Abstract
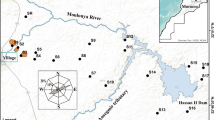
The potentially hazardous contents of mine tailings can pose a serious threat to the environment. Tailings dispersed around the abandoned Monica mine (Bustarviejo) in the Autonomous Region of Madrid (Central Spain) were studied to determine the concentration of several potential toxic elements and their geochemical impact in the surrounding soils. A total of 17 surface soil samples were collected from both mixed sulfide mine tailings sites and unmined soils, within a radius of 1900 m from the mine entrance. The processing of minerals (basically arsenopyrite, matildite and sphalerite) produced tailings with a pH as low as 2.9. Elements such as As, Cu, Zn, Cd, Pb, W, Ag, Fe were found in very high concentrations, contaminating the soil to varying degrees (these elements were sometimes 10- to 20-times higher in the tailings than in the unmined soils). Given its short distance and accessibility from such a large city as Madrid, it is of undeniable environmental and educational interest. Among other factors, there is a need for improvements to tailings management strategies.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abreu MM, Matias MJ, Magalhães MC, Basto MJ (2016) Impacts on water, soil and plants from the abandoned Miguel vacas copper mine, Portugal. J Geochem Explor 96(2–3):161–170
Acosta JA, Faz A, Martinez-Martinez S, Zornoza R, Carmona DM, Kabas S (2011) Multivariate statistical and GIS-based approach to evaluate heavy metals behavior in mine sites for future reclamation. J Geochem Explor 109:8–17
Adriano DC (2001) Trace elements in terrestrial environments. Biogeochemistry, bioavailability and risk of metals, 2nd edn. Springer, New York
Agrawal M, Singh J, Jha AK, Singh JS (1993) Coal-based environmental problems in a low rainfall tropical region. In: Keefer RF, Sajwan KS (eds) Trace elements in coal combustion residues. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, pp 27–57
Angel P, Barton C, Warner R, Agouridis C, Taylor T, Hall S (2008) Tree growth, natural regeneration, and hydrologic characteristics of three loose-graded surface mine spoil types in Kentucky. In: Barnhisel RI (ed) Proceedings, 25th conference of the American Society of mining and reclamation. Lexington, pp 28–65
Aucamp P, van Schalkwyk A (2003) Trace element-pollution of soils by abandoned gold-mine tailings near Potchefstroom. S Afr Bull Eng Geol Environ 62:123–134
Bini C (2012) Environmental impact of abandoned mine waste: a review. Nova, Hauppauge
BOCM (2007) Orden 2720/2006, de 11 de agosto, por la que se establecen niveles genéricos de referencia de metales pesados y otros elementos de traza de suelos contaminados de la Comunidad de Madrid, vol 204. Comunidad de Madrid, Madrid, pp 29–30
Boszke L, Sobczynski T, Kowalski A (2004) Distribution of mercury and other heavy metals in bottom sediments of the Middle Odra River (Germany/Poland). Polish J Environ Stud 13:495–502
Bouso JL (2004) La antigua mina de plata de Bustarviejo. Rocas y minerales: Técnicas y procesos de minas y canteras, 391:24–29. ISSN:0378-3316
Bruce SL, Noller BN, Grigg AH, Mullen BF, Mulligan DR, Ritchie PJ, Currey N, Ng JC (2003) A field study conducted at Kidston Gold Mine, to evaluate the impact of arsenic and zinc from mine tailings to grazing cattle. Toxicol Lett 137:23–34
Conde P, Bellido E, Martín Rubí JA, Jiménez Ballesta R (2008) Concentration and spatial variability of mercury and other heavy metals in surface soil samples of periurban waste mine tailing along a transect in the Almadén mining district (Spain). Env Geol 56(5):815–824
Dang Z, Liu C, Haigh MJ (2002) Mobility of heavy metals associated with the natural weathering of coal mine soils. Environ Pollut 118:419–426
De Miguel E, Callaba A, Arranz JC, Cala V, Chacón E, Gallego E, Alberuche E. Alonso C, Fernández-Canteli P, Iribarren I, Palacios H (2002) Determinación de niveles de fondo y niveles de referencia de metales pesados y otros elementos traza en suelos de la Comunidad de Madrid. Serie Medio Ambiente, Terrenos contaminados, no 2, Instituto Geológico y Minero de España, Madrid, p 167
Duffus JH (2002) Heavy metals—a meaningless term? Pure Appl Chem 74(5):793–807
FAO-ISRIC-ISSS (2006) World reference base for soil resources. A framework for international classification, correlation and communication. World soil resources reports 103, p 132
