Abstract
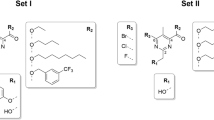
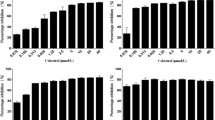
The opportunistic bacteria Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis often form rigid biofilms on wounds and artificial surfaces and thereby become extremely resistant to antimicrobials. Here, we report the effect of four novel 2(5H)-furanone derivatives on the cell growth and biofilm formation by these microorganisms. Using the differential fluorescence staining of viable and dead cells, we demonstrated that furanones increase the antibacterial efficacy of chloramphenicol against both biofilm-embedded S. aureus and S. epidermidis with F35 being the most efficient compound, probably by increasing the accessibility of cells against antimicrobials. Compounds F6, F8, and F83 inhibited the biofilm formation at concentrations of 2.5–10 μg/ml, although exhibiting high cytotoxicity for human skin fibroblasts with CC50 of 0.5–1.1 μg/ml. F35 demonstrated minimal biofilm inhibition concentration of 10 μg/ml, while its cytotoxicity was ten times lower than that of the other compounds (CC50 13.1 μg/ml), suggesting its chemotype seems a promising starting point for the development of new antibiofilm agents.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hoiby, N., Bjarnsholt, T., Givskov, M., Molin, S., Ciofu, O. (2010). Antibiotic resistance of bacterial biofilms. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, 35, 322–332.
Lönn-Stensrud, J., Landin, M. A., Benneche, T., Petersen, F. C., Scheie, A. A. (2009). Furanones, potential agents for preventing Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm infections? Antimicrob Chemother, 63, 309–316.
Trizna, E. Y., Khakimullina, E. N., Latypova, L. Z., et al. (2015). Thioderivatives of 2(5H)-furanone as inhibitors against Bacillus subtilis biofilms. Acta Naturae, 2, 102–107.
Kayumov, A. R., Khakimullina, E. N., Sharafutdinov, I. S., et al. (2015). Inhibition of biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis by new halogenated furanones. The Journal of Antibiotics, 68, 297–301.
Saising, J., Dube, L., Ziebandt, A. K., Voravuthikunchai, S. P., et al. (2012). Activity of gallidermin on Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 56, 5804–5810.
Vuong, C., Voyich, J. M., Fischer, E. R., Braughton, K. R., Whitney, A. R., et al. (2004). Polysaccharide intercellular adhesin (PIA) protects Staphylococcus epidermidis against major components of the human innate immune system. Cellular Microbiology, 6, 269–275.
Kayumov A. R., Nureeva A. A., Trizna E. Yu., Gazizova G. R., Bogachev M. I. et al. (2015) New derivatives of pyridoxine exhibit high antibacterial activity against biofilm-embedded Staphylococcus cells. BioMed Research International, 2015, 890968.
Hoang, L. T., Kurbangalieva, A. R., Ezhova, A. S., Berdnikov, E. A., Chmutova, G. A. (2015). The bis-thioethers based on 3,4-dichloro-2(5H)-furanone and propane-1,3-dithiol. Butlerov Communications, 42, 33–40.
Kurbangalieva, A. R., Devyatova, N. F., Bogdanov, A. V., Berdnikov, E. A., Mannafov, T. G., Krivolapov, D. B., et al. (2007). Synthesis of novel arylthio derivatives of mucochloric acid. Phosphorus, Sulfur, Silicon, Relat. Elem, 182, 607–630.
Gumulka W., Kokosinski J. (1976). Derivatives of mucochloric acid. Part I. Pseudoesters and pseudothioesters of mucochloric acid. Pol. Organika, 1, 45–60.
O’Toole, G. A., & Kolter, R. (1998). Initiation of biofilm formation in Pseudomonas fluorescens WCS365 proceeds via multiple, convergent signalling pathways: a genetic analysis. Molecular Microbiology, 28, 449–461.
McCann, J., & Ames, B. N. (1976). A simple method for detecting environmental carcinogens as mutagens. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 271, 5–13.
Oda, Y., Nakamura, S., Oki, I., Kato, T., Shinagawa, H. (1985). Evaluation of the new system (umu-test) for the detection of environmental mutagens and carcinogens. Mutation Research, 147, 219–229.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (RSF 15-14-00046) and by the Russian Government Program to support the competitive development of the Kazan Federal University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trizna, E., Latypova, L., Kurbangalieva, A. et al. 2(5H)-Furanone Derivatives as Inhibitors of Staphylococcal Biofilms. BioNanoSci. 6, 423–426 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-016-0258-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-016-0258-1