Abstract
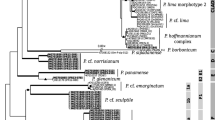
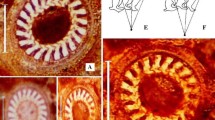
Outbreaks of paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) and dense blooms caused by Alexandrium species in Jinhae-Masan Bay, Korea have been nearly annual events for many years. However, excluding some Alexandrium species responsible for PSP, there are no critical reports on the morphology of Alexandrium species in this bay. To identify the Alexandrium species based on detailed morphological features, vegetative cells collected water samples and established by the incubation of resting cysts isolated from sediment trap samples were analyzed. Four species of Alexandrium were identified: Alexandrium affine, A. fundyense, A. catenella, and A. insuetum. Morphological features of these species were basically consistent with those outlined in previous studies. However, the ventral pore and the connecting pore on the sulcal plate, which have been accepted as diagnostic characteristics for the identification of A. fundyense and A. catenella, need to be reevaluated, indicating that useful morphological features for identifying these two species should be recommended to avoid confusion in the classification of species in genus Alexandrium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alpermann TJ, Tillmann U, Beszteri B, Cembella AD, John U (2010) Phenotypic variation and genotypic diversity in a planktonic population of the toxigenic marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense (Dinophyceae). J Phycol 46:18–32
Anderson DM, Alpermann TJ, Cembella AD, Collos Y, Masseret E, Montresor M (2012) The globally distributed genus Alexandrium: multifaceted roles in marine ecosystems and impacts on human health. Harmful Algae 14:10–35
Anderson D, Kulis D, Doucette G, Gallagher J, Balech E (1994) Biogeography of toxic dinoflagellates in the genus Alexandrium from the northeastern United States and Canada. Mar Biol 120:467–478
Balech E (1989) Redescription of Alexandrium minutum Halim (Dinophyceae) type species of the genus Alexandrium. Phycologia 28:206–211
Balech E (1995) The genus Alexandrium Halim (Dinoflagellata). Sherkin Island marine station, Cork, 151 p
Bravo I, Garces E, Diogene J, Fraga S, Sampedro N, Figueroa RI (2006) Resting cysts of the toxigenic dinoflagellate genus Alexandrium in recent sediments from the Western Mediterranean coast, including the first description of cysts of A. kutnerae and A. peruvianum. Eur J Phycol 41:293–302
Bravo I, Vila M, Maso M, Figueroa RI, Ramilo I (2008) Alexandrium catenella and Alexandrium minutum blooms in the Mediterranean Sea: toward the identification of ecological niches. Harmful Algae 7:515–522
Cembella AD, Lewis NI, Quilliam MA (2000) The marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) as the causative organism of spirolide shellfish toxins. Phycologia 39:67–74
Chang DS, Shin IS, Pyeun JH, Park YH (1987) A study on paralytic shellfish poison of sea mussel Mytilus edulis. Bull Kor Soc Fish Technol 20:293–299
Collins C, Graham J, Brown L, Bresnan E, Lacaze J-P, Turrell EA (2009) Identification and toxicity of Alexandrium tamarense (Dinophyceae) in Scottish waters. J Phycol 45:692–703
Crespo BG, Keafer BA, Ralston DK, Lind H, Farber D, Anderson DM (2011) Dynamics of Alexandrium fundyense blooms and shellfish toxicity in the Nauset Marsh System of Cape Cod (Massachusetts, USA). Harmful Algae 12:26–38
Delgado M, Garces E, Vila M, Camp J (1997) Morphological variability in three populations of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium taylori. J Plankton Res 19:749–757
Gu HF, Zeng N, Liu TT, Yang WD, Muller A, Krock B (2013) Morphology, toxicity, and phylogeny of Alexandrium (Dinophyceae) species along the coast of China. Harmful Algae 27:68–81
Hallegraeff GM, Bolch CJ, Blackburn SI, Oshima Y (1991) Species of the toxigenic dinoflagellate genus Alexandrium in southeastern Australian waters. Bot Mar 34:575–587
Hallegraeff GM (1998) Transport of toxic dinoflagellates via ships’ ballast water: bioeconomic risk assessment and efficacy of possible ballast water management strategies. Mar Ecol-Prog Ser 168:297–309
Han M-S, Jeon J-K, Kim Y-O (1992) Occurrence of dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense, a causative organism of paralytic shellfish poisoning in Chinhae Bay, Korea. J Plankton Res 14:1581–1592
Han M-S, Jeon J-K, Yoon Y-H (1993) Distribution and toxin profiles of Alexandrium tamarense (Lebour) Balech (Dinoflagellata) in the southeastern coastal waters, Korea. Korean J Phycol 8:7–13
Hansen PJ, Cembella AD, Moestrup O (1992) The marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii: paralytic shellfish toxin concentration, composition, and toxicity to a tintinnid ciliate. J Phycol 28: 597–603
John U, Litaker RW, Montresor M, Murray S, Brosnahan ML, Anderson DM (2014) Formal revision of the Alexandrium tamarense species complex (Dinophyceae) taxonomy: the introduction of five species with emphasis on molecular-based (rDNA) classification. Protist 165:779–804
Kim CH (1995) Paralytic shellfish toxin profiles of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium species isolated from benthic cysts in Jinghae Bay, Korea. J Korean Fish Soc 28:364–372
