Abstract
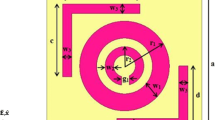
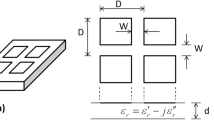
In this paper, a broadband metamaterial absorber has been presented for practical applications. The unit cell of the proposed structure comprises metallic patch of single circular split-ring imprinted on top surface of a metal-backed dielectric substrate. The geometrical dimensions of the structure have been optimized in such a way that the structure exhibits broadband absorptivity response of 9.12 GHz from 6.70 to 15.82 GHz with more than 90 % absorptivity. Three distinct absorption peaks are observed at 7.16, 10.74 and 14.96 GHz. The absorption phenomena at these three frequencies have been analyzed and the roles of several geometrical parameters involved in the design are investigated. The proposed structure has been studied under oblique incidence, both for TE and TM polarizations where it shows wideband absorption characteristics up to 30° incident angle for TE polarization and 45° incident angle for TM polarization. The proposed structure is very thin (~λ/8.4 with respect to the centre frequency of absorption bandwidth) compared to the commercially available microwave absorbers.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. R. Smith, W. J. Padilla, D. C. Vier, S. C. Nemat-Nasser, and S. Schultz, Composite medium with simultaneously negative permeability and permittivity, Phys. Rev. Lett., 84 (2000) 4184–4187.
C. Caloz, T. Itoh, and A. Rennings, CRLH metamaterial leaky-wave and resonant antennas, IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag., 50 (2008) 25–39.
A. Erentok, and R. W. Ziolkowski, Metamaterial-inspired efficient electrically small antennas, IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag., 56 (2008) 691–707.
S. A. Cummer, B. I. Popa, D. Schurig, D. R. Smith, and J. B. Pendry, Full wave simulations of electromagnetic cloaking structures, Phys. Rev. E, 74 (2006) 036621.
H. Suthar, D. Sarkar, K. Saurav, and K. V. Srivastava, Gain enhancement of microstrip patch antenna using near-zero index metamaterial lens, 2015 twenty first national conference on communication, pp. 1–6, India, 27 February–1 March, 2015.
S. Li, T. Cao, T. Liu, and H. Yang, Double-layer perfect metamaterial absorber and its application for RCS reduction of antenna, Radioengineering, 23 (2014) 222–228.
R. Hayashi, R. Kanaura, S. Yagitani, T. Imachi, M. Ozaki, Y. Yoshimura, and H. Sugiura, Radio-frequency power distribution measurement system using thin metamaterial absorber, 2016 international workshop on antenna technology (IWAT), pp. 157–160, Florida, USA, 29 February–2 March 2016.
P. Maagt, R. Gonzalo, Y. C. Vardaxoglou, and J. -M. Baracco, Electromagnetic bandgap antennas and components for microwave and (sub)millimeter wave applications, IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag., 51 (2003) 2667–2677.
N. Pohl, and M. Gerding, A dielectric lens-based antenna concept for high precision industrial radar measurements at 24 GHz, 2012 Ninth European Radar Conference (EuRAD), pp. 405–408, 31 October–2 November, 2012, Amsterdam, Netherlands.
H. Li, L. H. Yuan, B. Zhou, X. P. Shen, Q. Cheng, and T. J. Cui, Ultrathin multiband gigahertz metamaterial absorbers, J. Appl. Phys., 110 (2011) 014909.
H. Tao, N. Landy, C. M. Bingham, X. Zhang, R. D. Averit, and W. J. Padilla, A metamaterial absorber for the terahertz regime: design, fabrication and characterization, Optics Express, 16 (2008) 7181–7188.
G. Dayal, and S. A. Ramakrishna, Design of highly absorbing metamaterials for infrared frequencies, Optics Express, 20 (2012) 17503–17508.
S. Bhattacharyya, H. Baradiya, and K. V. Srivastava, An ultra thin metamaterial absorber using electric field driven LC resonator with meander lines, 2012 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation and USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, pp. 1–2, 8–13 July, 2012.
S. Bhattacharyya, S. Ghosh, H. Baradiya, and K. V. Srivastava, Study on ultra-thin dual frequency metamaterial absorber with retrieval of electromagnetic parameters, 2014 Twentieth National Conference on Communication, pp. 1–6, 28 February–2 March, 2014, India.
S. Bhattacharyya, and K. V. Srivastava, An ultra thin electric field driven LC resonator structure as metamaterial absorbers for dual band applications, 2013 URSI International Symposium on Electromagnetic Theory (EMTS), pp. 722–725, 20–24 May, 2013.
