Abstract
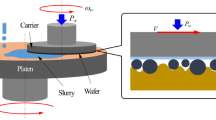
In chemical mechanical planarization (CMP) industry, reducing slurry consumption without avoiding the drop in productivity is one of the most important requirements for environmental sustainability. In this paper, we propose a spray slurry nozzle to reduce the slurry consumption and increase the material removal rate (MRR) in SiO2 CMP. The spray slurry nozzle is compared with a commonly used tube-type slurry nozzle in terms of MRR, material removal uniformity, friction force, and process temperature. And, a case study on the greenhouse gas (GHG) emission associated with the slurry consumption is provided by polishing patterned wafers. Adopting the spray slurry nozzle in CMP process provides higher MRR, higher friction force, and shorter process time than the normal tubetype slurry nozzle. Thus, the spray slurry nozzle will diminish the carbon dioxide equivalent (CDE) associated with the slurry and electricity consumptions. Furthermore, using the spray nozzle decreases the process temperature and it may be used as a cooling system for the CMP process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Branham, M. S. and Gutowski, T. G., “Deconstructing Energy use in Microelectronics Manufacturing: an Experimental Case Study of a Mems Fabrication Facility,” Environmental Science & Technology, Vol. 44, No. 11, pp. 4295–4301, 2010.
Lee, H., Dornfeld, D. A., and Jeong, H., “Mathematical Model-based Evaluation Methodology for Environmental Burden of Chemical Mechanical Planarization Process,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Tech., Vol. 1, No. 1, pp. 11–15, 2014.
Lee, H. and Jeong, H., “A Wafer-Scale Material Removal Rate Profile Model for Copper Chemical Mechanical Planarization,” International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, Vol. 51, No. 5, pp. 395–403, 2011.
Kwark, H., Yang, W. Y., and Sung, I. H., “Slurry Particle behavior inside Pad Pore during Chemical Mechanical Polishing,” J. Korean Soc. Tribol. Lubr. Eng., Vol. 28, No. 1, pp. 7–11, 2012.
Lee, H., Joo, S., and Jeong, H., “Mechanical Effect of Colloidal Silica in Copper Chemical Mechanical Planarization,” Journal of Materials Processing Technology, Vol. 209, No. 20, pp. 6134–6139, 2009.
Jindal, A., Hegde, S., and Babu, S. V., “Chemical Mechanical Polishing of Dielectric Films using Mixed Abrasive Slurries,” Journal of The Electrochemical Society, Vol. 150, No. 5, pp. 314–318, 2003.
Seo, Y. J. and Lee, W. S., “Effects of Mixed Abrasive Slurry in Oxide-Chemical Mechanical Polishing,” Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 45, pp. 618–621, 2004.
Kim, N. H., Seo, Y. J., and Lee, W. S., “Temperature Effects of Pad Conditioning Process on Oxide CMP: Polishing Pad, Slurry Characteristics, and Surface Reactions,” Microelectronic Engineering, Vol. 83, No. 2, pp. 362–370, 2006.
Li, W., Shin, D. W., Tomozawa, M., and Murarka, S. P., “The Effect of the Polishing Pad Treatments on the Chemical-Mechanical Polishing of SiO2 Films,” Thin Solid Films, Vol. 270, No. 1, pp. 601–606, 1995.
Hsueh, C. T., “Analysis on Pad Performances and Planarization Effects for CMP,” Ms.C. Thesis, Department of Mechanical Engineering, National Taiwan University of Science and Technology, 2011.
Yang, J. C., Kim, H., Lee, C. G., Lee, H. D., and Kim, T., “Optimization of CMP Pad Surface by Laser Induced Micro Hole,” Journal of The Electrochemical Society, Vol. 158, No. 1, pp. 15–20, 2011.
Lee, H., Park, S., and Jeong, H., “Evaluation of Environmental Impacts during Chemical Mechanical Polishing (CMP) for Sustainable Manufacturing,” Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, Vol. 27, No. 2, pp. 511–518, 2013.
Suh, S. H., Woo, I. K., and Noh, S. K., “Development of an Automatic Trajectory Planning System (ATPS) for Spray Painting Robots,” Proc. of IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 1948–1955, 1991.
Bauck, L. and Doins, R., “Slurry Pump Affects on CMP,” Proc. of the 2nd PacRim International Conference on Planarization CMP and its Application Technology, 2005.
Park, K., Jung, J., Lee, H., Seo, H., Jeong, S., and et al., “The Effect of Pad Groove Density on CMP Characteristics,” J. Korean Soc. Precis. Eng., Vol. 22, No. 8, pp. 27–33, 2005.
Philipossian, A. and Mitchell, E., “Slurry Utilization Efficiency Studies in Chemical Mechanical Planarization,” Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Vol. 42, No. 12, pp. 7259, 2003.
Lee, H., Park, B., and Jeong, H., “Mechanical Effect of Process Condition and Abrasive Concentration on Material Removal Rate Profile in Copper Chemical Mechanical Planarization,” Journal of Materials Processing Technology, Vol. 209, No. 4, pp. 1729–1735, 2009.
Lee, H., Guo, Y., and Jeong, H., “Temperature Distribution in Polishing Pad during CMP process: Effect of Retaining Ring,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 13, No. 1, pp. 25–31, 2012.
Boyd, S. B., Horvath, A., and Dornfeld, D. A., “Life-Cycle Assessment of Computational Logic Produced from 1995 through 2010,” Environmental Research Letters, Vol. 5, No. 1, Paper No. 014011, 2010.
Kim, S. and Overcash, M., “Energy in Chemical Manufacturing Processes: GatetoGate Information for Life Cycle Assessment,” Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, Vol. 78, No. 9, pp. 995–1005, 2003.
Korea Power Exchange (KPX), “Greenhouse Gas Emission,” http://www.kpx.or.kr/KOREAN/htdocs/popup/pop_1224.html (Accessed April 30, 2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, H., Park, Y., Lee, S. et al. Preliminary study on the effect of spray slurry nozzle in CMP for environmental sustainability. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 15, 995–1000 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-014-0427-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-014-0427-5