Abstract
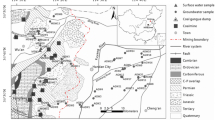
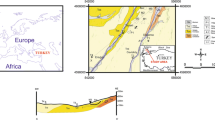
Surface water and groundwater samples were collected from 20 locations, situated in the vicinity of the abandoned coal mine fields south of Bochum. The main objective of this research is to assess the environmental impacts of these mines on the surface water and groundwater quality as well as to determine the factors controlling these impacts. The water samples were collected from stream sources, groundwater, surface water and engineered channels during April 2011. Physicochemical parameters were measured during fieldwork. Water samples were analysed for major ions and aluminium, iron, manganese, ferrous iron, zinc and hydrogen sulphide. The hydrochemistry of the surface water and the groundwater of this area is characterized by near-neutral to alkaline conditions, represented by predominance of calcium bicarbonate and sometimes calcium sulphate water types. Hence, the surface water and the groundwater quality in this region is significantly affected by abandoned coal mines. These effects resulted from oxidation of iron disulphide minerals that release iron, sulphate and hydrogen. The presence of carbonate-rich materials, which contained within the landfilling materials, has led the releasing of calcium, magnesium and bicarbonate. These materials could be the main source responsible for raising the alkalinity of the affected water. The environmental hazard of the abandoned coal mines in this area is related to the high concentration of Fe especially in the groundwater that possess the highest Fe concentration compared to other water sources: the Fe is 18 times larger than the allowed value in drinking water. Significant spatial variations of the water pollution were noted in this study. For this reason, the environmental hazards of the abandoned coal mines in Germany should be considered at closure of coal mines in the near future. Otherwise, these mines will be sources of environmental threats unless all necessary measures are taken to reduce their impact.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auffermann U (2010) Ruhrgebiet., Grünes River zwischen Rhein, Lippe und Wupper 2Ausg. Bergverlag Rother, Essen
Banks D (2003) Geochemical processes controlling mine water pollution. In: Prokop G, Younger P, Roehl KE (eds) Groundwater management in mining areas. Proceedings of the 2nd Image-Train advanced study course, Federal Environment Agency, Wien/Vienna
Banks D, Younger PL, Arnesen RT, Iversen ER, Banks SB (1997) Mine-water chemistry: the good, the bad and the ugly. Environ Geol J 32(3):157–174
Bayerisches Landesamt für Umwelt BLFU (2004) UmweltWissen Ammoniak und Ammo-nium, Bayerisches Landesamt für Umwelt. http://www.lfu.bayern.de/umweltwissen/index.htm. Accessed Aug 2013
Bell FG, Bullock SET, Halbichc TFJ, Lindsay p (2001) Environmental impacts associated with an abandoned mine in the Witbank coalfield, South Africa. Int J Coal Geol 45:195–216
Bode H, Evers P, Albrecht DR (2003) Integrated water resources management in the Ruhr river basin Germany. Water Sci Technol 47(7–8):6–81
Cherry RA, Freeze JA (1979) Groundwater. Prentice-Hall, New Jersey
Costello C (2003). Acid mine drainage: innovative treatment technologies. US Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response, Technology Innovation Office, Washington. http://www.brownfieldstsc.org/pdfs/AMDInnovativeTrtTech_03.pdf. Accessed Oct 2003
Cravotta CA III, Brady KBC, Rose AW, Douds JB (1999) Frequency distribution of the pH of coal-mine drainage in pennsylvania. US Geological Survey, Charleston, South Carolina. http://www.toxics.usgs.gov/pubs/wri99-4018/Volume1/sectionD/1507_Cravotta/index.html. Accessed March 1999
Drever JI (1997) The geochemistry of natural waters: surface and groundwater environments, 3rd edn. Prentice-Hall, New Jersey
Evangelou VP, Zhang YL (1995) A review: pyrite oxidation mechanisms and acid mine drainage prevention. Crit Rev Env Sci Tec 25(2):141–199
Fritz S (1994) A survey of charge-balance errors on published analyses of potable ground and surface waters. Groundwater 32(4):539–546
Geologische Landesamt Nordrhein-Westfalen GLA-NRW (1988) Geologische Karte von Nordrhein Westfalen 1:25000. Erläuteringen zu Blatt 4509 Bochum. Geologisches Landesamt Nordrhein-Westfalen, Bochum
