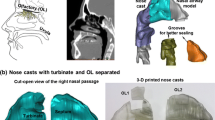
Abstract
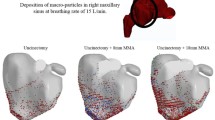
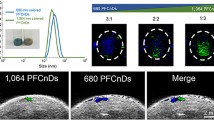
The location and concentration of particle deposition of pollen by filtration in the human nasal cavity were visualized in a transparent silicone nasal airway model using laser-induced fluorescence (LIF) to clarify the relationship between flow and particle deposition. The model was created from a water-soluble plaster mold fabricated by a 3D printer based on X-ray computed tomography images. The working fluid was air and the tracer particles as a substitute for cedar pollen were lycopodium powder doped with fluorescent dye (Rhodamine 6G). After particle deposition, the nasal airway model was filled with an aqueous solution of glycerin that had the same refractive index as silicone. Then, LIF was applied to illuminate the deposited particles with a YAG laser sheet. Results revealed that particle deposition in the right and left cavities was highly heterogeneous and was related to the complex flow structure in the nasal cavities.
Graphical Abstract

.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bishoff JS, Noga M, Finlay WH (2008) Deposition of micrometer-sized aerosol particles in infant nasal airway replicas. J Aerosol Sci 39:1055–1065
Doorly DJ, Taylor DJ, Franke P, Schroter RC (2008) Experimental investigation of nasal airflow. J Eng Med 222:439–453
Eccles R (1996) A role for the nasal cycle in respiratory defence. Eur Respir J 9:371–376
Elad D, Wolf M, Keck T (2008) Air-conditioning in the human nasal cavity. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 163:121–127
Hopkins LM, Kelly JT, Wexler AS (2000) Particle image velocimetry measurements in complex geometries. Exp Fluids 29:91–95
Kelly JT, Asgharian B, Kimbell JS, Wong BA (2004) Particle deposition in human nasal airway replicas manufactured by different methods. Part I: inertial regime particles. Aerosol Sci Technol 38:1063–1071
Kim SK, Chung SK (2009) Investigation on the respiratory airflow in human airway by PIV. J Vis 12:259–266
Kundoor V, Dalby RN (2009) Assessment of nasal spray deposition pattern in a silicone human nose model using a color-based method. Pharm Res 27:30–36
Liu Y, Matida EA, Gu J, Johnson MR (2007) Numerical simulation of aerosol deposition in a 3-D human nasal cavity using RANS, RANS/EIM, and LES. J Aerosol Sci 38:683–700
Nakane I (2012) Cedar pollen suspension and saltation transport behavior. Trans Jpn Soc Mech Eng Ser 78:1220–1234
Nishizawa T, Takano R, Watanabe Y, Tanaka G (2011) PIV measurement of airflow in the human nasal cavities. Proceedings of the 11th Asian symposium on visualization: po-07
Okuda M, Ohkubo K, Gotoh M, Hiroshima K, Ishida Y, Hori K (2005) Dynamics of airborne pollen particles from inhalation to allergic reaction in the nose. Rhinology 43:29–33
Saito Y, Ide T, Murayama K (2006) Kahunsyo no kagaku. Kagakudojin, Kyoto
Su W, Cheng Y (2005) Deposition of fiber in the human nasal airway. Aerosol Sci Technol 39:888–901
Wang Z, Hopke PK, Ahmadi G, Cheng Y, Baron P (2008) Fibrous particle deposition in human nasal passage: the influence of particle length, flow rate, and geometry of nasal airway. J Aerosol Sci 39:1040–1054
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. T. Matsuzawa at Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology and Dr. S. Ishikawa at Kanazawa Municipal Hospital for their advice in the nasal cavity model preparation. We also thank Prof. R. C. Schroter, Prof. D. J. Doorly and Dr. D. J. Taylor at Imperial College London for helpful discussions in carrying out the present study. The present study was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (22560187) from Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakai, H., Watanabe, Y., Sera, T. et al. Visualization of particle deposition in human nasal cavities. J Vis 18, 349–357 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-014-0238-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-014-0238-x