Abstract
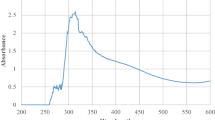
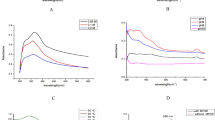
Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles is an interesting issue of nanotechnology. In the present study, zinc oxide nanoparticles were synthesized using Salvadora oleoides leaf aqueous extract and effect of pH on formation of zinc oxide nanoparticles was evaluated. The formation of zinc oxide nanoparticles was characterized by various spectral analysis like UV–Vis spectroscopy, zeta potential measurements, TGA-DTA analysis, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, and transmission electron microscopy analysis. The pH affected some characterization parameters distinctly while others were not affected. pH affected the size of nanoparticles synthesized. Zinc oxide nanoparticles at pH 5 exhibited good broad spectrum of antibacterial activity as compared to pH 8. Though size and antibacterial activity were affected by pH, both are good as antibacterial agents. Hence, zinc oxide nanoparticles could be developed as antibacterial agents against a wide range of bacteria to control and prevent bacterial infections.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sindhura, K. S., Prasad, T. N. V. K. V., Selvam, P. P., & Hussain, O. M. (2014). Synthesis, characterization and evaluation of effect of phytogenic zinc nanoparticles on soil exo-enzyme. Applied Nanoscience, 4, 819–827.
Sharma, D., Sharma, S., Kaith, B. S., Rajput, J., & Kaur, M. (2011). Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using surfactant free in air and microwave method. Applied Surface Science, 257, 9661–9672.
Shoeb, M., Singh, B. R., Khan, J. A., Khan, W., Singh, B. N., Singh, H. B., & Naqvi, A. H. (2013). ROS-dependent anticandidal activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized by using egg albumen as a biotemplate. Advances in Natural Sciences: Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 4, 1–11.
Raghupathi, K. R., Koodali, R. T., & Manna, A. C. (2011). Size dependent bacterial growth inhibition and mechanism of antibacterial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Langmuir, 27, 4020–4028.
Nagajyothi, P. C., Sreekath, T. V. M., Tettery, C. O., Jun, Y. I., & Mook, S. H. (2014). Characterization antibacterial, antioxidant and cytotoxic activities of ZnO nanoparticles using Coptidis rhizoma. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 24, 4208–4303.
Salem, W., Leitner, D. R., Zingl, F. G., Schratter, G., Prassi, R., Goessler, W., et al. (2015). Antibacterial activity of silver and zinc nanoparticles against Vibrio cholera and enterotoxin Escherichia coli. International Journal of Medical Microbiology, 305, 85–95.
Espitia, P. J. P., Soares, N. F. F., Coimbra, J. S. R., Andrade, N. J., Cruz, R. S., & Medeiros, E. A. A. (2012). Zinc oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, antimicrobial activity and food packaging applications. Food Bioprocess Technology, 5, 1447–1464.
Rekha, K., Nirmala, M., Nair, M. G., & Anukaliani, A. (2010). Structural, optical, photocatalytic and antibacterial activity of zinc oxide and manganese doped zinc oxide nanoparticles. Physcia B, 405, 3180–3185.
Divyapriya, S., Sowmia, C., & Saaikala, S. (2014). Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles and antimicrobial activity of Murraya koenigii. World Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 3(12), 1635–1645.
Padalia, H., Moteriya, P., & Chanda, S. (2015). Green synthesis of sliver nanoparticles from marigold flower and its synergistic antimicrobial potential. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 8, 732–741.
Moteriya, P., & Chanda, S. (2014). Low cost and ecofriendly phytosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Cassia roxburghii stem extract and its antimicrobial and antioxidant efficacy. American Journal of Advanced Drug Delivery, 2(4), 557–575.
Vidya, C., Hiremath, S., Chandraprabha, M. N., Antonyraj, M. A. L., Gopal, I. V., Jain, A., & Bansal, K. (2013). Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles by Calotropis gigantea. International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology, 1, 118–120.
