Abstract
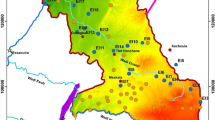
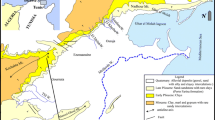
In the Ziz Basin, located in arid area in southeastern Morocco, surface waters are scarce and local populations are entirely dependent on groundwater resources for drinking and irrigation. In order to evaluate the main factors controlling the origin and salinization of groundwater resources, we have investigated the chemical and stable isotope compositions of groundwater and surface water in different areas in the Ziz basin, upstream and downstream from the Hassan Addakhil dam, which is the major man-made reservoir in the basin. A large variation in water quality was observed, specifically an increase in salinity from north (upstream to the reservoir with TDS ~ 460 mg/L) to south (downstream; TDS ~ 16,000 mg/L). In the northern portion of the basin, the low saline groundwater is composed primarily of Ca2+ and Mg2+ due to dissolution of carbonate formations in the High Atlas Mountains. In contrast, the major dissolved consequents of saline waters are Cl−, SO4 2− and Na+, apparently due to dissolution of evaporite minerals (gypsum and halite). In some areas elevated nitrate contents imply anthropogenic contamination derived from local agriculture. The stable isotopes data (δ18O = −8.6 to −8.3 ‰ and δ2H = −55.7 to −53.8 ‰) indicate that the High Atlas Mountains, upstream of the reservoir constitute the major source of water to the Ziz Basin. Given that this arid basin is entirely dependent on groundwater resources, long-term salinization of groundwater in the Ziz Basin could lead to negative effects and reduction of the local agricultural productivity in addition to the degradation of drinking water quality in this region.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed MA, Abdel Samie SG, Badawy HA (2013) Factors controlling mechanisms of groundwater salinization and hydrogeochemical processes in the Quaternary aquifer of the Eastern Nile Delta. Egypt. Environ Earth Sci 68:369–394. doi:10.1007/s12665-012-1744-6
Amharref M (1991) Contribution to the Hydrological study of the valley of the Ziz (province of Errachidia in the south east of Morocco) the respective effects of drought and the Hassan Addakhil dam on the downstream water resources. Thèse de Doctorat, Université de Besançon France. Num 1991BESA2034
Ammary B (2007) Etude géochimique et isotopique des principaux aquifères du bassin Crétacé d’Errachidia et de la plaine de Tafilalet. Thèse de doctorat, Université Mohammed V, Faculté des sciences, Agdal. Rabat n° d’ordre 2376
Bouabdellaoui Y, Michelot J L, Long A (1992) Hydrochemistry studies in Errachidia basin: application of environmental isotopic techniques and geochemical models in the characterisation of arid zone deep aquifer systems. In: Symposium on isotopes techniques in water resources management, IAEA, Vienna
Bouchaou L, Hsissou Y, Krimissa M, Krimissa S, Mudry J (2005) 2H and 18O isotopic study of ground waters under a semiarid climate. In: Lichtfouse E, Schwarzbauer J, Robert D (ed) Environmental chemistry, green chemistry and pollutants in ecosystems. Springer, Berlin, pp 57–64. doi:10.1007/3-540-26531-7_6
Bouchaou L, Michelot JL, Vengosh A, Hsissou Y, Qurtobi M, Gaye CB, Bullen TD, Zuppi GM (2008) Application of multiple isotopic and geochemical tracers for investigation of recharge, salinization, and residence time of water in the Souss-Massa aquifer, Southwest of Morocco. J Hydrol 352:267–287. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.01.022