S. Bhattacharyya, S. Ghosh, and K. V. Srivastava, Bandwidth enhanced metamaterial absorber using electric field driven LC Resonator for airborne radar applications, Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett., 55 (2013) 2131–2137.
S. Ghosh, S. Bhattacharyya, and K. V. Srivastava, Bandwidth-enhancement of an ultra-thin polarization insensitive metamaterial absorber, Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett., 56 (2014) 350–355.
S. Bhattacharyya, and K. V. Srivastava, Triple band polarization-independent ultra-thin metamaterial absorber using ELC resonator, J. Appl. Phys., 115 (2014) 064508.
S. Bhattacharyya, S. Ghosh, and K. V. Srivastava, Triple band polarization-independent metamaterial absorber with bandwidth enhancement at X-band, J. Appl. Phys., 114 (2013) 094514.
S. Ghosh, S. Bhattacharyya, Y. Kaiprath, and K. V. Srivastava, Bandwidth-enhanced polarization insensitive microwave metamaterial absorber and its equivalent circuit model, J. Appl. Phys., 115 (2014) 104503.
J. Sun, L. Liu, G. Dong, and L. Zhou, An extremely broadband metamaterial absorber based on destructive interference, Optics Express, 19 (2011) 21155–21162.
S. Bhattacharyya, and K. V. Srivastava, Dual layer polarization insensitive dual band metamaterial absorber with enhanced bandwidths, 2014 IEEE Asia Pacific Microwave Conference (APMC), pp. 816–818, 4–7 November, 2014.
S. Bhattacharyya, S. Ghosh, D. Chaurasiya, and K. V. Srivastava, Bandwidth-enhanced dual-band dual-layer polarization-independent ultra-thin metamaterial absorber, Springer Appl. Phys. A, 118 (2015) 207–215.
H. Xiong, J. S. Hong, C. M. Luo, and L. -L. Hong, An ultrathin and broadband metamaterial absorber using multi-layer structures, J. Appl. Phys., 114 (2013) 064109.
A. Noor, and Z. Hu, Metamaterial dual polarized resistive Hilbert curve array radar absorber, IET Microw. Antennas Propag., 4 (2010) 667–673.
F. Costa, and A. Monorchio, Multiband electromagnetic wave absorber based on reactive impedance ground planes, IET Microw. Antennas Propag., 4 (2010) 1720–1727.
J. Yang, and Z. Shen, A thin and broadband absorber using double-square loops, IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett., 6 (2007) 388–391.
S. Li, J. Guo, X. Cao, W. Li, Z. Zhang, and D. Zhang, Wideband, thin, and polarization-insesnsitive perfect absorber based on the double octagonal rings metamaterials and lumped resistances, J. Appl. Phys., 116 (2014) 043710.
W. Yuan, and Y. Cheng, Low-frequency and broadband metamaterial absorber based on lumped elements: design, characerization and experiment, Springer Appl. Phys. A, 117 (2014) 1915–1921.
C. L. Holloway, M. A. Mohamed, E. F. Keuster, and A. Dienstfrey, Reflection and transmission properties of a metafilm: with an application to a controllable surface composed of resonant particles, IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat., 47 (2005) 853–865.
D. Ye, Z.Wang, Z. Wang, K. Xu, B. Zhang, J. Hunagfu, C. Li, and L. Ran, Towards experimentally perfectly-matched layers with ultra thin metamaterial surfaces, IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag., 60 (2012) 5164–5172.
K. R. Carver, and J. W. Mink, Microstrip antenna technology, IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag., 29 (1981) 2–24.
J. S. Hong, Microstrip filters for RF/microwave applications, Wiley, Singapore, (2011), pp. 82–85.
C. A. Balanis, Antenna theory: analysis and design, 2nd ed., Wiley, New Delhi, (2007), pp. 727–730.
S. Ghosh, and K. V. Srivastava, An equivalent circuit model of FSS based metamaterial absorber using coupled line theory, IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett., 14 (2015) 511–514.
Acknowledgement
The author wants to acknowledge Dr. Kumar Vaibhav Srivastava and Mr. Saptarshi Ghosh of Electrical Engineering Department, IIT Kanpur for their support to conduct experimental part.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhattacharyya, S. A Broadband Microwave Metamaterial Absorber with Octave Bandwidth. MAPAN 31, 299–307 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12647-016-0180-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12647-016-0180-6