Abstract
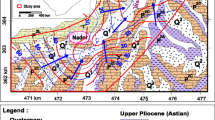
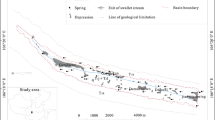
This paper aims at evaluating the level of groundwater vulnerability to pollution in Wadi Al-Waleh wells and South Amman area based on SINTACS model. The Wadi Al-Waleh Catchment (WWC) is considered to be one of the most important sub-basins in the middle part of Jordan. This study creates a map of groundwater vulnerability that shows areas with potential pollution. Areas are then classified into units with different levels of vulnerability based on anthropogenic and hydrogeological factors. The parameters of the SINTACS model are rated and evaluated by weight numerical indices. The vulnerability parameter is set upon fixed percentage interval of the sub-basin’s area. SINTACS index values have been categorized into four groups of pollution: very low (green), low (yellow), medium (orange), and medium to high (red). The results reveal that the units with very low levels of vulnerability to pollution cover an area of 0.17 km2. In addition, units with low, medium, and medium to high levels of vulnerability to pollution cover areas of 44.13, 1102.37, and 654.97 km2, respectively. The vulnerability maps show that most of the sub-surface area of WWC is characterized by medium to high levels of vulnerability to pollution, while units with very low and low vulnerability to pollution cover small areas of the western part of WWC. As well, the vulnerability maps show that there is moderate–high risk of pollution in the middle to eastern parts of WWC sub-basin. The risk of pollution in WWC mainly stems from intensive agricultural activities in the area.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al Kuisi M, El-Naqa A, Hammouri N (2006) Vulnerability mapping of shallow groundwater aquifer using SINTACS model in the Jordan valley area, Jordan. Environ Geol 50:651–667. doi:10.1007/s00254-006-0239-8
Al-Fawwaz M (2010) Role of the geologic structures on the aquifers vulnerability in arid areas: case study from Swaqa-Ghabawi/Jordan. Jordan Journal of Civil Engineering 4(2)
Aller L, Bennet T, Lehr JH, Petty RJ, Hacket G (1987) DRASTIC: a standardized system for evaluating ground water pollution potential using hydrogeologic settings. US Environmental Protection Agency Report (EPA/600/2-87/035), Robert S. Kerr Environmental Research Laboratory, p 455
Al-Rawabdeh A, Al-Ansari N, Al-Taani A, Knutsson S (2013) A GIS-based drastic model for assessing aquifer vulnerability in Amman-Zerqa groundwater basin, Jordan. Engineering 5:490–504. doi:10.4236/eng.2013.55059
Al-Shatnawi A, Al-Shboul R, Al-Fawwaz B, Al-Sharafat W, Bani Khalf R (2014) Vulnerability assessment using raster calculation and DRASTIC model for the Jordan Valley subsurface basin (AB1) imaging maps. Journal of Geographic Information System 6:585–593. doi:10.4236/jgis.2014.66048
Amadi AN, Olasehinde PI, Nwankwoala HO, Dan-Hassan MA, Okoye N (2014) Aquifer vulnerability studies using DRASTICA model. International Journal of Engineering Science Invention 3(3):1–10
Civita M (1990) Legenda unificata per le Carte della vulnerabilità dei corpi idrici sotterranei/Unified legend for the aquifer pollution vulnerability maps. Studi sulla Vulnerabilità degli Acquiferi, 1 (Append.), Pitagora Edit, Bologna, p 13
Civita M (1994) Le carte dellavulnerabilit`adegliacquiferi all’ inquinamiento: teoria e pratica [Contamination vulnerability mapping of the aquifer: theory and practice]. Quaderni di Tecniche di ProtezioneAmbientale, Pitagora
Civita M, De Maio M (1997) SINTACS. Un sistema parametrico per la valutazione e la cartografia della vulnerabilita` degli acquiferi all’inquinamento. Metodologia and Automatizzazione, vol. 60. Pitagora Editrice, Bologna, p 191
Civita MV, De Maio M (1998) Mapping groundwater vulnerability in areas impacted by flash food disasters. In: Proc 13th Eur User Conf, Firenze, Italy, 7–9 Oct 1998
Cordova CE (2008) Floodplain degradation and settlement history in Wadi al-Wala and Wadi ash-Shallalah, Jordan. Geomorphology 101(3):443–457. doi:10.1016/j.geomorph.2007.04.026
Cordova CE, Foley C, Nowell A, Bisson M (2005) Landforms, sediments, soil development, and prehistoric site settings on the Madaba Dhiban Plateau, Jordan. Geoarchaeology 20(1):29–56. doi:10.1002/gea.20036
Ducci D (2010) Aquifer vulnerability assessment methods: the non-independence of parameters problem. Journal of Water Resource and Protection 2(4):298–308. doi:10.4236/jwarp.2010.24034
Hammouri N, El-Naqa A (2008) GIS based hydrogeological vulnerability mapping of groundwater resources in Jerash Area-Jordan. Geofísica internacional [Int Geophys] 47(2):85–97
Hasiniaina F, Zhou J, Guoyi L (2010) Regional assessment of groundwater vulnerability in Tamtsag basin, Mongolia using drastic model. J Am Sci 6(11):65–78, Marsland Press
Jha MK, Sabastian J (2005) Vulnerability study of pollution upon shallow groundwater using drastic/GIS, a paper presented in the 8th Annual International Conference and Exhibition in India, Map India 2005 Geomatics 2005, New Delhi, 7–9 February.
Kalbouneh A, Bani-Khalaf R, Ulaimat A, Abu-Hejleh A (2011) Water resources protection plan for Zara–Ma`een–Mujib project watershed. The 6th Jordanian International Mining Conference, 1–3 November 2011, Amman, Jordan.
Kumar S, Thirumalaivasan D, Radhakrishnan N, Mathew S (2013) Groundwater vulnerability assessment using SINTACS model. Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk 4(4):339–354
Murthy KR, Dhanakumar S, Sundararaj P, Mohanraj R, Kumaraswamy K (2015) GIS-based modified SINTACS model for assessing groundwater vulnerability to pollution in Vellore District (part of Palar River Basin), Tamil Nadu, India. In Environmental management of river basin ecosystems, Springer Earth System Sciences, 429–453. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-13425-3_20.
MWI (Ministry of Water and Irrigation, Jordan) (2014) The water information system
Tilahum K, Merkel BJ (2010) Assessment of groundwater vulnerability to pollution in Dire Dawa, Ethiopia using DRASTIC. Environ Earth Sci 59:1485–1496. doi:10.1007/s12665-009-0134-1
Water Authority of Jordan (WAJ) (2015) Internal files for groundwater basins in Jordan, Amman, Jordan
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Shatnawi, A.M., El-Bashir, M.S., Khalaf, R.M.B. et al. Vulnerability mapping of groundwater aquifer using SINTACS in Wadi Al-Waleh Catchment, Jordan. Arab J Geosci 9, 67 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2080-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2080-4