., Pérez-Matute, P. & Oteo, J.A. Gut microbiota: a key player in health and disease. A review focused on obesity. J Physiol Biochem 71, 509–525 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-015-0390-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-015-0390-3