Abstract
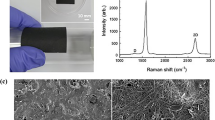
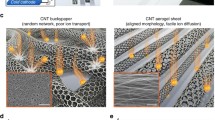
In this work, we report a thermobattery that can efficiently harvest low-grade waste heat. The thermobattery utilizes temperature dependence of ferri/ferrocyanide (Fe(CN)6 3−/Fe(CN)6 4−) redox potential and employs the porous carbon textile electrode that is coated with single-walled carbon nanotube (SWNT). Simple and scalable dipping and drying process was applied to prepare the SWNT coated textile electrodes (SWNT-CT). The SWNT coating not only decreases the sheet conductance of the textile remarkably but also provides the number of available reaction sites for thermogalvanic conversion, resulting in improving electrical outputs. The capability for power generation in the thermobattery was quantitatively investigated by measuring potential versus current curves. Discharge behavior of the thermobattery was also discussed to provide an understanding of the internal resistances that limit output electrical power.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hasnain, S. M., “Review on Sustainable Thermal Energy Storage Technologies, Part I: Heat Storage Materials and Techniques,” Energy Conversion and Management, vol. 39, no. 11, pp. 1127–1138, 1998.
Starner, T., “Human-powered Wearable Computing,” IBM Systems Journal, Vol. 35, No. 3.4, pp. 618–629, 1996.
Paradiso, J. A. and Starner, T., “Energy Scavenging for Mobile And Wireless Electronics,” IEEE Pervasive Computing, Vol. 4, No.1, pp. 18–27, 2005.
Bhandari, B., Poudel, S. R., Lee, K. T., and Ahn, S. H., “Mathematical Modeling of Hybrid Renewable Energy System: A Review on Small Hydro-Solar-Wind Power Generation,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Tech., vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 157–173, 2014.
Bhandari, B., Lee, K. T., Lee G. Y., Cho, Y. M., and Ahn S. H., “Optimization of Hybrid Renewable Energy Power Systems: A Review,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Tech., vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 99–112, 2015.
Bell, L. E., “Cooling, Heating, Generating Power, and Recovering Waste Heat with Thermoelectric Systems,” Science, vol. 321, no. 5895, pp. 1457–1461, 2008.
Gou, X., Xiao, H., and Yang, S., “Modeling, Experimental Study and Optimization on Low-temperature Waste Heat Thermoelectric Generator System,” Applied Energy, vol. 87, no. 10, pp. 3131–3136, 2010.
Hsu, C. T., Huang, G. Y., Chu, H. S., Yu, B., and Yao, D. J., “Experiments and Simulations on Low-temperature Waste Heat Harvesting System by Thermoelectric Power Generators,” Applied Energy, vol. 88, no. 4, pp. 1291–1297, 2011.
Navid, A., Vanderpool, D., Bah, A., and Pilon, L., “Towards Optimization of a Pyroelectric Energy Converter for Harvesting Waste Heat,” International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, vol. 53, no. 19–20, pp. 4060–4070, 2010.
Niu, X., Yu, J., and Wang, S., “Experimental Study on Low-Temperature Waste Heat Thermoelectric Generator,” Journal of Power Sources, vol. 188, no. 2, pp. 621–626, 2009.
Wu, C., “Analysis of Waste-Heat Thermoelectric Power Generators,” Applied Thermal Engineering, vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 63–69, 1996.
Yu, C. and Chau, K. T, “Thermoelectric Automotive Waste Heat Energy Recovery using Maximum Power Point Tracking,” Energy Conversion and Management, vol. 50, no. 6, pp. 1506–1512, 2009.
Ujihara, M., Carman, G. P, and Lee, D. G., “Thermal Energy Harvesting Device using Ferromagnetic Materials,” Applied Physics Letters, vol. 91, no. 9, Paper No. 093508, 2007.
Nam, S. K. and Lee, S. K., “The Effect of Ti Adhesion Layer on the Thermoelectric Noise of a High Resolution Thermopile for Nanowatt Heat Flux Sensor,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., vol. 15, no. 11, pp. 2391–2396, 2014.
Kim, H., Lee, Y., and Lee, K. H., “Design of a Thermoelectric Layer for a Micro Power Generator,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 261–267, 2012.
