Abstract
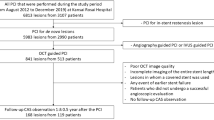
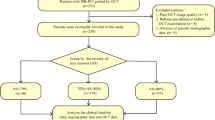
There are still some patients who require repeat revascularization despite of drug-eluting stent (DES) implantation. The present study aimed to investigate the relationship between optical coherence tomography (OCT) findings and recurring target lesion revascularization (TLR) after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) for in-stent restenosis (ISR). We reviewed 50 patients (54 coronary lesions) who underwent PCI for ISR, which included 25 DES-ISR lesions. The PCI strategy depended on the interventionalist’s discretion, and DES implantation was performed for 38 (70 %) lesions. Tissue characteristics were assessed qualitatively and quantitatively using the frame showing maximal lumen narrowing (minimal lumen area). In qualitative analysis, OCT detected coexistence of eccentric tissue proliferation and strong signal attenuation (ESA). ESA was observed in six lesions (11 %) in five patients (10 %). Hemodialysis (80 vs. 20 %, p = 0.013) and DES-ISR (100 vs. 40 %, p = 0.0069) were significantly more frequent in ESA patients/lesions than in others. One-year follow-up revealed that re-TLR was more frequently performed for ESA lesions (83 vs. 8 %, p = 0.0002). The findings reveal that ESA detected in OCT images of ISR is related to TLR after PCI for DES-ISR especially in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ikari Y, Tanabe K, Koyama Y, Kozuma K, Sano K, Isshiki T, et al. Sirolimus eluting coronary stent implantation in patients on maintenance hemodialysis. Circ J. 2012;76:1856–63.
Sato K, Costopoulos C, Takebayashi H, Naganuma T, Miyazaki T, Goto K, et al. The role of integrated backscatter intravascular ultrasound in characterizing bare metal and drug-eluting stent restenotic neointima as compared to optical coherence tomography. J Cardiol. 2014;64:488–95.
Maeda T, Okamura T, Yamada J, Nao T, Tateishi H, Yoshimura M, et al. Serial three-dimensional optical coherence tomography assessment of strut coverage and intraluminal structures after drug-eluting stent implantation. Cardiovasc Interv Ther. 2014;29:31–9.
Suzuki N, Kozuma K, Maeno Y, Yamamoto H, Shiratori Y, Ishikawa S, et al. Quantitative coronary optical coherence tomography image analysis for the signal attenuation observed in-stent restenotic tissue. Int J Cardiol. 2010;145:392–4.
Suzuki N, Kozuma K, Isshiki T. Role of microvessels in occlusive in-stent restenosis. Rev Esp Cardiol. 2012;65:376.
Suzuki N, Guagliumi G, Bezerra HG, Sirbu V, Rosenthal N, Musumeci G, et al. The impact of an eccentric intravascular ImageWire during coronary optical coherence tomography imaging. EuroIntervention. 2011;6:963–9.
Kubo T, Akasaka T, Shite J, Suzuki T, Uemura S, Yu B, et al. OCT compared with IVUS in a coronary lesion assessment: the OPUS-CLASS study. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013;6:1095–104.
Sianos G, Morel MA, Kappetein AP, Morice MC, Colombo A, Dawkins K, et al. The SYNTAX Score: an angiographic tool grading the complexity of coronary artery disease. EuroIntervention. 2005;1:219–27.
Suzuki N, Kozuma K, Kyono H, Otsuki S, Fu Q, Hosogoe N, et al. Predominant microvessel proliferation in coronary stent restenotic tissue in patients with diabetes: insights from optical coherence tomography image analysis. Int J Cardiol. 2013;168:843–7.
Guagliumi G, Musumeci G, Sirbu V, Bezerra HG, Suzuki N, Fiocca L, et al. Optical coherence tomography assessment of in vivo vascular response after implantation of overlapping bare-metal and drug-eluting stents. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2010;3:531–9.
Gonzalo N, Serruys PW, Okamura T, van Beusekom HM, Garcia-Garcia HM, van Soest G, et al. Optical coherence tomography patterns of stent restenosis. Am Heart J. 2009;158:284–93.
Xu C, Schmitt JM, Carlier SG, Virmani R. Characterization of atherosclerosis plaques by measuring both backscattering and attenuation coefficients in optical coherence tomography. J Biomed Opt. 2008;13:034003.
