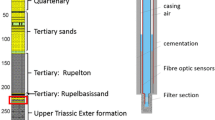
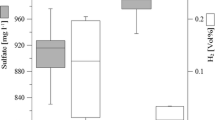
Abstract
At a pilot site for CO2 storage in Ketzin (Germany), a drastic decrease in injectivity occurred in a well intended for injection. This was attributed to an obstruction of the pore throats due to microbial degradation of the organic drill mud and subsequent iron sulfide (FeS) precipitation in the highly saline brine (240 g L−1). To better understand the biogeochemical processes, the response of the autochthonous microbial community to drill mud exposure was investigated. Pristine cores of two aquifers with different salinity were incubated under simulated in situ conditions (50 bar, 40 °C and 45 bar, 25 °C, respectively) and CO2 atmosphere. For the first time, rock cores obtained from the CO2 plume of the storage formation were investigated. The influence of acetate as a biodegradation product of drill mud polymers and the effectiveness of a biocide were additionally tested. Increased microbial diversities were observed in all long-term (8–20 weeks) incubations, even including biocide. Biofilm-like structures and small round-shaped minerals of probable microbiological origin were found. The results indicate that the microbial community remains viable after long-term CO2 exposure. Microorganisms hydrolyzing cellulose polymers (e.g., Burkholderia spp., Variovorax spp.) biodegraded organic components of the drill mud and most likely produced low molecular weight acids. Although the effects of drill mud were less strong as observed in situ, it was demonstrated that acetate supports the growth of sulfate-reducing bacteria (i.e., Desulfotomaculum spp.). The microbial-induced precipitation of amorphous FeS reduced the injectivity in the near-well area. Therefore, when using organic drill mud, the well must be cleaned intensively to minimize the hazards of bacterial stimulation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al Hashem A, Carew JA, Al Borno A (2004) Screening test for six dual biocide regimes against planktonic and sessile populations of bacteria. NACE International. NACE-04748
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215(3):403–410. doi:10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2
Balkwill DL, Drake GR, Reeves RH, Fredrickson JK, White DC, Ringelberg DB, Chandler DP, Romine MF, Kennedy DW, Spadoni CM (1997) Taxonomic study of aromatic-degrading bacteria from deep-terrestrial-subsurface sediments and description of Sphingomonas aromaticivorans sp. nov., Sphingomonas subterranea sp. nov., and Sphingomonas stygia sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47(1):191–201. doi:10.1099/00207713-47-1-191
Bauer S, Beyer C, Dethlefsen F, Dietrich P, Duttmann R, Ebert M, Feeser V, Görke U, Köber R, Kolditz O, Rabbel W, Schanz W, Schäfer D, Würdemann H, Dahmke A (2013) Impacts of the use of the geological subsurface for energy storage: an investigation concept. Environ Earth Sci 70:3935–3943. doi:10.1007/s12665-013-2883-0
Bergmann P, Schmidt-Hattenberger C, Kiessling D, Rücker C, Labitzke T, Henninges J, Baumann G, Schütt H (2012) Surface-downhole electrical resistivity tomography applied to monitoring of CO2 storage at Ketzin, Germany. Geophysics 77:B253–B267. doi:10.1190/geo2011-0515.1
Boersma FGH, Otten R, Warmink JA, Nazir R, van Elsas JD (2010) Selection of Variovorax paradoxus-like bacteria in the mycosphere and the role of fungal-released compounds. Soil Biol Biochem 42(12):2137–2145. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2010.08.009
Czarnetzki AB, Tebbe CC (2004) Diversity of bacteria associated with Collembola—a cultivation-independent survey based on PCR-amplified 16S rRNA genes. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 49:217–227. doi:10.1016/j.femsec.2004.03.007