Gunawan, A., Lin, C.-H., Buttry, D. A., Mujica, V., Taylor, R. A., et al., “Liquid Thermoelectrics: Review of Recent and Limited New Data of Thermogalvanic Cell Experiments,” Nanoscale and Microscale Thermophysical Engineering, Vol. 17, No.4, pp. 304–323, 2013.
Hu, R., Cola, B. A., Haram, N., Barisci, J. N., Lee, S., et al., “Harvesting Waste Thermal Energy using a Carbon-nanotube-based Thermo-electrochemical Cell,” Nano Letters, vol. 10, no. 3, pp. 838–846, 2010.
Romano, M. S., Li, N., Antiohos, D., Razal, J. M., Nattestad, A., et al., “Carbon Nanotube-Reduced Graphene Oxide Composites for Thermal Energy Harvesting Applications,” Advanced Materials, vol. 25, no. 45, pp. 6602–6606, 2013.
Kang, T. J., Fang, S., Kozlov, M. E., Haines, C. S., Li, N., et al., “Electrical Power from Nanotube and Graphene Electrochemical Thermal Energy Harvesters,” Advanced Functional Materials, vol. 22, no. 3, pp. 477–489, 2012.
Bonetti, M., Nakamae, S., Roger, M., and Guenoun, P., “Huge Seebeck Coefficients in Nonaqueous Electrolytes,” The Journal of Chemical Physics, Vol. 134, No.11, pp. 114513, 2011.
Kuzminskii, Y. V., Zasukha, V. A., and Kuzminskaya, G. Y., “Thermoelectric Effects in Electrochemical Systems. Nonconventional Thermogalvanic Cells,” Journal of Power Sources, vol. 52, no. 2, pp. 231–242, 1994.
Abraham, T. J., MacFarlane, D. R., and Pringle, J. M., “Seebeck Coefficients in Ionic Liquids-Prospects for Thermo-Electrochemical Cells,” Chemical Communications, vol. 47, no. 22, pp. 6260–6262, 2011.
Hu, L., Pasta, M., Mantia, F. L., Cui, L., Jeong, S., et al., “Stretchable, Porous, and Conductive Energy Textiles,” Nano Letters, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 708–714, 2010.
Kang, T. J., Choi, A., Kim, D. H., Jin, K., Seo, D. K., et al., “Electromechanical Properties of CNT-coated Cotton Yarn for Electronic Textile Applications,” Smart Materials and Structures. Vol. 20, No.1, Paper No. 015004, 2011.
Jiang, L., Gao, L., and Sun, J., “Production of Aqueous Colloidal Dispersions of Carbon Nanotubes,” Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, vol. 260, no. 1, pp. 89–94, 2003.
Kang, T. J., Yoon, J. W., Kim, D. I., Kum, S. S., Huh, Y. H., et al., “Sandwich-Type Laminated Nanocomposites Developed by Selective Dip-Coating of Carbon Nanotubes,” Advanced Materials, vol. 19, no. 3, pp. 427–432, 2007.
Hu, C. Y., Xu, Y. J., Duo, S. W., Zhang, R. F., and Li, M. S. “Non-Covalent Functionalization of Carbon Nanotubes with Surfactants and Polymers,” Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society, vol. 56, no. 2, pp. 234–239, 2009.
Moore, V. C., Strano, M. S., Haroz, E. H., Hauge, R. H., and Smalley, R. E., “Individually Suspended Single-walled Carbon Nanotubes in Various Surfactants,” Nano Letters, vol. 3, no. 10, pp. 1379–1382, 2003.
Luo, H., Shi, Z., Li, N., Gu, Z., and Zhuang, Q., “Investigation of the Electrochemical and Electrocatalytic Behavior of Single-wall Carbon Nanotube Film on a Glassy Carbon Electrode,” Analytical Chemistry, vol. 73, no. 5, pp. 915–920, 2001.
Wang, J., Li, M., Shi, Z., Li, N., and Gu, Z., “Direct Electrochemistry of Cytochrome c at a Glassy Carbon Electrode Modified with Single-wall Carbon Nanotubes,” Analytical Chemistry, vol. 74, no. 9, pp. 1993–1997, 2002.
Zhao, Q., Gan, Z., and Zhuang, Q., “Electrochemical Sensors based on Carbon Nanotubes,” Electroanalysis, vol. 29, no. 9, pp. 1609–1613, 2010.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bae, K.M., Yang, H.D., Tufa, L.T. et al. Thermobattery based on CNT coated carbon textile and thermoelectric electrolyte. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 16, 1245–1250 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-015-0162-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-015-0162-6