Fernández-Caliani JC, Barba-Brioso C, González I, Galán E (2009) Heavy metal pollution in soils around the abandoned mine sites of the Iberian pyrite belt (South-west Spain). Water Air Soil Pollut 200:211–226
García-Salgado S, Quijano MA (2014) Levels of toxic arsenic species in native terrestrial plants from soils polluted by former mining activities. Environ Sci Process Impacts 16:604–612
Gee GW, Bauder JW (1986) Particle-size analysis. In: Klute A (ed) Methods of soil analysis. Part 1. Physical and mineralogical methods, 2nd edn. Madison, ASA-SSSA, pp 383–411 (Agronomy Monograph No. 9)
Grangeia C, Avila P, Matias M, Ferreira da Silva E (2011) Mine tailings integrated investigations: the case of Rio tailings (Panasqueira Mine, Central Portugal). Eng Geol 123(4):359–372
Haigh M (1992) Problems in the reclamation of coal-mine disturbed lands in Wales. Int J Surf Min Reclam 6:31–37
Hasan AB, Sohail Kabir AHM, Reza S, Zaman MN, Ahsan A, Rashid M (2013) Enrichment factor and geo-accumulation index of trace metals in sediments of the ship breaking area of Sitakund Upazilla (Bhatiary–Kumira), Chittagong, Bangladesh. J Geochem Explor 125:130–137
He-rong G, Man-li L, Wei-hua P (2015) Heavy metals in coal mine groundwater responding to mining activity: concentration, temporal variation and speciation. Water Pract Technol 10(2):390–401
Hooda PS (ed) (2010) Trace elements in soils. Wiley, Chichester. http://ec.europa.eu/environment/integration/research/newsalert/pdf/230na6.pdf
Hu Z, Caudle RD, Chong SK (1992) Evaluation of firm land reclamation effectiveness based on reclaimed mine properties. Int J Surf Min Reclam Environ 6:129–135
Jiménez Ballesta R, Conde Bueno P, Martín Rubí JÁ, García Giménez R (2010) Pedo-geochemical baseline content levels and soil quality reference values of trace elements in soils from the Mediterranean (Castilla la Mancha, Spain). Cent Eur J Geosci 2(4):441–454
Jiménez R, Jordá L, Jordá R, Prado P (2004) Madrid: la minería metálica desde 1417 hasta nuestros días. Bocamina 14:89–91
Jordá L (2003) Breve historia de la minería de los metales en la Comunidad de Madrid. Tierra y Tecnología 25:63–68 (in Spanish)
Jordá L (2008) La Minería de los metales en la provincia de Madrid: Patrimonio Minero y puesta en valor del espacio subterráneo. Doctoral thesis. Universidad Politécnica de Madrid, p 780 (in Spanish)
Jordá L, Puche O, Mazadiego LF (2005) La minería de los metales y la metalurgia en Madrid (1417–1983). Ed Instituto Geológico y Minero de España. Serie Recursos Minerales n. 7, p 192 (in Spanish)
Kim M, Jung Y (2004) Vertical distribution and mobility of arsenic and heavy metals in and around mine tailings of an abandoned mine. J Environ Sci Health Part A 39:203–222
Kisch H (1990) Recommendations on illite crystallinity. IGCP Project 294, VIGM, pp 1–9
Koushik S, Kalyan A, Anuruddha G (2012) Effect of mine spoil on native soil of Lower Gondwana coal fields: Raniganj coal mines areas, India. Int J Environ Sci 2(3):1675–1687
Lee M, Paik I, Kim I, Kang H, Lee S (2007) Remediation of heavy metal contaminated groundwater originated from abandoned mine using lime and calcium carbonate. J Hazard Mater 144:208–214
Lee H, Kabir MI, Kwon PS, Kim JM, Kim JG, Hyun SH, Rim YT, Bae MS, Ryu ER, Jung MS (2009) Contamination assessment of abandoned mines by integrated pollution index in the Han River watershed. Open Environ Pollut Toxicol J 1:27–33
Li XY, Liu LJ, Wang YG, Luo GP, Chen X, Yang XL, Gao B, He XY (2012) Integrated assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments from a coastal industrial basin, NE China. PLoS One 7(6):e39690. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0039690
Li Z, Ma Z, Jan T, van der Kuijp Z, Yuan LH (2014) A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: pollution and health risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 468–469:843–853
Lim HS, Lee JS, Chon HT, Sager M (2008) Heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment in the vicinity of the abandoned Songcheon Au–Ag mine in Korea. J Geochem Explor 96:223–230
Liu HY, Probst A, Liao BH (2005) Metal contamination of soils and crops affected by the Chenzhou lead/zinc mine spill (Hunan, China). Sci Total Environ 339:153–166
