Abstract
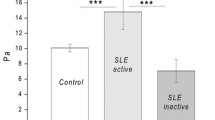
Thrombotic complications in systemic lupus erythematosus contribute significantly to the morbidity and mortality rates. Abnormal formation and structure of fibrin clots add substantially to hypercoagulability and thrombosis. We used dynamic turbidimetry to assess in vitro the kinetics of fibrin polymerization and t-PA-induced fibrinolysis in recalcified plasma of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus compared to healthy subjects. Fibrin structure was studied using scanning electron microscopy. Clots from the pathological plasma samples polymerized significantly slower, resulting in formation of fibrin with a higher optical density and less compact fibrin networks with larger pores. These changes were associated with a prolonged clot lysis time and reduced lysis rate. The results show that in the blood of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus fibrin clots have a pro-thrombotic phenotype that comprises an important mechanism underlying lupus-related thrombophilia.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hinojosa-Azaola, A., Romero-Diaz, J., Vargas-Ruiz, A. G., Nuñez-Alvarez, C. A., Cicero-Casarrubias, A., Ocampo-Torres, M. C., et al. (2016). Venous and arterial thrombotic events in systemic lupus erythematosus. Journal of Rheumatology, 43(3), 576–586.
Litvinov, R. I., & Weisel, J. W. (2016). What is the biological and clinical relevance of fibrin? Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis, 42(4), 333–343.
Dhillon, P. K., & Adams, M. J. (2013). Thrombosis in systemic lupus erythematosus: role of impaired fibrinolysis. Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis, 39(4), 434–440.
Weisel, J. W., & Nagaswami, C. (1992). Computer modeling of fibrin polymerization kinetics correlated with electron microscope and turbidity observations: clot structure and assembly are kinetically controlled. Biophysical Journal, 63, 111–128.
Zubairova, L. D., Nabiullina, R. M., Nagaswami, C., Zuev, Y. F., Mustafin, I. G., Litvinov, R. I., et al. (2015). Circulating microparticles after formation, structure, and properties of fibrin clots. Science Reports, 5, 17611. doi:10.1038/s17611.
Collet, J. P., Lesty, C., Montalescot, G., Weisel, J. W. (2003). Dynamic changes of fibrin architecture during fibrin formation and intrinsic fibrinolysis of fibrin-rich clots. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278(24), 21331–21335.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Program for Competitive Growth of Kazan Federal University. Scanning electron microscopy was performed at the Interdisciplinary Center for Analytical Microscopy of Kazan Federal University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nabiullina, R.M., Shakurova, M.A., Maksudova, A.N. et al. Fibrin Clot Structure and Properties are Altered in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. BioNanoSci. 6, 345–347 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-016-0234-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-016-0234-9