Deng S, Dong H, Lv G, Jiang H, Yu B, Bishop ME (2010) Microbial dolomite precipitation using sulfate reducing and halophilic bacteria: results from Qinghai Lake, Tibetan Plateau, NW China. Chem Geol 278:151–159. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2010.09.008
Detmers J, Strauss H, Schulte U, Bergmann A, Knittel K, Kuever J (2004) FISH shows that Desulfotomaculum spp. are the dominating sulfate-reducing bacteria in a pristine aquifer. Microb Ecol 47(3):236–242. doi:10.1007/s00248-004-9952-6
Doudoroff M (1940) The oxidative assimilation of sugars and related substances by Pseudomonas saccharophila with a contribution to the problem of the direct respiration of di- and polysaccharides. Enzymologia 9:59–72
Douglas S, Beveridge TJ (1998) Mineral formation by bacteria in natural microbial communities. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 26:79–88. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6941.1998.tb00494.x
Ehinger S, Seifert J, Kassahun A, Schmalz L, Hoth N, Schlömann M (2009) Predominance of Methanolobus spp. and Methanoculleus spp. in the archaeal communities of saline gas field formation fluids. Geomicrobiol J 26(5):326–338. doi:10.1080/01490450902754441
Ekperigin MM (2007) Preliminary studies of cellulase production by Acinetobacter anitratus and Branhamella sp. Afr J Biotechnol 6(1):028–033
Falcone-Dias MF, Vaz-Moreira I, Manaia CM (2012) Bottled mineral water as a potential source of antibiotic resistant bacteria. Water Res 46(11):3612–3622. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2012.04.007
Fischer S, Liebscher A, Wandrey M, The CO2SINK group (2010) CO2–brine–rock interaction—first results of long-term exposure experiments at in situ P–T conditions of the Ketzin CO2 reservoir. Chem Erde Geochem 70(S3):155–164. doi:10.1016/j.chemer.2010.06.001
Fischer S, Zemke K, Liebscher A, Wandrey M, The CO2SINK Group (2011) Petrophysical and petrochemical effects of long-term CO2-exposure experiments on brine-saturated reservoir sandstone. Energy Proc 4:4487–4494. doi:10.1016/j.egypro.2011.02.404
Fleshman R, Obren-Likic H (1999) Artificial lift for high volume production. Oilfield Rev 11(1):49–63
Fredrickson JK, Balkwill DL, Romine MF, Shi T (1999) Ecology, physiology, and phylogeny of deep subsurface Sphingomonas sp. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 23(4–5):273–283
Ghosh W, Roy P (2006) Mesorhizobium thiogangeticum sp. nov., a novel sulfur-oxidizing chemolithoautotroph from rhizosphere soil of an Indian tropical leguminous plant. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56(1):91–97. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.63967-0
Giangiacomo LA, Dennis DM (1997) Field testing of the biocompetitive exclusion process for control of iron and hydrogen sulfides. Soc Petrol Eng J SPE 38351:125–135. doi:10.2118/38351-MS
Jaiswal P, Al-Hadrami F, Atekwana EA, Atekwana EA (2014) Mechanistic models of biofilm growth in porous media. J Geophys Res Biogeosci 119:1418–1431. doi:10.1002/2013JG002440
Jin L, Kim KK, Ahn CY, Oh HM (2012) Variovorax defluvii sp. nov., isolated from sewage. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62(8):1779–1783. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.035295-0
Kasina M, Bock S, Würdemann H, Pudlo D, Picard A, Lichtschlag A, März C, Wagenknecht L, Wehrmann LM, Vogt C, Meister P (2017) Mineralogical and geochemical analysis of Fe-phases in drill-cores from the Triassic Stuttgart Formation at Ketzin CO2 storage site before CO2 arrival (submitted in this issue)
Kim SJ, Moon JY, Weon HY, Hong SB, Seok SJ, Kwon SW (2014) Undibacterium jejuense sp. nov. and Undibacterium seohonense sp. nov., isolated from soil and freshwater, respectively. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64(1):236–241. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.056846-0