Maiti SK (2003) Moef report, an assessment of overburden dump rehabilitation technologies adopted in CCL, NCL, MCL, and SECL mines (Grant No. J-15012/38/98-IA IIM)
Maiti SK (2007) Bioreclamation of coalmine overburden dumps—with special emphasis on micronutrients and heavy metals accumulation in tree species. Environ Monit Assess 125:111–122
Martín Peinado FJ, Romero-Freire A, García Fernández I, Sierra Aragón M, Ortiz-Bernad I, Simón Torres M (2015) Long-term contamination in a recovered area affected by a mining spill. Sci Total Environ 514:219–223
Martín-Moreno C, Martín Duque JF, Nicolau Ibarra JM, Hernando Rodríguez N, Sanz Santos MA, Sánchez Castillo L (2016) Effects of topography and surface soil cover on erosion for mining reclamation: the experimental spoil heap at El Machorro Mine (Central Spain). Land Degrad Dev 27(2):145–159
Moreno MR, Cala Rivero V, Jiménez Ballesta R (2005) Selenium distribution in topsoils and plants of a semi-arid Mediterranean environment. Environ Geochem Health 27:513–519
Moreno-Jiménez E, Peñalosa JM, Manzano R, Carpena-Ruiz RO, Gamarra R, Esteban E (2009) Heavy metals distribution in soils surrounding an abandoned mine in NW Madrid (Spain) and their transference to wild flora. J Hazard Mater 162:854–859
Moreno-Jiménez E, Manzano R, Esteban E, Peñalosa J (2010) The fate of arsenic in soils adjacent to an old mine site (Bustarviejo, Spain): mobility and transfer to native flora. J Soils Sediments 10:301–312
Mu Y, Yuee H, Jun L, Chaopin L (2015) Characterization of heavy metals in soil near coal mines and a power plant in Huainan, China. Anal Lett 48(4):726–737
Müller G (1979) Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geojournal 2:108–118
Pederson TA, Rogowski AS, Pennock R (1988) Physical characteristics of some mine spoils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 144:131–140
Puche O, García I, Mazadiego LF (2000) El Patrimonio Minero de la mina del Cerro de la Plata de Bustarviejo (Madrid). III Reunión Científica de la SEDPGYM. Patrimonio Minero- Metalúrgico, 13–15 Noviembre 1998. La Rábida (Huelva), 15 pp, in: Actuaciones sobre Patrimonio Minero- Metalúrgico. Servicio de Publicaciones de la Universidad de Huelva (in Spanish)
Rodríguez L, Ruiz E, Aloso-Azcárate J, Rincón J (2009) Heavy metal distribution and chemical speciation in tailing and soils around a Pb–Zn mine in Spain. J Environ Manag 90:1106–1116
Sencindiver JC, Ammons JT (2000) Minesoil genesis and classification. In: Barnhisel RI, Darmody RG, Daniels WL (eds) Reclamation of drastically disturbed lands. Agronomy Monograph No. 41, ASA, CSSA, SSSA, Madison, pp 595–613
Smart D, Callery S, Courtney R (2015) The Potential for waste-derived materials to form soil covers for the restoration of Mine Tailings in Ireland. Land Degrad Dev 27:542–549. doi:10.1002/ldr.2465
Soil Survey Staff (2006) Keys to soil taxonomy, 10th edn. U.S Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service, Washington, DC
Soulard CE, Acevedo W, Stehman SV, Parker OP (2016) Mapping extent and change in surface mines within the United States for 2001 to 2006. Land Degrad Dev 2(2):248–257. doi:10.1002/ldr.2412
Thomas GW (1996) Soil pH and soil acidity. In: Sparks DL (ed) Methods of soil analysis: chemical methods. Part 3. Soil Sci Soc Am, Madison
USEPA (1994) Design and evaluation of tailings dams. Technical report—EPA530-R-94-038. USEPA, Office of Solid Waste, Special Waste Branch, Washington
VROM (2000) Circular on target values and intervention values for soil remediation Netherlands Ministry of Housing. Spatial Planning and Environment, The Hague
Wray DS (1998) The impact of unconfined mine tailings and anthropogenic pollution on a semi-arid environment—an initial study of the Rodalquilar mining district, South East Spain. Environ Geochem Health 20:29–38
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the reviewers of this paper for providing constructive comments, which have contributed to the improvement of the present version.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
García-Giménez, R., Jiménez-Ballesta, R. Mine tailings influencing soil contamination by potentially toxic elements. Environ Earth Sci 76, 51 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6376-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6376-9