Abstract
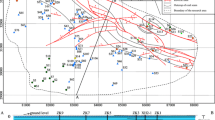
Within the Pingdingshan coalfield, the spatial distribution characteristics of key groundwater chemical components were studied in four aquifers that influence coal-mining operations. Thirty-six water samples were collected from the four aquifers, which were divided into smaller units. Discriminant models of mine-water inrush sources were developed for the three divisions I, III, and IIII, and engineering verification was conducted. The results showed that the main indices influencing groundwater chemical characteristics were Na++K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Cl−, SO4 2−, and HCO3− in the Pingdingshan coalfield with regional variations according to faults and synclines. The Guodishan fault was the primary groundwater chemical division structure, which divides the Pingdingshan coalfield into two primary groundwater chemically characteristic units, divisions I and II. The Likou syncline was the secondary groundwater chemically characteristic structure, which divides division II into two secondary groundwater chemically characteristic units: divisions III and IIII. Discriminant models of water inrush sources in divisions I, III, and IIII (12 discriminant functions) were developed, and engineering verification showed that discrimination accuracy for 16 groundwater samples in four aquifers of three divisions was 93.75 %.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander YS, Alan M, Sitakanta M (2009) Comparison of deterministic ensemble Kalman filters for assimilating hydrogeological data. Adv Water Resour 32:280–292
Chidambaram S, Anandhan P, Prasanna MV, Srinivasamoorthy K, Vasanthavigar M (2013) Major ion chemistry and identification of hydrogeochemical processes controlling groundwater in and around Neyveli Lignite Mines, Tamil Nadu, South India. Arab J Geosci 6(9):3451–3467
Clemens R, Peter F, Robert GG (2002) Factor analysis applied to regional geochemical data: problems and possibilitie. Appl Geochem 17(3):185–206
Frondini F, Zucchini A, Comodi P (2014) Water-rock interactions and trace elements distribution in dolomite aquifers. Geochem J 48:231–246
Gwo JP, Eduardo FD, Hartmut F, Melanie M, Yeh GT, Phil J (2001) HBGC123D: a high-performance computer model of coupled hydrogeological and biogeochemical processes. Comput Geosci 27:1231–1242
Huang PH, Chen JS (2011a) Fisher indentify and mixing model based on multivariate statistical analysis of mine water inrush sources. J China Coal Soc 36(s1):131–136
Huang PH, Chen JS (2011b) The chemical features of ground water and FDA model used to distinguish source of water burst in Jiaozuo mine area. Coal Geol Explor 39(2):42–51
Huang GX, Sun JC, Chen ZY, Chen X, Jing JH, Liu JT, Zhang YX (2012) Levels and sources of phthalate esters in shallow groundwater and surface water of Dongguan city, South China. Geochem J 46:421–428
Jin PG, Eduardo FDA, Hartmut F (2001) HBGC123D: a high-performance computer model of coupled hydrogeological and biogeochemical processes. Comput Geosci 27:1231–1242
Kuldip S, Harkanwal SH, Dhanwinder S (2011) Geochemistry and assessment of hydrogeochemical processes in groundwater in the southern part of Bathinda district of Punjab, northwest India. Environ Earth Sci 64(7):1823–1833
Lahcen Z, Christian G, Jacky M, Benoit D, Abdel EHZ (2004) Spatial distribution of resistivity in the hydrogeological systems and identification of the catchment area in the Rharb basin. Hydrol Sci J Sci Hydrol 49(3):387–398
Lavoie D, Rivard C, Lefebvre R, Séjourné S, Thériault R, Duchesne MJ, Ahad JME, Wang B, Benoit N, Lamontagne C (2014) The Utica Shale and gas play in southern Quebec: geological and hydrogeological syntheses and methodological approaches to groundwater risk evaluation. Int J Coal Geol 126:77–91
Li QK (2008) Application of gray state synthetic assessment in coalmine water bursting water source differentiation. Coal Geol China 20(7):47–48
Masaoki U, Hikaru I, Hitomi N, Tetsuya Y, Tsuyoshi I, Masaharu T (2014) Elemental transport upon hydration of basic schists during regional metamorphism Geochemical evidence from the Sanbagawa metamorphic belt. Geochem J 48:29–49
Pierre J, Jonny R, Donald V, Julio G, Patrick FD, Mark W, Craig H, Andrea B (2014) A 3D hydrogeological and geomechanical model of an Enhanced Geothermal system at The Geysers. Geothermics 51:240–252
Rajesh R, Brindha K, Murugan R, Elango L (2012) Influence of hydrogeochemical processes on temporal changes in groundwater quality in a part of Nalgonda district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Earth Sci 65(4):1203–1213
Soren J, Flemming L, Dieke P, Pham HV, Nguyen TH, Pham QN, Dang DN, Mai TD, Nguyen TMH, Trieu DH, Tran TL, Dang HH, Rasmus J (2008) Palaeo-hydrogeological control on groundwater As levels in Red River delta, Vietnam. Appl Geochem 23(11):3116–3126
Srinivasamoorthy K, Chidambaram S, Vasanthavigar M, Anandhan P, Sarma VS (2014) Geophysical investigations for groundwater in a hard rock terrain, Salem district, Tamil Nadu, India. Bull Eng Geol Environ Geophys 73(2):357–368
Vittecoq B, Deparis J, Violette S, Jaouën T, Lacquement F (2014) Influence of successive phases of volacnic construction and erosion on Mayotte Island’s hydrogeological functioning as determined from a helicopter-borne resistivity survey correlated with borehole geological and permeability data. J Hydrol 509:519–538
Wang GC, Li JS (1992) Groundwater flow systems and karst development in Pingdingshan area. Hydrogeol Eng Geol 4:16–18
Wang XY, Xu T, Huang D (2011) Application of distance discriminance in identifying water inrush resource in similar coalmine. J China Coal Soc 36(8):1354–1358
Wang JS, Wen HJ, Fan HF, Zhu JJ (2012) Sm-Nd geochronology, REE geochemistry and C and O isotope characteristics of calcites and stibnites from the Banian antimony deposit, Guizhou Province, China. Geochem J 46:393–407
Zhou J, Shi XZ, Wang HY (2010) Water-bursting source determination of mine based on distance discriminant analysis model. J China Coal Soc 35(2):278–282
Zhuk EE, Serikova EV (2005) Effectiveness of the step-by-step discriminatory analysis at choosing the informative attributes. Autom Remote Control 66(11):1768–1781
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science of Foundation of China (Grant 41272250) and Technological Innovation Team of Colleges and Universities in Henan Province of China (Grant 15IRTSTHN027).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Ji, H., Wang, Q. et al. Divisions based on groundwater chemical characteristics and discrimination of water inrush sources in the Pingdingshan coalfield. Environ Earth Sci 75, 872 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5616-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5616-3