Abstract
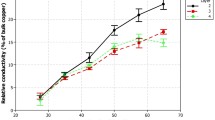
Copper nanoparticles are preferred as a printable conductive material in printed electronics because they cost less than noble nano particles such as gold and silver. Only disadvantage is that copper is easily oxidized, which may deteriorate the conductivity. Copper is thermodynamically unstable at atmospheric condition and is easily oxidized into either Cu2O or CuO, both of which are less conductive compared to pure copper. To alleviate these problems, we propose a sintering process using laser in the study. The laser source in this study is a laser having 532 nm wavelength and 5 W maximum output power. The size of used copper particle is 100∼120 nm. In order to measure the absorptivity at 532 nm, UV visible-spectrometer was used. Copper nano ink was spin-coated on the glass substrate, and various irradiated laser powers and scan rates were applied in air. The resistivity of the conductive film, after laser sintering under the condition of air, was below 5.3 μΩcm which was three times as much as that of bulk copper.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calvert, P., “Inkjet Printing for Materials and Devices,” Chemistry of Materials, Vol. 13, No. 10, pp. 3299–3305, 2001.
Arias, A., Ready, S., Lujan, R., Wong, W., Paul, K., and et al., “All Jet-Printed Polymer Thin-Film Transistor Active-Matrix Backplanes,” Applied Physics Letters, Vol. 85, No. 15, pp. 3304–3306, 2004.
Sabnis, R. W., “Color Filter Technology for Liquid Crystal Displays,” Displays, Vol. 20, No. 3, pp. 119–129, 1999.
Lee, S. H., Shin, K. Y., Hwang, J. Y., Kang, K. T., and Kang, H. S., “Silver Inkjet Printing with Control of Surface Energy and Substrate Temperature,” Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, Vol. 18, No. 7, Paper No. 075014, 2008.
Rahman, K., Khan, A., Nam, N. M., Choi, K.H., and Kim, D. S., “Study of Drop-on-Demand Printing through Multi-Step Pulse Voltage,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 12, No. 4, pp. 663–669, 2011.
Jeong, S., Woo, K., Kim, D., Lim, S., Kim, J. S., and et al., “Controlling the Thickness of the Surface Oxide Layer on Cu Nanoparticles for the Fabrication of Conductive Structures by InkJet Printing,” Advanced Functional Materials, Vol. 18, No. 5, pp. 679–686, 2008.
Han, W. S., Hong, J. M., Kim, H. S., and Song, Y. W., “Multi-Pulsed White Light Sintering of Printed Cu Nanoinks,” Nanotechnology, Vol. 22, No. 39, Paper No. 395705, 2011.
Yabuki, A. and Arriffin, N., “Electrical Conductivity of Copper Nanoparticle Thin Films Annealed at Low Temperature,” Thin Solid Films, Vol. 518, No. 23, pp. 7033–7037, 2010.
Park, B. K., Kim, D., Jeong, S., Moon, J., and Kim, J. S., “Direct Writing of Copper Conductive Patterns by Ink-Jet Printing,” Thin Solid Films, Vol. 515, No. 19, pp. 7706–7711, 2007.
Joo, M., Lee, B., Jeong, S., and Lee, M., “Comparative Studies on Thermal and Laser Sintering for Highly Conductive Cu Films Printable on Plastic Substrate,” Thin Solid Films, Vol. 520, No. 7, pp. 2878–2883, 2012.
Dearden, A. L., Smith, P. J., Shin, D. Y., Reis, N., Derby, B., and O’Brien, P., “A Low Curing Temperature Silver Ink for Use in Ink-Jet Printing and Subsequent Production of Conductive Tracks,” Macromolecular Rapid Communications, Vol. 26, No. 4, pp. 315–318, 2005.
Park, J. H. and Natesan, K., “Oxidation of Copper and Electronic Transport in Copper Oxides,” Oxidation of Metals, Vol. 39, No. 5–6, pp. 411–435, 1993.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, J.H., Kang, KT., Hwang, J.Y. et al. Rapid sintering of copper nano ink using a laser in air. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 15, 1051–1054 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-014-0435-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-014-0435-5