Hou J, Jia H, Liu H, Han Z, Yang S, Xu C, et al. Neointimal tissue characteristics following sirolimus-eluting stent implantation: OCT quantitative tissue property analysis. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2012;28:1879–86.
Fu Q, Suzuki N, Kozuma K, Miyagawa M, Nomura T, Kawashima H, et al. Quantitative optical coherence tomography analysis for late in-stent restenotic lesions. Int Heart J. 2015;56:13–7.
Coletta J, Suzuki N, Nascimento BR, Bezerra HG, Rosenthal N, Guagliumi G, et al. Use of optical coherence tomography for accurate characterization of atherosclerosis. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2010;94:250–4.
Yabushita H, Bouma BE, Houser SL, Aretz HT, Jang IK, Schlendorf KH, et al. Characterization of human atherosclerosis by optical coherence tomography. Circulation. 2002;106:1640–5.
Jia H, Abtahian F, Aguirre AD, Lee S, Chia S, Lowe H, et al. In vivo diagnosis of plaque erosion and calcified nodule in patients with acute coronary syndrome by intravascular optical coherence tomography. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62:1748–58.
Kang SJ, Park DW, Mintz GS, Lee SW, Kim YH, Lee CW, et al. Long-term vascular changes after drug-eluting stent implantation assessed by serial volumetric intravascular ultrasound analysis. Am J Cardiol. 2010;105:1402–8.
Nakazawa G, Otsuka F, Nakano M, Vorpahl M, Yazdani SK, Ladich E, et al. The pathology of neoatherosclerosis in human coronary implants bare-metal and drug-eluting stents. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;57:1314–22.
Kang SJ, Mintz GS, Akasaka T, Park DW, Lee JY, Kim WJ, et al. Optical coherence tomographic analysis of in-stent neoatherosclerosis after drug-eluting stent implantation. Circulation. 2011;123:2954–63.
Hakim DA, Mintz GS, Sanidas E, Rusinova R, Weisz G, Leon MB, et al. Serial gray scale intravascular ultrasound findings in late drug-eluting stent restenosis. Am J Cardiol. 2013;111:695–9.
Fu Q, Suzuki N, Takada K, Yamamoto H, Ishikawa S, Yokoyama N, et al. Effect of cilostazol on optimized standard antiplatelet therapy in a patient with a cytochrome P450 2C19 *2/*2 genotype. Cardiovasc Interv Ther. 2011;26:79–82.
Yonetsu T, Kato K, Kim SJ, Xing L, Jia H, McNulty I, et al. Predictors for neoatherosclerosis: a retrospective observational study from the optical coherence tomography registry. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2012;5:660–6.
Ishihara T, Fujita M, Iida O, Tsujimura T, Uematsu M. Rupture of calcified nodule 105 months after sirolimus-eluting stent implantation observed on coronary angioscopy and optical frequency domain imaging in vivo. Circ J. 2015;79:2278–9.
Suzuki N, Angiolillo DJ, Monteiro C, Shuja S, Futamatsu H, Kawaguchi R, et al. Variable histological and ultrasonic characteristics of restenosis after drug-eluting stents. Int J Cardiol. 2008;130:444–8.
Imai M, Kadota K, Goto T, Fujii S, Yamamoto H, Fuku Y, et al. Incidence, risk factors, and clinical sequelae of angiographic peri-stent contrast staining after sirolimus-eluting stent implantation. Circulation. 2011;123:2382–91.
Kozuma K, Kimura T, Suzuki N, Miyazawa A, Waseda K, Honda Y, et al. Peri-stent contrast staining and very late stent thrombosis after sirolimus-eluting stent implantation: an observation from the RESTART (REgistry of Stent Thrombosis for review And Re-evaluaTion) angiographic substudy. EuroIntervention. 2013;9:831–40.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement of human rights
All procedures performed in this study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suzuki, N., Kozuma, K., Kyono, H. et al. The clinical characteristics and prognosis of lesions with in-stent eccentric tissue proliferation and strong signal attenuation detected by optical coherence tomography. Cardiovasc Interv and Ther 31, 210–217 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12928-015-0369-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12928-015-0369-6