Monica, R. C., & Cremonini, R. (2009). Nanoparticles and higher plants. Caryologia, 62(2), 161–165.
Singh, S., Naresh, V., & Sharma, S. K. (2013). Isolation of novel phytoconstituents from the bark of Salvadora oleoides Decne. International Journal of Herbal Medicine, 1(2), 9–13.
Kumar, S., Dhankhar, S., Arya, V. P., Yadav, S., & Yadav, J. P. (2012). Antimicrobial activity of Salvadora oleoides Decne. against some microorganisms. Journal of Medicinal Plant Research, 6(14), 2754–2760.
Natubhai, P. M., Pandya, S. S., & Rabari, H. A. (2013). Anti-inflammatory activity of leaf extracts of Salvadora oleoides Decne. International Journal of Pharma and Biosciences, 4(1), 985–993.
Simonsen, H. T. (2001). In vitro screening of Indian medicinal plants for antiplasmodial activity. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 74, 195–204.
Perez, C., Paul, M., & Bazerque, P. (1990). An antibiotic assay by the agar well diffusion method. Acta Biologiae Medicine Experimentalis, 15, 113–115.
Akash, S., Kumar, S. S. S., & Dhamodhar, P. (2015). Inhibition of group a Streptococcus by green synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles. International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences, 6(2), 85–98.
Jayaseelan, C., Rahuman, A. A., Kirthi, A. V., Marimuthu, S., Santhoshkumar, T., Bagavan, A., et al. (2012). Novel microbial route to synthesize ZnO nanoparticles using Aeromonas hydrophila and their activity against pathogenic bacteria and fungi. Spectrochimica Acta. Part A, Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 90, 78–84.
Suresh, D., Udayabhanu, Nethravathi, P. C., Lingaraju, K., Rajanaika, H., Sharma, S. C., & Nagabhushana, H. (2015). EGCG assisted green synthesis of ZnO nanopowders: photodegradative, antimicrobial and antioxidant activities. Spectrochimica Acta. Part A, Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 136, 1467–1474.
Ramesh, M., Anbuvannan, M., & Viruthagiri, G. (2015). Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Solanum nigrum leaf extracts and their activity. Spectrochimica Acta. Part A, Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 136, 864–870.
Raliya, R., & Tarafdar, J. C. (2014). Biosynthesis and characterization of zinc, magnesium and titanium nanoparticles: an eco-friendly approach. International Nano Letters, 4(93), 1–10.
Sharma, D., Rajput, J., Kaith, B. S., Kaur, M., & Sharma, S. (2010). Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and study of their antibacterial and antifungal properties. Thin Solid Film, 519, 1224–1229.
Kairyte, K., Kadys, A., & Luksiene, Z. (2013). Antibacterial and antifungal activity of photoactivated ZnO nanoparticles in suspension. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology, 128, 78–84.
Uddin, R., & Akrema. (2016). Extracellular synthesis of silver dimer nanoparticles using Callistemon viminalis (bottlebrush) extract and evaluation of their antibacterial activity. Spectroscopy Letter. doi:10.1080/00387010.2016.1140654.
Moteriya, P., & Chanda, S. (2016). Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Caesalpinia pulcherrima flower extract and assessment of their in vitro antimicrobial, antioxidant, cytotoxic and genotoxic activities. Artificial cell Nanomedicine and Biotechnology. (In Press).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Department of Biosciences (UGC-CAS) for providing excellent research facilities. One of the authors Ms. Hemali Padalia is thankful to UGC-CAS, New Delhi, India for providing Junior Research Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Padalia, H., Baluja, S. & Chanda, S. Effect of pH on Size and Antibacterial Activity of Salvadora oleoides Leaf Extract-Mediated Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. BioNanoSci. 7, 40–49 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-016-0387-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-016-0387-6