Lane DJ (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. Wiley, New York, pp 115–175
Lappan RE, Fogler HS (1992) The effects of bacterial polysaccharide production on formation damage. Soc Petrol Eng SPE 19418:165–172. doi:10.2118/19418-PA
Liang Y-L, Zhang Z, Wu M, Wu Y, Feng J-X (2014) Isolation, screening, and identification of cellulolytic bacteria from natural reserves in the subtropical region of China and optimization of cellulase production by Paenibacillus terrae ME27-1. BioMed Res Int. doi:10.1155/2014/512497
Lorite MJ, Muñoz S, Olivares J, Soto MJ, Sanjuán J (2010) Characterization of strains unlike Mesorhizobium loti that nodulate Lotus spp. in saline soils of Granada, Spain. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(12):4019–4026. doi:10.1128/AEM.02555-09
Martens S, Möller F, Streibel M, Liebscher A (2014) Completion of five years of safe CO2 injection and transition to the post-closure phase at the Ketzin Pilot site. Energy Proc 59:190–197. doi:10.1016/j.egypro.2014.10.366
Ménez B, Dupraz S, Gérard E, Guyot F, Rommevaux-Jestin C, Libert M, Jullien M, Michel C, Delorme F, Battaglia-Brunet F, Ignatiadis I, Garcia B, Blanchet D, Huc AY, Haeseler F, Oger P, Dromart G, Ollivier B, Magot M (2007) Impact of the deep biosphere on CO2 storage performance. Geotechnol Sci Rep 9:150–163
Morozova D, Wandrey M, Zimmer M, Pilz P, Zettlitzer M, Würdemann H, The CO2SINK Group (2010) Monitoring of the microbial community composition in saline aquifers during CO2 sequestration by fluorescence in situ hybridisation. Int J Greenh Gas Control 4:981–989. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2009.11.014
Morozova D, Let D, Würdemann H (2013) Analysis of the microbial community from a saline aquifer prior to CO2 injection in Ketzin using improved fluorescence in situ hybridisation method. Energy Proc 40:276–284. doi:10.1016/j.egypro.2013.08.032
Moser DP, Gihring TM, Brockman FJ, Fredrickson JK, Balkwill DL, Dollhopf ME, Lollar BS, Pratt LM, Boice E, Southam G, Wanger G, Baker BJ, Pfiffner SM, Lin LH, Onstott TC (2005) Desulfotomaculum and Methanobacterium spp. dominate a 4- to 5-kilometer-deep fault. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(12):8773–8783. doi:10.1128/AEM.71.12.8773-8783.2005
Muyzer G, de Waal EC, Uitterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:695–700
Nedelkova M, Radeva G, Selenska-Pobell S (2005) Molecular bacterial diversity in water at the deep-well monitoring site at Tomsk-7. In: Tsang CF, Apps J (eds) Underground injection science and technology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 521–536
Park JM, Kim TY, Lee SY (2011) Genome-scale reconstruction and in silico analysis of the Ralstonia eutropha H16 for polyhydroxyalkanoate synthesis, lithoautotrophic growth, and 2-methyl citric acid production. BMC Syst Biol 5:101. doi:10.1186/1752-0509-5-101
Pavel AB, Vasile CI (2012) PyElph—a software tool for gel images analysis and phylogenetics. BMC Bioinform 13:9
Pchalek J, Bergerhoff H, Polleschner G, Borsdorf K, Lange M, Oswald B (1964) Ergebnisbericht u¨ber die geologische Speichererkundung der Struktur Brandenburg, Ketzin, Strukturteil Ost (Knoblauch). VEB UGS Burg
Pellizzari L, Neumann D, Alawi M, Voigt D, Norden B, Würdemann H (2013) Use of tracers to assess drill mud penetration depth into sandstone rock cores during deep drilling: method development and application. Environ Earth Sci 70:3727–3738. doi:10.1007/s12665-013-2715-2
Pellizzari Morozova D, Neumann D, Kasina M, Klapperer S, Zettliter M, Würdemann H (2016) Comparison of the microbial community composition of pristine rock cores and technical influenced well fluids from the Ketzin pilot site for CO2 storage. Environ Earth Sci 75:1323. doi:10.1007/s12665-016-6111-6
