Abstract
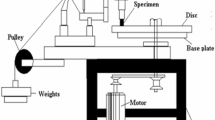
An experimental study was carried out to investigate the dry sliding friction and wear characteristics of woven glass epoxy composites filled with Al particulates sliding against steel using a pin-on-disc tribometer. The glass fiber weight fraction was kept constant at 60 wt% and Al wt% varied as 0, 5, 10, and 15%. The composite was fabricated by a hand lay-up technique followed by light compression molding. Friction and wear behavior under dry sliding condition are presented as a function of sliding speed varying between 1–5 m/s and normal load ranging between 10–40 N. Friction characteristics of composites depend strongly on a combination of filler content, sliding speed and load. Wear loss increases with both sliding speed and load. Incorporation of a smaller amount of Al filler reduces wear loss compared to un-filled glass epoxy composites. An attempt has also been made to observe the distribution of fiber and Al particles in the composite, and to correlate the wear behavior using Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) observations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hull D, Clyne TW (1996) An introduction to composite materials. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Wallenberger FT, Watson JC, Li H (2001) Glass fibers. ASM International, Materials Park
Wang RM, Zheng SR, Zheng YG (2011) Polymer matrix composites and technology. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Abot JL, Yasmin A, Jacobsen AJ, Daniel IM (2004) In-plane mechanical, thermal and viscoelastic properties of a satin fabric carbon/epoxy composite. Compos Sci Technol 64:263–268
Park R, Jang J (1998) The effects of hybridization on the mechanical performance of aramid/ polyethylene intraply fabric composites. Compos Sci Technol 58:1621–1628
Bijwe J, Rattan R (2007) Influence of weave of carbon fabric in polyetherimide composites in various wear situations. Wear 263:984–991
Zaini MJ, Fuad MA, Ismail Z, Mansor MS, Mustafah J (1996) The effect of filler content and size on the mechanical properties of polypropylene/oil palm wood flour composites. Polym Int 40:51–55
Suresha B, Chandramohan G, Prakash JN, Balusamy V, Sankaranarayanasamy K (2006) The role of fillers on friction and slider wear characteristics in glass-epoxy composite system. J Miner Mater Charact Eng 5:87–101
Sampathkumaran P, Seetharamu S, Thomas P, Janardhana M (2005) A study on the effect of the type and content of filler in epoxy–glass composite system on the friction and slide wear characteristics. Wear 259:634–641
Suresha B, Chandramohan G, Rao PS, Sampathkumaran P, Seetharamu S, Venkateswarlu V (2006) Friction and slide wear characteristics of glass-epoxy and glass-epoxy filled with SiCp composites. Indian J Eng Mater Sci 13:535–541
Shivamurthy B, Siddaramaiah, Prabhuswamyc MS (2009) Influence of SiO2 fillers on sliding wear resistance and mechanical properties of compression moulded glass epoxy composites. J Miner Mater Charact Eng 8:513–530
Raju BR, Suresha B, Swamy RP, Kanthraju BSW (2013) Investigations on mechanical and tribological behaviour of particulate filled glass fabric reinforced epoxy composites. J Miner Mater Charact Eng Article ID 35101:1–8
Mohan N, Mahesha CR, Raja R (2014) Tribo-mechanical behavior of SiC filled glass-epoxy composites at elevated temperatures. Int J Eng Sci Technol 6:44–56
Debnath K, Singh I, Dvivedi A (2013) Dry sliding wear behavior of glass fibre reinforced epoxy composites filled with natural fillers. Reason-A Tech J 12:61–68
Nak-Ho S, Suh NP (1979) Effect of fiber orientation on friction and wear of fiber reinforced polymeric composites. Wear 53:129–141
Chang HW (1983) Wear characteristics of composites: effect of fiber orientation. Wear 85:81–91
Cirino M, Friedrich K, Pipes RB (1988) The effect of fiber orientation on the abrasive wear behavior of polymer composite materials. Wear 121:127–141
Bhattacharya SK (1986) Metal filled polymers. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Vasconcelos PV, Lino FJ, Baptista AM, Neto RJ (2006) Tribological behavior of epoxy based composites for rapid tooling. Wear 260:30–39
Vasconcelos PV, Lino FJ, Magalhaes A, Neto RJ (2005) Impact fracture study of epoxy-based composites with aluminum particles and milled fibres. J Mater Process Technol 170:277–283
Nuruzzaman DM, Rahaman ML, Chowdhury MA (2012) Friction coefficient and wear rate of polymer and composite materials at different sliding speeds. Int J Surf Sci Eng 6:231–245
Mimaroglu A, Unal H, Arda T (2007) Friction and wear performance of pure and glass fibre reinforced poly-ether-imide on polymer and steel counterface materials. Wear 262:1407–1413
Bhushan B (1999) Principles and applications of tribology. Wiley, New York
Unal H, Sen U, Mimaroglu A (2004) Dry sliding wear characteristics of some industrial polymers against steel counterface. Tribol Int 37:727–732
Vishwanath B, Verma AP, Rao CVSK (1993) Effect of reinforcement on friction and wear of fabric reinforced polymer composites. Wear 167:93–99
Suresha B, Chandramohan G, Samapthkumaran P, Seetharamu S, Vynatheya S (2006) Friction and wear characteristics of carbon-epoxy and glassepoxy woven roving fiber composites. J Reinf Plast Compos 25:771–782
Zhou W (2011) Effect of coupling agents on the thermal conductivity of aluminum particle/epoxy resin composites. J Mater Sci 46:3883–3889
Archard J (1953) Contact and rubbing of flat surfaces. J Appl Phys 24:981–988
Friedrich K (1986) Friction and wear of polymer composites, composite materials series, vol 1. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 233–287
Acknowledgements
Authors gratefully acknowledge the support of University Grants Commission (UGC), Govt. of India through Major Research Project [F. No. 42-882/2013(SR)] in Engineering.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarkar, P., Modak, N. & Sahoo, P. Effect of Aluminum Filler on Friction and Wear Characteristics of Glass Epoxy Composites. Silicon 10, 715–723 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-016-9520-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-016-9520-y