Geologisches Landesamt Nordrhein Westfalen GLA-NRWa (1988) Geologische Karte von Nordrhein-Westfalen 1:25000, 4509 Bochum. Geologisches Landesamt Nordrhein-Westfalen, Bochum
Geologisches Landesamt Nordrhein Westfalen GLA-NRWb (1988) Geologische Karte von Nordrhein-Westfalen 1:25000: Hydrogeologische Karte 1:50000, 4509. Geologisches Landesamt Nordrhein-Westfalen, Bochum
Grudzielanek M, Steinrücke M, Eggenstein J, Holmgren D, Ahlemann D, Zimmermann B (2011). Das Klima in Bochum, Über 100 Jahre stadtklimatologische Messungen. GeoLoge 1(34–42)
Hammack RA, Watzlaf GR (1990) The effect of oxygen on pyrite oxidation. Proceedings of the 1990 Mining and Reclamation Conference and Exhibition, West Virginia University, Charleston, pp 257–264
Hesemann J (1975) Geology of north Rhine-Westphalia. Bochum Geographical works, Special series band 2, Paderborn
Hime W (2001) Chemical methods of analysis of concrete. In: Ramachandran VS, Beaudoin JJ (eds) Handbook of analytical techniques in concrete science and technology, principles, techniques and applications. William Andrew, New York
Hiscock K (2005) Hydrogeology principles and practice. Blackwell, Oxford
International Network for Acid Prevention INAP (2009) Global acid rock drainage guide (GARD Guide). The International Network for Acid Prevention, http://www.inap.com.au/GARDGuide.htm. Accessed June 2009
Jennings SR, Neuman DR, Blicker SP (2008) A review: acid mine drainage and effects on fish health and ecology. Northern Alaska Environmental Centre, http://northern.org/media-library/document-archive/clean-water-mining/mining. Accessed June 2008
Johnson D (2003) Chemical and microbiological characteristics of mineral spoils and drainage waters at abandoned coal and metal mines. Water Air Soil Poll 3(1):47–66
Kelly RA (2009) Energy supply and renewable resources. Infobase, New York
Kleinmann RLP (1998) Bactericidal control of acidic drainage. In: Brady KBC, Smith MW, Schueck J (eds) Coal mine drainage prediction and pollution prevention in pennsylvania. Department of environmental protection, Harrisburg
Kukuk P, Hahne C (1962) Die Geologie des Niederrheinisch-Westfälischen Steinkohlengebietes. Kartenberg Verlag, Essen
Lackey JB (1938) The flora and fauna of surface waters polluted by acid mine drainage. US Public Health Rept 53(34):1499–1507
Landesamt für Natur, Umwelt und Verbraucherschutz Nordrhein-Westfalen LANUV (2010) Klima und Klimawandel in Nordrhein-Westfalen-Daten und Hintergründe. Fachbericht 27, Landesamt für Natur, Umwelt und Verbraucherschutz Nordrhein-Westfalen, Recklinghausen. http://www.lanuv.nrw.de/veroeffentlichungen/fachberichte/fabe27/fabe27KW.pdf. Accessed 2010
Landwirtschaftskammer Nordrhein Westfalen LNW (2012) Düngung mit Phosphat, Kali, Magnes- ium, Landwirt-schaftskammer Nordrhein Westfalen. http://www.landwirtschaftskamme-r.de/. Accessed June 2012
Littke R, Malmsheimer KW, Mensink H, Rautenschlein M (1986) Die Geologie im Gebiet des Kemnader Sees südlich Bochum. Hrsg. vom Institut für Geologie der Ruhr-Universität Bochum, Bochum
Lottermoser BG (2007) Mine wastes characterization, treatment, environmental impacts, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin
Md Equeenuddin Sk, Tripathy S, Panigrahi MK (2010) Hydrogeochemical characteristics of acid mine drainage and water pollution at Makum coalfield India. J Geochem Explor 105:75–82
Melzer D (2011) Natürliche Strahlenexposition der Bevölkerung in Baden-Württemberg: Hat die Nutzung von Erdwärme für Wohnhäuser einen Einfluß auf diese Exposition? KIT wissenschafliche Bericht 7581. Karlsruhe Institut für Technology
Miller B (2010) Clean coal engineering technology. Elsevier, Burlington
Mudgal V, Madaan N, Mudgal A, Singh RB, Mishra S (2010) Effect of toxic metals on human health. Open Nutraceuticals J 3:94–99
Nielsen GL, Nielsen DM (2006) The essential handbook of ground-water sampling. CRC Press LLC, Boca Raton
Rose AW, Cravotta CAIII (1998) Geochemistry of coal mine drainage. In: Brady KBC, Smith MW, Schueck J (eds) Coal mine drainage prediction and pollution prevention in pennsylvania. Department of Environmental Protection, Harrisburg
