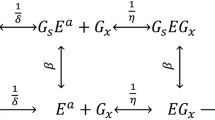Abstract
The first and nth order kinetic models are usually used to describe cellulose pyrolysis. In this work, the local sensitivities of the conversion and derivative conversion with respect to the frequency factor, the logarithm of the frequency factor, the activation energy and the reaction order for the first and nth order kinetic models are calculated by using the finite difference method. The results show that the sensitivities of the first and nth order kinetic models with respect to the activation energy and the logarithm of the frequency factor are significant, while the frequency factor and the reaction order affect the nth order kinetic model slightly. Compared with the frequency factor, the natural logarithm of the frequency factor is a better choice in the parameter estimation of the first and nth order kinetic models.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ODE:
-
Ordinary differential equation
- RSS:
-
Residual sum of squares
- TG:
-
Thermo-gravimetric
- DTG:
-
Derivative thermo-gravimetric
- DSC:
-
Differential scanning calorimetry
- Q-DTA:
-
Differential thermal analysis under quasi-isothermal, quasi-isobaric conditions
- α:
-
Degree of conversion
- n :
-
Reaction order
- A :
-
Frequency factor
- E :
-
Activation energy
- R :
-
Universal gas constant
- β :
-
Heating rate
- t :
-
Time
- T :
-
Absolute temperature.
- T 0 :
-
Starting temperature
- p :
-
Kinetic parameter in the model
- n d :
-
Number of data points
- exp:
-
Experimental data
- cal:
-
Calculated data
- i :
-
The ith data point
- c :
-
Corresponding kinetic parameter value for cellulose pyrolysis
References
Sindhu, R., Binod, P., Pandey, A.: Biological pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass—an overview. Bioresour. Technol. 199, 76–82 (2016)
Hassan, H., Lim, J.K., Hameed, B.: Recent progress on biomass co-pyrolysis conversion into high-quality bio-oil. Bioresour. Technol. 221, 645–655 (2016)
Muley, P.D., Henkel, C., Abdollahi, K.K., Marculescu, C., Boldor, D.: A critical comparison of pyrolysis of cellulose, lignin, and pine sawdust using an induction heating reactor. Energy Convers. Manag. 117, 273–280 (2016)
Sánchez-Jiménez, P.E., Pérez-Maqueda, L.A., Perejón, A., Pascual-Cosp, J., Benítez-Guerrero, M., Criado, J.M.: An improved model for the kinetic description of the thermal degradation of cellulose. Cellulose. 18, 1487–1498 (2011)
Lédé, J.: Cellulose pyrolysis kinetics: an historical review on the existence and role of intermediate active cellulose. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis. 94, 17–32 (2012)
Paulik, J., Paulik, F.: Complex thermoanalytical method for the simultaneous recording of T, TG, DTG, DTA, TGT, DTGT, TD and DTD curves Part I. Development and characterization of equipment. Thermochim. Acta. 3, 13–15 (1971)
Paulik, F., Bessenyey-Paulik, E., Walther-Paulik, K.: Transformation-governed heating technique in thermal analysis. Part III. Normalisation of experimental conditions. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 69, 339–351 (2002)
Paulik, F., Bessenyey-Paulik, E., Walther-Paulik, K.: Differential thermal analysis under quasi-isothermal, quasi-isobaric conditions (Q-DTA) Part II. Water evaporation and the decomposition mechanism of compounds with structural and crystal water. Thermochim. Acta. 424, 75–82 (2004)
White, J.E., Catallo, W.J., Legendre, B.L.: Biomass pyrolysis kinetics: a comparative critical review with relevant agricultural residue case studies. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis. 91, 1–33 (2011)
Várhegyi, G.: Aims and methods in non-isothermal reaction kinetics. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis. 79, 278–288 (2007)
Saltelli, A., Tarantola, S., Campolongo, F., Ratto, M.: Sensitivity Analysis in Practice: A Guide to Assessing Scientific Models: Wiley, Hoboken, NJ (2004)
Saltelli, A., Tarantola, S., Campolongo, F.: Sensitivity Analysis as an Ingredient of Modeling. Stat. Sci. 15, 377–395 (2000)
Mezaki, R., Kittrell, J.R.: Parametetric sensitivity in fitting nonlinear kinetic models. Ind. Eng. Chem. 59, 63–69 (1967)
Burnham, A.K., Zhou, X., Broadbelt, L.J.: Critical review of the global chemical kinetics of cellulose thermal decomposition. Energy & Fuels. 29, 2906–2918 (2015)
Antal, M.J., Varhegyi, G., Jakab, E.: Cellulose pyrolysis kinetics: revisited. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 37, 1267 (1998)
Lin, Y.-C., Cho, J., Tompsett, G.A., Westmoreland, P.R., Huber, G.W.: Kinetics and mechanism of cellulose pyrolysis. J. Phys. Chem. C. 113, 20097–20107 (2009)
Bradbury, A.G.W.: A kinetic model for pyrolysis of cellulose. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 23, 3271–3280 (1979)
Nguyen-Tuan, L., Lahmer, T., Datcheva, M., Schanz, T.: Global and local sensitivity analyses for coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical problems. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 41(5), 707–720 (2016). doi: 10.1002/nag.2573
Santos, K., Lobato, F., Lira, T., Murata, V., Barrozo, M.A.: Sensitivity analysis applied to independent parallel reaction model for pyrolysis of bagasse. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 90, 1989–1996 (2012)
Xavier, T.P., Lira, T.S., Schettino, M.A. Jr., Barrozo, M.A.S.: A study of pyrolysis of macadamia nut shell: parameteric sensitivity analysis the IPR model. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 33, 115–122 (2016)
Cai, J.: A distributed activation energy model for the pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass. Green Chem. 15, 1331–1340 (2013)
Carrier, M., Auret, L., Bridgwater, A., Knoetze, J.H.: Using apparent activation energy as a reactivity criterion for biomass pyrolysis. Energy & Fuels. 30, 7834–7841 (2016)
Sørensen, O.T., Rouquerol, J. (eds.): Sample Controlled Thermal Analysis: Origin, Goals, Multiple Forms Applications and Future. Springer, New York, (2013)
Cai, J., Yao, F., Yi, W., He, F.: New temperature integral approximation for nonisothermal kinetics. ALChE J. 52, 1554–1557 (2006)
Johansen, S.: The Welch-James approximation to the distribution of the residual sum of squares in a weighted linear regression. Biometrika. 67, 85–92 (1980)
Morgan, J., Tatar, J.: Calculation of the residual sum of squares for all possible regressions. Technometrics. 14, 317–325 (1972)
Saltelli, A., Ratto, M., Tarantola, S., Campolongo, F.: Sensitivity analysis for chemical models. Chem. Rev. 105, 2811–2828 (2005)
Saltelli, A., Chan, K., Scott, E.M.: Sensitivity Analysis Wiley, New York, (2009)
Acknowledgement
Financial support from participation in research program at Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Project No. T150PRP31027) is greatly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, Z., Xie, L., Yang, Y. et al. Local Sensitivity Analysis of Kinetic Models for Cellulose Pyrolysis. Waste Biomass Valor 10, 975–984 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-017-0097-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-017-0097-5