Bouchaou L, Michelot JL, Qurtobi M, Zine N, Gaye CB, Aggarwal PK, Marah H, Zerouali A, Taleb H, Vengosh A (2009) Origin and residence time of groundwater in the Tadla basin (Morocco) using multiple isotopic and geochemical tools. J Hydrol 379:323–338
Bouchaou L, Tagma T, Michelot J L, Boutaleb S, Massault M, Hsissou Y, Bouragba L, El Faskaoui M (2013) Isotopic Tracers to Study Relationship between Surface Water and Groundwater. In: Case of souss upstream catchment (Morocco). TECDOC, IAEA, Austria (in press)
Bouhlassa S, Ammary B, Elyahyaoui A (2007) Environmental tritium measurements and lumped parameter modelling in the Tafilalet aquifer, south-east Morocco. Radiochim Acta 95:607–616. doi:10.1524/ract.2007.95.10.607
CAG (1988) Geophysical synthesis of the Fès-Meknès and Errachidia-Boudnib basins (Morocco). PNUD/DTCD MOR 86/004 Project
Cappy S (2006) Hydrological Characterization of the Upper Drâa Catchment: Morocco. PhD Thesis, Faculty of Mathematics and Sciences, University of Bonn, Germany
Chaponniere A, Smakhtin V (2006) A review of climate change scenarios and preliminary rainfall trend analysis in the Oum erRbia Basin, Morocco. Working Paper 110 (Drought Series: Paper 8) Colombo, Sri Lanka: International Water Management Institute (IWMI)
Choubert G, Faure-Muret A (1962) Évolution du domaine atlasique marocain depuis les temps paléozoïques. Livre à la mémoire du Professeur Paul Fallot, Mém H S Soc géol, Paris, France 1:447–527
Clark ID, Fritz P (1997) Environmental Isotopes in Hydrogeology. CRC Press Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton
Craig H (1961) Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 133:1702–1703
Direction de la Recherche et de la Planification de l’Eau (D.R.P.E.) (1984) Synthèse des données hydrologiques et des travaux exécutés dans le bassin sédimentaire d’Errachidia et Goulmima. Rapport interne
DRH-GRZ (2008) Rapport d’élaboration du bilan hydrologique des bassins de Guir, Rhéris, Ziz et Maider Errachidia
Du Dresnay R (1979) Jurassic sediments of the atlasic domains of Morocco. In: Symposium “Sedimentation of western European Jurassic” Association of French Sedimentologists (ASF) special publication 1:345–365
El Ouali A (1999) Modalités d’alimentation et échanges entre aquifères de piémont en conditions climatiques arides. Cas des systèmes aquifères du Haut Atlas/bassin cretace d’Errachidia (Maroc). Thèse d’Etat, Université Mohamed V, Ecole Mohammadia d’Ingénieurs, Rabat
El Ouali A, Mudry J, Mania J, Chauve P, Elyamine N, Marzouk M (1999) Present recharge of an aquifer in a semi-arid region: an example from the Turonian limestones of the Errachidia basin Morocco. Environ Geolo 38(2):171–176
Farid I, Trabelsi R, Zouari K, Abid K, Ayachi M (2013) Hydrogeochemical processes affecting groundwater in an irrigated land in Central Tunisia. Environ Earth Sci 68:1215–1231. doi:10.1007/s12665-012-1788-7
Gibbs RJ (1970) Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 170:1088–1090
Hasnaoui MD, Ouazar D (2007) ISESCO Science and Technology Vision 3(4):13–22
Andrew L. Herczeg and W. Mike Edmunds 2000: Inorganic Ions as Tracers. Environmental Tracers in Subsurface Hydrology. In: Peter G, Cook and Andrew L, Herczeg (ed). Kluwer Academic Publishers, p 31
Joly F, Margat J (1955) L’évolution récente du réseau hydrographique dans la plaine du Tafilalt (Sud-Est marocain). Notes et Mémoires, Service Géologique, Maroc 123:59–72
Jossen J A, Filali M J (1989) Southern slope of the central and eastern upper Atlas-northern rim of the Errachidia-Boudnib basin, Stratigraphical and structural synthesis. In: Contribution to the study of deep aquifers. PNUD Project MOR 86/004