Kim CJ (2000) PSP toxin production and molecular biological identification of regional isolates of the genus Alexandrium (Dinophyceae) occurring in Korean coastal waters. M.D. Thesis, Pukyong National University, 88 p
Kim CH, Park TG, Lee C (2010) Harmful dinoflagellates and mitigation strategies in Korea. Philipp J Sci 139:139–147
Kim K-Y, Yoshida M, Fukuyo Y, Kim C-H (2002) Morphological observation of Alexandrium tamarense (Lebour) Balech, A.catenella (Whedon et Kofoid) Balech and one related morphotype (Dinophyceae) in Korea. Algae 17:11–19
Kremp A, Lindholm T, Dressler N, Erler K, Gerdts G, Eirtovaara S, Leskinen E (2009) Bloom forming Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) in shallow waters of the Aland Archipelago, Northern Baltic Sea. Harmful Algae 8:318–328
Lebour MV (1925) The dinoflagellates of Northern Seas. Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, Plymouth, 250 p
Lee JS, Jeon JK, Han MS (1992) Paralytic shellfish toxins in the Mytilus edulis and dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense from Jinhae Bay, Korea. Bull Korean Fish Soc 25:144–150
Lee SG, Park JS, Kim HG (1993) Taxonomy of marine toxic flagellates occurring in the southern coastal waters of Korea. Bull Nat Fish Res Dev Agency 48:1–23
Lilly EL, Halanych KM, Anderson DM (2007) Species boundaries and global biogeography of the Alexandrium tamarense complex (Dinophyceae). J Phycol 43:1329–1338
Lim AS, Jeong HJ, Kim JH, Lee SY (2015) Description of the new phototrophic dinoflagellate Alexandrium pohangense sp. nov. from Korean coastal waters. Harmful Algae 46:49–61
Loeblich LA, Loeblich III AR (1975) The organism causing New England red tides: Gonyaulax excavata. In: Lo Cicero V (ed) Toxic dinoflagellate blooms. Proceedings of the first international conference on toxic dinoflagellate blooms. Massachusetts Science and Technology Foundation, Wakefield, pp 207–224
Matsuoka K, Fukuyo Y (2000) Technical guide for modern dinoflagellate cyst study. WESTPAC-HAB, Tokyo
MacKenzie L, de Salas M, Adamson J, Beuzenberg V (2004) The dinoflagellate genus Alexandrium (Halim) in New Zealand coastal waters: comparative morphology, toxicity and molecular genetics. Harmful Algae 3:71–92
Murray SA, Hoppenrath M, Orr RJS, Bolch C, John U, Diwan R, Yauwenas R, Harwood T, de Salas M, Neilan B, Hallegraeff G (2014) Alexandrium diversaporum sp. nov., a new non-saxitoxin producing species: phylogeny, morphology and sxtA genes. Harmful Algae 31:54–65
Orlova TY, Selina MS, Lilly EL, Kulis DM, Anderson DM (2007) Morphogenetic and toxin composition variability of Alexandrium tamarense (Dinophyceae) from the east coast of Russia. Phycologia 46:534–548
Shim JH, Shin EY, Choi JK (1981) A taxonomical study on the dinoflagellates of the coastal waters in the vicinity of Yeosu, Korea. J Oceanol Soc Korea 16:57–98
Shin HH, Baek SH, Li Z, Han M-S, Oh SJ, Youn S-H, Kim YS, Kim D, Lim W-A (2014) Resting cysts, and effects of temperature and salinity on the growth of vegetative cells of the potentially harmful species Alexandrium insuetum Balech (Dinophyceae). Harmful Algae 39:175–184
Shin HH, Yoon YH, Kawami H, Iwataki M, Matsuoka K (2008) The first appearance of toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense (Gonyaulacales, Dinophyceae) responsible for the PSP contaminations in Gamak Bay, Korea. Algae 23:251–255
Tillmann U, Krock B, Alpermann TJ, Cembella A (2016) Bioactive compounds of marine dinoflagellate isolates from western Greenland and their phylogenetic association within the genus Alexandrium. Harmful Algae 51:67–80
Van Wagoner RM, Misner I, Tomas CR, Wright JLC (2011) Occurrence of 12-methylgymnodimine in a spirolide-producing dinoflagellate Alexandrium peruvianum and the biogenetic implications. Tetrahedron Lett 52:4243–4246
Varela D, Paredes J, Alves-de-Souza C, Seguel M, Sfeir A, Frangopulos M (2012) Intraregional variation among Alexandrium catenella (Dinophyceae) strains from southern Chile: morphological, toxicological and genetic diversity. Harmful Algae 15:8–18
Vila M, Garcés E, Maso M, Camp J (2001) Is the distribution of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella expanding along the NW Mediterranean coast? Mar Ecol-Prog Ser 222:73–83
Wang D-Z, Lin L, Gu H-F, Chan LL, Hong H-S (2008) Comparative studies on morphology, ITS sequence and protein profile of Alexandrium tamarense and A. catenella isolated from the China Sea. Harmful Algae 7:106–113
Whedon WF, Kofoid CA (1936) Dinoflagellata of the San Francisco region. I. On the skeletal morphology of two new species, Gonyaulax catanella and G. acatenella. Univ Calif Publs Zool 41:25–34
Yoo JS, Fukuyo Y, Cheun B, Lee SG, Kim HG (2000) Toxic algal bloom caused by dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense in Chindong Bay, Korea. Korean J Fish Aquat Sci 3:26–32
Yuki K, Yoshimatsu S (1990) New record of Alexandrium insuetum Balech (Dinophyceae) from Japan with some supplementary observations on thecal morphology. Bull Plankton Soc Jpn 36:121–126
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, E.S., Li, Z., Oh, S.J. et al. Morphological identification of Alexandrium species (Dinophyceae) from Jinhae-Masan Bay, Korea. Ocean Sci. J. 52, 427–437 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12601-017-0031-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12601-017-0031-6