Abstract
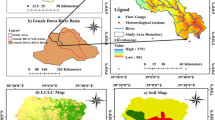
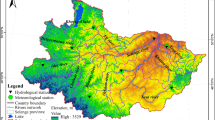
Thermokarst lake is a significant indicator of permafrost degradation. However, the evaluation of thermokarst lake development is very difficult through physical mechanism analysis because the development is influenced by many factors. In the present study, the factors influencing thermokarst lake development were investigated from the perspective of frozen soil and the geographical environment. The influences of six factors on thermokarst lake development in Beiluhe basin, located in the hinterland of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, were analyzed: permafrost type, ground temperature, vegetation type, soil type, hydrogeological type, and slope. Sensitivity coefficients were calculated for these factors using statistical methods. The results show that thermokarst lake development was influenced by the analyzed factors as follows: permafrost > soil type > ground temperature > hydrogeological type. Furthermore, 80.1% of the study area was highly sensitive to thermokarst lake development. Overall, thermokarst lake development in the Beiluhe basin was thoroughly evaluated based on sensitivity factors and an established statistical evaluation method. The method detailed in this paper provides a reference for evaluating the likelihood and severity of thermokarst lake development.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aniya M (1985) Landslide-susceptibility mapping in the Amahata River basin, Japan. Ann Assoc Am Geogr 75(1):102–114
Cheng G (2004) Influences of local factors on permafrost occurrence and their implications for Qinghai–Xizang Railway design. Sci China Ser D Earth Sci 47(8):704–709
Cheng G, Wu T (2007) Responses of permafrost to climate change and their environmental significance, Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. J Geophys Res Earth Surf 112(F2):S03
Grosse G, Romanovsky VK, Walter K, Morgenstern A, Lantuit H, Zimov S (2008) Distribution of thermokarst lakes and ponds at three yedoma sites in Siberia. In: Kane DL, Hinkel KM (eds) Proceedings of the ninth international conference on permafrost, June 29–July 3, 2008, Fairbanks, Alaska. Institute of Northern Engineering, University of Alaska Fairbanks, Fairbanks, Alaska, pp 551–556
Hinkel KM, Frohn RC, Nelson FE, Eisner WR, Beck RA (2005) Morphometric and spatial analysis of thaw lakes and drained thaw lake basins in the western Arctic Coastal Plain, Alaska. Permafr Periglac Process 16(4):327–341
Hinkel KM, Jones BM, Eisner WR, Cuomo CJ, Beck RA, Frohn R (2007) Methods to assess natural and anthropogenic thaw lake drainage on the western Arctic coastal plain of northern Alaska. J Geophys Res Earth Surf 112(F2):S16
Jin H, Wei Z, Wang S, Yu Q, Lü L, Wu Q, Ji Y (2008) Assessment of frozen-ground conditions for engineering geology along the Qinghai–Tibet highway and railway, China. Eng Geol 101(3):96–109
Jin H, He R, Cheng G, Wu Q, Wang S, Lü L, Chen X (2009) Changes in frozen ground in the source area of the Yellow River on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, China, and their eco-environmental impacts. Environ Res Lett 4(4):045206
Jones BM, Grosse G, Arp CD, Jones MC, Walter Anthony KM, Romanovsky VE (2011) Modern thermokarst lake dynamics in the continuous permafrost zone, northern Seward Peninsula, Alaska. J Geophys Res Biogeosci 116:G00M03. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011JG001666
Jorgenson MY, Shur YL, Osterkamp TE (2008) Thermokarst in Alaska. In: Kane DL, Hinkel KM (eds) Proceedings of the ninth international conference on permafrost, June 29–July 3, 2008, Fairbanks, Alaska, Institute of Northern Engineering, University of Alaska Fairbanks, Fairbanks, Alaska, pp 869–876
Karlsson JM, Lyon SW, Destouni G (2012) Thermokarst lake, hydrological flow and water balance indicators of permafrost change in Western Siberia. J Hydrol 464–465:459–466
Kokelj SV, Jorgenson MT (2013) Advances in thermokarst research. Permafr Periglac Process 24(2):108–119
Li L, Yang S, Wang Z, Zhu X, Tang H (2010) Evidence of warming and wetting climate over the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Arct Antarct Alp Res 42(4):449–457
Lin Z, Niu F, Xu Z, Xu J, Wang P (2010) Thermal regime of a thermokarst lake and its influence on permafrost, Beiluhe basin, Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Permafr Periglac Process 21(4):315–324
Lin Z, Niu F, Liu H, Lu J (2011) Hydrothermal processes of alpine tundra lakes, Beiluhe basin, Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Cold Reg Sci Technol 65(3):446–455
Liu X, Chen B (2000) Climatic warming in the Tibetan Plateau during recent decades. Int J Climatol 20(14):1729–1742
Lu J, Niu F, Lin Z, Liu H, Luo J (2012) Permafrost modeling and mapping along the Qinghai–Tibet engineering corridor considering slope-aspect. Geogr Geoinf Sci 28(3):63–67
Luo J, Niu F, Lin Z, Liu M, Yin G (2015) Thermokarst lake changes between 1969 and 2010 in the Beilu River basin, Qinghai–Tibet plateau, China. Sci Bull 60(5):556–564
Nan Z, Li S, Cheng G (2005) Prediction of permafrost distribution on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau in the next 50 and 100 years. Sci China Ser D Earth Sci 48(6):797–804
Niu F, Lin Z, Liu H, Lu J (2011) Characteristics of thermokarst lakes and their influence on permafrost in Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Geomorphology 132(3–4):222–233
Niu F, Luo J, Lin Z, Liu M, Yin G (2014) Morphological characteristics of thermokarst lakes along the Qinghai–Tibet engineering corridor. Arct Antarct Alp Res 46(4):963–974
Smith LC, Sheng Y, MacDonald GM, Hinzman LD (2005) Disappearing arctic lakes. Science 308(5727):1429
Walter KM, Edwards ME, Grosse G, Zimov SA, Chapin FS (2007) Thermokarst lakes as a source of atmospheric CH4 during the last deglaciation. Science 318(5850):633–636
Wang S, Jin H, Li S, Lin Z (2000) Permafrost degradation on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and its environmental impacts. Permafr Periglac Process 11(1):43–53
Wang G, Li Y, Wu Q, Wang Y (2006) Impacts of permafrost changes on alpine ecosystem in Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Sci China Ser D Earth Sci 49(11):1156–1169
Wu Q, Liu Y, Zhang J, Tong C (2002) A review of recent frozen soil engineering in permafrost regions along Qinghai-Tibet highway, China. Permafr Periglac Process 13(3):199–205
Wu Q, Liu Y (2004) Ground temperature monitoring and its recent change in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Cold Reg Sci Technol 38(2):85–92
Wu Q, Zhang T, Liu Y (2010) Permafrost temperatures and thickness on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Glob Planet Change 72(1):32–38
Yoshikawa K, Hinzman LD (2003) Shrinking thermokarst ponds and groundwater dynamics in discontinuous permafrost near Council, Alaska. Permafr Periglac Process 14(2):151–160
Zhang G, Yao T, Xie H, Zhang K, Zhu F (2014) Lakes’ state and abundance across the Tibetan Plateau. Chin Sci Bull 59(24):3010–3021
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the China International Postdoctoral Exchange Fellowship Program 2016, which was supported by the office of the China Postdoctoral Council. This study was also supported by the State Key Program of National Natural Science of China (Grant No. 41730640).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Liu, H. & Ni, W. Factors influencing thermokarst lake development in Beiluhe basin, the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Environ Earth Sci 76, 816 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7143-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7143-2