Abstract
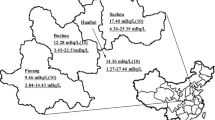
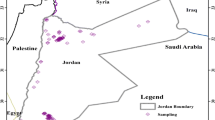
In this study, 226Ra and heavy metal concentrations were studied to represent the radiotoxicity risk of groundwater of Abuja, North Central Nigeria. Groundwater samples were collected from five areas in Abuja, and measurements were taken by using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer. Radium (226Ra) concentrations were determined from 0.067 to 0.216 µg/L. The mean annual effective dose from the natural radionuclide of 226Ra for the inhabitants was estimated to be 2.2 × 10−5 mSv. In addition, life average daily dose and cancer mortality risk were calculated. As a result, radiological risks of 226Ra in groundwater are quite low, typically in the magnitude of 10−7 when compared with the international reference dose level.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida R, Lauria D, Ferreira A, Sracek O (2004) Groundwater radon, radium and uranium concentrations in Região dos Lagos, Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil. J Environ Radioact. doi:10.1016/j.jenvrad.2003.10.006
Amakom CM, Jibiri NN (2010) Chemical and radiological risk assessment of uranium in borehole and well waters in the Odeda area, Ogun State, Nigeria. Int J Phys Sci 5:1009–1014
Gans I, Fusban H, Wollenhaupt H, Kiefer J, Glöbel B, Berlich J, Porstendörfer J (1987) Radium- 226 und Andere Natürliche Radionuklide im Trinkwasser und in Getränken in der Bundesrepublik Deutschland. WaBoLu-Hefte 4/87, Institut für Wasser- Boden-und Lufthygiene des Bundesgesund-heitsamtes
Gbadebo A (2011) Natural radionuclides distribution in the granitic rocks and soils of abandoned quarry sites, Abeokuta, Southwestern Nigeria. Asian J Appl Sci. doi:10.3923/ajaps.2011.176.185
Internal Commission on Radiological Protection (1993) Age-dependent doses to members of the public from intake of radionuclides: part 2 ingestion dose coefficients, Annals on the ICRP, ICRP publication 67. Pergamon Press, Oxford
International Agency for Research on Cancer, IARC, (1997) IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans 87: 1–43
Iyengar MA (1990) The natural distribution of radium. The environmental behavior of radium. IAEA Tech Rep Ser 310(1):9–128
Job C (2008) Compliance with the EPA regulatory standard for arsenic in drinking water. GroundW Monit Remediat. doi:10.1111/j.1745-6592.2008.00208.x
Kobal I, Vaupotič J, Mittć D, Kristan J, Ančik M, Jerančič S, Škofljanec M (1990) Natural radioactivity of fresh waters in Slovenia, Yugoslavia. Environ Int. doi:10.1016/0160-4120(90)90154-x
Kurttio P, Komulainen H, Leino A, Salonen L, Auvinen A, Saha H (2004) Bone as a possible target of chemical toxicity of natural uranium in drinking water. Environ Health Perspect Environ Health Perspect. doi:10.1289/ehp.7475
Lucas H, Markun F (1992) The determination of 226Ra and 228Ra in water and solids by the least squares gamma spectrometric method. J Environ Radioact. doi:10.1016/0265-931x(92)90039-v
Marović G, Senčar J, Franić Z, Lokobauer N (1996) Radium-226 in thermal and mineral springs of Croatia and associated health risks. J Environ Radioact. doi:10.1016/0265-931x(95)00056-g
Mesko MF, Mello PA, Bizzi CA, Dressler VL, Knapp G, Flores EM (2010) Iodine determination in food by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry after digestion by microwave-induced combustion. Anal Bioanal Chem 398:1125–1131
National Research Council (1999) Risk assessment of radon in drinking water. National Academic Press, Washington, DC
Omeje M, Wagiran H, Ibrahim N, Lee S, Soheil S (2013) Comparison of 238U, 232Th, and 40 K in different layers of subsurface structures in Dei-Dei and Kubwa, Abuja, Northcentral Nigeria. Radiat Phys Chem 91:70–80
Pereira-Barbosa JT, Moreira-Santos CM, Bispo LD, Lyra FH, David JM, Andrade-Korn MD, Moraes-Flores EM (2013) Bromine, chlorine, and iodine determination in soybean and its products by ICP-MS after digestion using microwave-induced combustion. Food Anal Methods 6(4):1065–1070
Rangaswamy DR, Srinivasa E, Srilatha MC, Sannappa J (2015) Measurement of radon concentration in drinking water of Shimoga district, Karnataka, India. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. doi:10.1007/s10967-015-4216-0
Rowland RE (1993) Low-level radium retention by the human body: a modification of the ICRP publication 20 retention equation. Health Phys 65:507–513
Sac MM, Ortabuk F, Kumru MN, Ichedef M (2012) Determination of radioactivity and heavy metals of Bakircay river in Western Turkey. Appl Radiat Isot 70(2012):2494–2499
Shapiro B (1992) Annual limits on intake of radionuclides by workers based on the 1990 recommendations. Eur J Radiol. doi:10.1016/0720-048x(92)90215-u
Srilatha MC, Rangaswamy DR, Sannappa J (2014) Studies on concentration of radon and physicochemical parameters ion ground water around Ramanagara and Tumkur districts, Karnataka, India. Int J Adv Sci Technical Res 2:641–660
United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) (2005) Arsenic in drinking water fact sheet
United States Environmental Protection Agency, EPA (1999) Cancer risk coefficients for environmental exposure to radionuclides. United State Environmental Protection Agency. Federal Guidance Report No -13(EPA. 402 R-99-001)
United Nations Scientific Committee on the effects of Atomic Radiation, UNSCEAR (2000) Sources, effect and risks of ionising radiation. Report to the general assembly with scientific annexes. United Nations. New York
World Health Organizations (2004) Guidelines on drinking water quality, 3rd edn. Geneva
World Health Organization, WHO (2006) Meeting the MDG drinking water and sanitation target, the urban and rural challenge of the decade. New York, pp 1–47
Zhuo W, Iida T, Yang X (2001) Occurrence of 222Rn, 226Ra, 228Ra and U in groundwater in Fujian Province, China. J Environ Radioact 53:111–120
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Management of Covenant University for the financial assistance to execute this research. More thanks to the Ministry of Higher Education (MOHE) for their funding through Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Research Grant Scheme Project Number: Q.J130000.2526.03H65. Thanks to Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia, 86400 Parit Raja for providing equipment for water analysis. The authors will gratefully acknowledge the Nigerian Geological Survey Agency and Federal Ministry of Water Resources for their support in this work. The authors wish to thank SYB Sinyoung Borehole Limited for providing the rig and compressor used in drilling the boreholes and Maxico Hydrosolution consult for providing the Campus Ohmega tetrameter.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6037-z.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maxwell, O., Wagiran, H., Zaidi, E. et al. Radiotoxicity risks of radium-226 (226Ra) on groundwater-based drinking at Dawaki, Kuje, Giri and Sabon-Lugbe area of Abuja, North Central Nigeria. Environ Earth Sci 75, 1084 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5884-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5884-y