Abstract
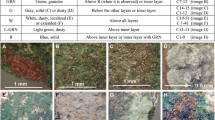
The excavations in the necropolis of the Francavilla Marittima archaeological area, in Calabria, have brought to light the rich burial artifacts and materials, dated between the end of the ninth and sixth centuries BCE. SEM/EDS analysis was conducted on some sections taken from a bronze artifact classifiable as an armilla or fibula fragment. Our aim was to elucidate the nature of the corrosion processes acting on the specimen. SEM investigation detected the segregation of tin towards the outer layer and a depletion of the copper content in the same region. Furthermore, the elemental distribution maps of the sections analyzed evidenced the presence of chloride ions in the border area between the corrosion patina and the metal alloy. Such anion migration of chloride ions into the interior of the alloy leads to a particular variant of the type of corrosion of structure that in the literature has been identified as structure I.
A cavity electrode designed for electrochemical measurements of powders was used to perform cyclic voltammetry experiments devoted to explore the activity of the patina covering the surface of the bronze fragment. The surface layer consists mainly of tin and tin oxides; the layer immediately beneath it contains copper oxides. An increase of reactivity was shown in an acidic environment. The activity of the patina is greatly reduced at pH 5 and appears to be zero at neutral pH.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benelli C (2016), Tables. http://www.lamm.unifi.it/tabelle/e0alf.htm. Accessed 02/02/2016.
Bertholon R (2001) The original surface of corroded metallic archaeological objects: characterization and location. La Revue de Metallurgie 98:817–823
Cachet-Vivier C, Vivier V, Cha CS, Nedelec JY, Yu LT (2001) Electrochemistry of powder material studied by means of the cavity microelectrode (CME). Elecrochim Acta 47:181–189
Chambers C and Holliday AK (2016) in Inorganic chemistry: Butterworths Intermediate Chemistry, Elsevier p. 173
Chiavari C, Rhmouni K, Takenouti H, Joiret S, Vernaut P, Robbiola L (2007) Composition and electrochemical properties of natural patinas of outdoor bronze. Elecrochim. Acta 52:7760–7769
Donaldson JD and Grimes SM (1989) in Chemistry of tin ed. Smith PG, Springer Science+Business Media, Dordrecht, pp. 62–92
Espi L, Aucouturier M (2001) Surface modification issues in art. La Revue de Metallurgie 98:751–766
Hassairi H, Bousselmi L, Triki E, Ingo GM (2007) Assessment of the interphase behaviour of two bronze alloys in archaeological soil. Mater Corros 58:121–128
Holleman AF, Wiberg E (2001) Inorganic chemistry. Academic Press, San Diego, p. 907
Ingo GM, De Caro T, Ricucci C, Angelini E, Grassini S, Balbi S, Bernardini P, Salvi D, Bousselmi S, Cilingiroglu A, Gener M, Gouda VK, Al Jarrah O, Khosroff S, Mahdjoub Z, Al Saad Z, El-Saddik W, Vassiliou P (2006) Large scale investigation of chemical composition, structure and corrosion mechanism of bronze archaeological artefacts from Mediterranean basin. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 83:513–520
La Niece S (1993) in Metal plating and patination: cultural, technical and historical developments, Burlington: Elsevier Science p. 252.
Lalli C, (2004) L’impatto ambientale delle opere d’arte esposte all’aperto: cause e problemi di degrado, in “Monumenti bronzei esposti all’aperto”, ed. Nardini-Firenze pp. 59–76
Papadoupulos JK (2003) Francavilla Marittima. The archaic votive metal objects, in La dea di Sibari e il santuario ritrovato. Studi sui rinvenimenti dal Timpone della Motta di Francavilla Marittima, II. 1 The Archaic Votive Metal Objects, (BdA volume speciale), ed. Istituto poligrafico e Zecca dello Stato, Libreria dello Stato, Roma, p. 81
Paparazzo E, Lea AS, Baer DR, Northover JP (2001) Scanning auger microscopy studies of an ancient bronze. J Vac Sci Technol 19:1126–1133
Piccardo P, Mille B, Robbiola L (2007) Tin and copper oxides in corroded archaeological bronzes. In: Dillmann P, Beranger G, Piccardo P, Matthiesen H (eds) Corrosion of metallic heritage artefacts, investigation, conservation and prediction for long-term behaviour, European federation of corrosion publications, no. 48. Woodhead Publishing Limited, CRC Press, Cambridge, pp. 239–262
Rahmouni K, Joiret S, Robbiola L, Srihri A, Takenouti H, Vivier V (2005) Corrosion and protection of high leaded tin bronze covered with patina in NaHCO3 + Na2SO4 solution simulating acid rain urban environment. Bulgarian Chem Com 1:26–34
Robbiola L, Blengino JM, Fiaud C (1998) Morphology and mechanisms of formation of natural patinas on archaeological Cu-Sn alloys. Corros Sci 40:2083–2111
Scott D (1990) Bronze disease: a review of some chemical problems and the role of relative humidity. JAIC 29(2) Article 7:193–206
Scott D (2011), in Ancient metals: microstructure and metallurgy, Los Angeles: Conservation Science Press, pp. 25–29
Scott D, Finnerty R, Taniguchi Y, Koseto E, Schmidtling R, Stos ZA (2003) Analytical studies of the Francavilla archaic metal objects, in La dea di Sibari e il santuario ritrovato. Studi sui rinvenimenti dal Timpone della Motta di Francavilla Marittima, II. 1 The Archaic Votive Metal Objects, (BdA volume speciale), ed. Istituto poligrafico e Zecca dello Stato, Libreria dello Stato, Roma, (a) p. 206; (b) p. 211
Sidot E, Souissi N, Bousselmi L, Triki E, Robbiola L (2006) Study of the corrosion behaviour of Cu–10Sn bronze in aerated Na2SO4 aqueous solution. Corros Sci 48:2241–2257
Souissi N, Bousselmi L, Khosrof S, Triki E (2004) Voltammetric behaviour of an archeaological bronze alloy in aqueous chloride media. Mater Corros 55:284–292
Souissi N, Sidot E, Bousselmi L, Triki E, Robbiola L (2007) Corrosion behaviour of Cu–10Sn bronze in aerated NaCl aqueous media—electrochemical investigation. Corros Sci 49:3333–3347
Spoto G, Ciliberto E, Allen GC, Younes CM, Piccardo P, Pinasco MR, Stagno IMG, Maggi R (2000) Chemical-and-structural-properties-of-ancient-metallic-artefacts-multitechnique-approach-to-study-of-early-bronzes. Br Corros J 35:43–47
Vivier V, Cachet-Vivier C, Cha CS, Nedelec JY, LT Y (2000) Cavity microelectrode for studying battery materials: application to polyaniline powder. Electrochem Commun 2:180–185
Vivier V, Cachet-Vivier C, Cha CS, Nedelec JY, Yu LT (1999) Cavity microelectrode for studying powder materials at a high potential scan rate. Electrochem Solid-State Lett 2:385–387
Walker R (1980) Corrosion and preservation of bronze artifacts. J Chem Educ 57:277–280
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the University of Calabria for financial support. The authors are grateful to Dr. Rossella Pace and the Association for the International School of Archeology “Lagaria” NPO for having given the permission to access the artifact and the literature data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Imbardelli, D., Gallucci, M.C. & Chidichimo, G. SEM and electrochemical characterization of bronze artifacts from the Francavilla archaeological site. Archaeol Anthropol Sci 9, 567–578 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12520-016-0396-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12520-016-0396-y