Lgourna Z, Warner N, Bouchaou L, Boutaleb S,Tagma T, Hsaissoune M, Ettayfi N, Vengosh A (2013) Investigation of groundwater salinity in the Ziz Basin, southeastern Morocco, by using hydrochemical and isotopic tools. Mineralogical Magazine, 77(5) 1594. DOI:10.1180/minmag.2013.077.5.12. In: Proceeding abstract Goldschmidt conference 25–30 August 2013 Florence, Italia
Margat J (1958) Les recherches hydrogéologiques et l’exploitation des eaux souterraines au Tafilalet. Mines et Géologie 4:43
Margat J (1962) Mémoire explicatif de la carte hydrogéologique au 1/50000 de la plaine de Tafilalt. Notes et Mémoires, Service Géologique, Rabat, n°150 bis, pp 13–67
McKenzie JM, Siegel DI, Patterson W, McKenzie DJ (2001) A geochemical survey of spring water from the main Ethiopian rift valley, southern Ethiopia: implications for well-head protection. Hydrogeol J 9:265–272. doi:10.1007/s100400100134
Michard A (1976) Eléments de Géologie marocaine. Notes et Mémoires, Service géologique de Maroc, pp 252–420
Ouda B, El Hamdaoui A, Ibn Majah M (2004) Isotopic composition of precipitation at three Moroccan stations influenced by oceanic and Mediterranean air masses. TECDOC, IAEA, Vienna, vol 1453, pp 125–140
Plummer LN, Busby RW, Hansaw BB (1990) Geochemical modeling of the Madison aquifer in parts of Montana, Wyoming, and South Dakota. Water Resour Res 26:1981–2014
Ruhard J P (1977) Le Bassin Quaternaire du Tafilalt. In : Notes et Mém Serv Géol, Maroc. Ressources en eau du Maroc, domaines atlasique et sud-atlasique, n°231:252–415
Salameh E (2002) Sources of water salinities in the Jordan Valley area, Jordan. Acta Hydrochim Hydrobiol 29:329–362
Smiler R (2005) Diagram. Avignon University, France, Laboratory of Hydrogeology
Stichler W, Schotterer U (2000) From accumulation to discharge: modification of stable isotopes during glacial and post-glacial processes. Hydrol Process 14:1423–1438
Su CL, Wang YX, Pan YL (2013) Hydrogeochemical andI isotopic evidences of the groundwater regime in Datong Basin Northern China. Environ Earth Sci 70(2):877–885. doi:10.1007/s12665-012-2176-z
Vengosh A (2003) Salinization and Saline Environments. In: Heinrich, Karl KT (eds) Treatise on Geochemistry. Pergamon, Oxford, pp 1–35
Vengosh A, Rosenthal E (1994) Saline groundwater in Israel: it’s bearing on the water crisis in the country. J Hydrol 156:389–430
Vengosh A, Warner N, Jackson R, Darrah T (2013) The Effects of Shale Gas Exploration and Hydraulic Fracturing on the Quality of Water Resources in the United States. Procedia Earth Planetary Sci 7:863–866
Warner N, Lgourna Z, Bouchaou L, Boutaleb S, Tagma T, Hsaissoune M, Vengosh A (2013) Integration of geochemical and isotopic tracers for elucidating water sources and salinization of shallow aquifers in the sub-Saharan Draa Basin, Morocco. Appl Geoch 34:140–151
Acknowledgments
This study is supported within the NATO Project (ESP.MD.SFPP 983,134) “Investigating salinity and radioactivity in water resources in Morocco”. The authors wish to express their gratitude to Hydraulic Agency of Guir-Ghris-Ziz Basin for their help throughout the project. Finally, we thank the two reviewers and the editor for their constructive remarks that significantly improved the quality of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lgourna, Z., Warner, N., Bouchaou, L. et al. Elucidating the sources and mechanisms of groundwater salinization in the Ziz Basin of southeastern Morocco. Environ Earth Sci 73, 77–93 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3396-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3396-1