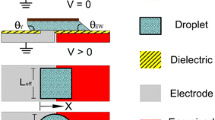
Abstract
Electrowetting (EW) effect is defined as changing in the interfacial energy of solid–liquid interface which causes to change in solid–liquid contact angle. In EW on dielectric (EWOD) actuations, the microliter drops are usually placed between two substrates which have some advantages. By modifying the voltages applied to the electrodes, it is possible to manipulate the droplets by setting up surface tension gradients along the plate. In this paper, the free energy based lattice Boltzmann method which has been recently extended by the authors for modeling and simulation of EW phenomenon has been applied to simulate EWOD. Also here we report the results of simulation of EW on superhydrophobic surfaces and pinning problem. The results have been compared with experimental data and show good accuracy of the numerical simulation.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
F Mugele and J C Baret J. Phys. Condens. Matter 17 R705 (2005)
H J I Verheijen and M W J Prins Langmuir 15 6616 (1999)
R Digilov Langmuir 16 6719 (2000)
O D Velev, B G Prevo and K H Bhatt Nature 426 515 (2003)
M Vallet, M Vallade and B Berge Eur. Phys. J. B 11 583 (1999)
T D Blake, A Clarke and E H Stattersfield Langmuir 16 2928 (2000)
A R Wheeler, H Moon, C-J Kim, J A Loo and R L Garrell Anal. Chem 76 4833 (2004)
J Fowler, H Moon and C J Kim Proc. IEEE 15th Annu Int. Conf. MEMS 97 (2002)
S K Cho and C J Kim Proc. IEEE 16th Annu. Int. Conf. MEMS 686 (2003)
S Walker and B Shapiro J. Microelectromech. Sys. 15 986 (2006)
S W Walker, B Shapiro and R H Nochetto Phys. Fluids 21 102103 (2009)
J Zhang Microfluidics and Nanofluidics 10 1 (2011)
A K Gunstensen, D H Rothman and G Zaleski Phys. Rev. A 43 4320 (1991)
D Grunau, S Chen, T Lookman and A S Lapedes Phys. Rev. Lett. 71 4198 (1993)
B M Boghosian and P V Coveney Computer Phys. Communi. 129 46 (2000)
X Shan and H Chen Phys. Rev. E 47 1815 (1993)
N S Martys and J F Douglas Phys. Rev. E 63 031205 (2001)
G Hazi, A R Imre, G Mayer and I Farkas Ann. Nuclear Energy 29 1421 (2002)
M R Swift, W R Osborn and J M Yeomans Phys. Rev. Lett. 75 830 (1995)
M R Swift, E Orlandini, W R Osborn and J M Yeomans Phys. Rev. E 54 5041 (1996)
D J Holdych, J G Geogiadis and R O Buckius Phys. Fluids 13 817 (2001)
J Briant, A J Wagner and J M Yeomans Phys. Rev. E 69 031602 (2004)
H Aminfar and M Mohammadpourfard Comput. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng. 198 3852 (2009)
H Aminfar and M Mohammadpourfard J. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 24 143 (2010)
H Li and H Fang Eur. Phys. J. Special Top. 171 129 (2009)
L Clime, D Brassard and T Veres Microfluidics and Nanofluidics 8 599 (2010)
L Clime, D Brassard and T Veres Comput. & Fluids 39 1510 (2010)
P G de Gennes Rev. Mod. Phys. 57 827 (1985)
J W Cahn J. Chem. Phys. 66 3667 (1977)
J Th. G Overbeek Colloids Surf. 51 61 (1990)
H W Lu, K Glasnner, A L Bertozzi and C J Kim J. Fluid Mech. 590 411 (2007)
Acknowledgments
The work is financially supported by research funds of Islamic Azad University, Tabriz Branch. The authors would like to thank F. Varnik for useful discussions and A. Dupuis for providing us a version of his LB code.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zamzamian, K., Mohammadpourfard, M. Electrowetting on dielectric and superhydrophobic surface: lattice Boltzmann study. Indian J Phys 86, 889–899 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-012-0158-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-012-0158-3