Prevedel B, Wohlgemuth L, Legarth B, Henninges J, Schütt H, Schmidt-Hattenberger C, Norden B, Förster A, Hurter S (2009) The CO2SINK boreholes for geological CO2-storage testing. Energy Proc 1:2087–2094. doi:10.1016/j.egypro.2009.01.272
Rosenqvist J, Kilpatrick AD, Yardley BWD, Rochelle CA (2014) Feldspar dissolution at CO2-saturated conditions. Geophysical Research Abstracts, vol 16, EGU2014-10909, 2014 EGU General Assembly
Rosnes JT, Graue A, Torleiv L (1991) Activity of sulfate-reducing bacteria under simulated reservoir conditions. Soc Petrol Eng SPE 19429:231–236. doi:10.2118/19429-PA
Russell AD, McDonnell G (2000) Concentration: a major factor in studying biocidal action. J Hosp Infect 44(1):1–3. doi:10.1053/jhin.1999.0654
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Satola B, Wübbeler JH, Steinbüchel A (2013) Metabolic characteristics of the specie Variovorax paradox. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:541–560. doi:10.1007/s00253-012-4585-z
Schwartz T, Jungfer C, Heissler S, Friedrich F, Faubel W, Obst U (2009) Combined use of molecular biology taxonomy, Raman spectrometry, and ESEM imaging to study natural biofilms grown on filter materials at waterworks. Chemosphere 77(2):249–257. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.07.002
Sørensen T (1948) A method of establishing groups of equal amplitude in plant sociology based on similarity of species and its application to analyses of the vegetation on Danish commons. Kongelige Danske Videnskabernes Selskab 5(4):1–34
Spark I, Patey I, Duncan B, Hamilton A, Devine C, McGovern-Traa C (2000) The effects of indigenous and introduced microbes on deeply buried hydrocarbon reservoirs, North Sea. Clay Miner 35:5–12
Spring S, Lapidus A, Schröder M, Gleim D, Sims D, Meincke L, Glavina Del Rio T, Tice H, Copeland A, Cheng JF, Lucas S, Chen F, Nolan M, Bruce D, Goodwin L, Pitluck S, Ivanova N, Mavromatis K, Mikhailova N, Pati A, Chen A, Palaniappan K, Land M, Hauser L, Chang YJ, Jeffries CD, Chain P, Saunders E, Brettin T, Detter JC, Göker M, Bristow J, Eisen JA, Markowitz V, Hugenholtz P, Kyrpides NC, Klenk HP, Han C (2009) Complete genome sequence of Desulfotomaculum acetoxidans type strain (5575). Stand Genom Sci 1(3):242–253. doi:10.4056/sigs.39508
Struchtemeyer CG, Davis JP, Elshahed MS (2011) Influence of the drilling mud formulation process on the bacterial communities in thermogenic natural gas wells of the Barnett Shale. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(14):4744–4753. doi:10.1128/AEM.00233-11
Suihko M-L, Skyttä E (2009) Characterisation of aerobically grown non-spore-forming bacteria from paper mill pulps containing recycled fibres. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36:53–64. doi:10.1007/s10295-008-0472-0
Talia P, Sede SM, Campos E, Rorig M, Principi D, Tosto D, Hopp HE, Grasso D, Cataldi A (2012) Biodiversity characterization of cellulolytic bacteria present on native Chaco soil by comparison of ribosomal RNA genes. Res Microbiol 163:221–232. doi:10.1016/j.resmic.2011.12.001
Van Beek CGDW, Kooper WF (1980) The clogging of shallow discharge wells in the Netherlands’ river region. Ground Water 18(6):578–586
Vandieken V, Knoblauch C, Jørgensen BB (2006) Desulfotomaculum arcticum sp. nov., a novel spore-forming, moderately thermophilic, sulfate-reducing bacterium isolated from a permanently cold fjord sediment of Svalbard. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56(4):687–690. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.64058-0
Verastegui Y, Cheng J, Engel K, Kolczynski D, Mortimer S, Lavigne J, Montalibet J, Romantsov T, Hall M, McConkey BJ, Rose DR, Tomashek JJ, Scott BR, Charles TC, Neufeld JD (2014) Multisubstrate isotope labeling and metagenomic analysis of active soil bacterial communities. mBio 5(4):01157-14. doi:10.1128/mBio.01157-14