Scharer JM, Pettit CM, Kirkaldy JL, Bolduc L, Halbert BE, Chambers DB (2000) Leaching of metals from sulphide mines wastes at neutral pH. In: ICARD Proceedings from the Fifth International Conference on Acid Rock Drainage, vol 1. Society for Mining, Metallurgy And Exploration, Denver, Colorado
Schulz D (2002a) Die Bergewirtschaft im Ruhrbergbau. Online source, http://www.dugs.de/Papers/papers.html. Accessed 2002
Schulz D (2002b) Ruhrbergbau und Wasser, Bergematerial und Grundwasser. Online source, http://www.dugs.de/Papers/Wassberg-2002.pdf. Accessed 2002
Singh G (1987) Mine water quality deterioration due to acid mine drainage. Mine Water Environ 6(1):49–61
Skousen JG, Rose A, Geidel G, Foreman J, Evans R, Hellier W (1998) A handbook of technologies for avoidance and remediation of acid mine drainage. West Virginia University, Morgantown
Skousen JG, Sexstone A, Ziemkiewicz PF (2000) Acid mine drainage control and treatment. In Barnheisel et al. (eds) Reclamation of drastically disturbed land. asa monograph 41
Strömberg B, Banwart SA (1999) Experimental study of acidity-consuming processes in mining waste rock: some influences of mineralogy and particle size. Appl Geochem 14(1):1–16
Tiedt M (2009) Der frühe Bergbau an der Ruhr. http://www.ruhrkohlenrevier.de/. Accessed 2009
Tiwary R (2001) Environmental impact of coal mining on water regime and its management. Water Air Soil Poll 132(1):185–199
Viebahn-Sell (2001) Konzept zur Naturnahen Entwicklung des Lottenbachs. Unveroffentlichtes Gutachten im Auftrag des Tiefbauamtes der Stadt BochumStadt Bochum, Tiefbauamt, Bochum
Viebahn-Sell (2006) Immissionsbetrachtung der Einleitungen in den Lottenbach,Phase I Gewasserokologische Bestandaufnahme und Bewertung. Unveroffentlichtes Gutachten im Auftrag des Tiefbauamtes der Stadt Bochum. Stadt Bochum, Tiefbauamt, Bochum
Watzlaf GR, Schroeder KT, Kleinmann, RLP, Kairies CL, Nairn RW (2004) The passive treatment of coal mine drainage. US Department of Energy and University of Oklahoma. http://www.netl.doe.gov-technologies/coalpower/ewr/water/pdfs/Passive%20-Treatment.pdf. Accessed Aug 2007
Webba JA, Sasowsky ID (1994) The interaction of acid mine drainage with a carbonate terrane: evidence from the Obey river, north-central Tennessee. J Hydrol 161(1–4):327–346
Wolkersdorfer C (2008) Water management at abandoned flooded underground mines–fundamentals, tracer tests, modelling, water treatment. Springer, Berlin
Wolkersdorfer C (2009) Hydrochemistry of mine water discharges in the abandoned upper Bavarian pitch coal mining district/Germany. In: Water Institute of Southern Africa and International Mine Water Association: Proceedings, International Mine Water Conference. http://www.imwa.info/docs/imwa_2009-/IMWA2009_Wolkersdorfer.pdf. Accessed Oct 2009
World Coal Institute WCI (2005). The coal resource, a comprehensive overview of coal. World Coal Institute, London. http://www.worldcoal.org/resources/wca-publications/. Accessed May 2005
Younger PL (1995) Hydrogeochemistry of mine waters flowing from abandoned coal workings in county Durham. Q J Eng Geol Hydroge 28:101–113
Younger PL (2001) Mine water pollution in Scotland: nature, extent and preventative strategies. Sci Total Environ 265(1–3):309–326
Younger PL (2003) Impacts of mining on physical hydrogeology. In Prokop G, Younger P, Roehl KE (eds) Groundwater management in mining areas, Proceedings of the 2nd Image-Train advanced study course, Federal Environment Agency, Wien/Vienna. http://www.umweltbundesamt.at/fileadmin/site/publikationen-/CP035.pdf. Accessed 2004
Younger PL, Banwart SA, Hedin RS (2002) Mine water hydrology, pollution, and remediation. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Acknowledgments
The scientific scholarship for this work was provided by the University of Damascus, Syrian Arab Republic. Laboratory works has been done in the Department of Applied Geology at the Ruhr University Bochum. The authors would like to thank all the technicians and scientific staffs who have contributed to the completion of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alhamed, M., Wohnlich, S. Environmental impact of the abandoned coal mines on the surface water and the groundwater quality in the south of Bochum, Germany. Environ Earth Sci 72, 3251–3267 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3230-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3230-9