Wagner D, Milodowski AE, West JM, Wragg J, Yoshikawa H (2013) Mineralogical comparisons of experimental results investigating the biological impacts on rock transport processes. Environ Sci Process Impacts 15(8):1501–1510. doi:10.1039/c3em00188a
Wakil SM, Onilude AA, Ball AS (2008) Dynamics and diversity of bacterial communities of fermented weaning foods via denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis PCR-DGGE. Res J Microbiol 3(11):630–640
Wandrey M, Morozova D, Zettlitzer M, Würdemann H, The CO2SINK Group (2010) Assessing drilling mud and technical fluid contamination in rock core and brine samples intended for microbiological monitoring at the CO2 storage site in Ketzin using fluorescent dye tracers. Int J Greenh Gas Control 4(6):972–980. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2010.05.012
Wandrey M, Pellizzari L, Zettlitzer M, Würdemann H (2011) Microbial community and inorganic fluid analysis during CO2 storage within the frame of CO2SINK—long-term experiments under in situ conditions. Energy Proc 4:3651–3657. doi:10.1016/j.egypro.2011.02.296
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173:697–703
Widdel F, Pfennig N (1977) A new anaerobic, sporing, acetate-oxidizing, sulfate-reducing bacterium, Desulfotomaculum (emend.) acetoxidans. Arch Microbiol 112:119–122. doi:10.1007/BF00446665
Wiese B, Böhner J, Enachescu C, Würdemann H, Zimmermann G (2010) Hydraulic characterisation of the Stuttgart formation at the pilot test site for CO2 storage, Ketzin, Germany. Int J Greenh Gas Control 4(6):960–971. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2010.06.013
Würdemann H, Möller F, Kühn M, Heidung W, Christensen NP, Borm G, Schilling FR (2010) CO2SINK-From site characterisation and risk assessment to monitoring and verification: One year of operational experience with the field laboratory for CO2 storage at Ketzin, Germany. Int J Greenh Gas Control 4(6):938–951. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2010.08.010
Xie CH, Yokota A (2005) Reclassification of Alcaligenes latus strains IAM 12599T and IAM 12664 and Pseudomonas saccharophila as Azohydromonas lata gen. nov., comb. nov., Azohydromonas australica sp. nov. and Pelomonas saccharophila gen. nov., comb. nov., respectively. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55(6):2419–2425. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.63733-0
Zettlitzer M, Möller F, Morozova D, Lokay P, Würdemann H, The CO2SINK Group (2010) Re-establishment of the proper injectivity of the CO2-injection well Ktzi 201 in Ketzin, Germany. Int J Greenh Gas Control 4:952–959. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2010.05.006
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all partners in the Ketzin projects and CO2 storage center for their continued support and contributions. Dr. Stephanie Lerm and Dr. Hannah Halm are acknowledged for critical reading of the manuscript. This research was funded by the Federal Ministry for Education and Research within the Geotechnologien program in the framework of CO2MAN (CO2 Reservoir Management 03G0760A-F) and within the H2STORE (hydrogen to store 03SF0434B) projects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of a Topical Collection in Environmental Earth Sciences on ‘Subsurface Energy storage.’ Guest edited by Sebastian Bauer, Andreas Dahmke and Olaf Kolditz.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pellizzari, L., Lienen, T., Kasina, M. et al. Influence of drill mud on the microbial communities of sandstone rocks and well fluids at the Ketzin pilot site for CO2 storage. Environ Earth Sci 76, 77 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6381-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6381-z