Abstract
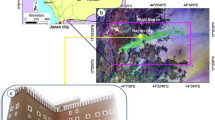
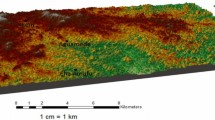
Over the years, the people of Akpugo community in Nkanu West L.G.A., Enugu State, South-East Nigeria have suffered from frequent building collapse without knowing the cause. This study integrates geotechnical and geophysical techniques to evaluate possible factors responsible for this anomaly. Areas with cracked and non-cracked buildings were studied to assess the geotechnical properties of the soils. Samples were taken at different locations and subjected to x-ray diffraction analysis, grain size analysis, specific gravity, Atterberg limits, permeability, compaction, and triaxial tests. Electrical resistivity method was also used to delineate the geo-electrical layers and to image the lateral variations of the subsurface. Results revealed that problematic zone (areas with cracked buildings) has lower permeability (4.018–7.016 × 10−7 m/s), lower angle of shearing resistance (10–14°), and medium to high plasticity index (25.1–38.33), while the non-problematic zone (areas without cracked buildings) has higher permeability (1.55–1.925 × 10−6 m/s), higher angle of shearing resistance (15–18°), and low plasticity index (18.1–19.4). The x-ray diffraction results of the problematic zone revealed a significant amount of smectite which has a very high swelling and shrinkage potential. The presence of substantial quantity of smectite in the soils of the problematic zone may be a strong factor in the structural problems. The electrical resistivity profiling delineated the boundary between the problematic zone and non-problematic zone and showed that the problematic zone has lower resistivity values (2–25 Ωm) while the non-problematic zone has higher resistivity values (20–170 Ωm).











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adepelumi AA, Olorunfemi MO (2000) Engineering geological and geophysical investigation of the reclaimed Lekki Peninsula, Lagos. Southwest Nigeria. Bull Eng Geol Environ 58:125–132
Adepelumi AA, Olorunfemi MO, Falebita DE, Bayowa OG (2009) Structural mapping of coastal plain sands using engineering geophysical technique: Lagos Nigeria case study. Nat Sci 1:2–9
Adesunloye MO (1987) Investigating the problem soil in Nigeria. Proceedings of the 9th Regional Conferences for Africa on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, Lagos. 103–112
Al-Kami AA (2011) Evaluation of shear strength of cohesionless soil due to excess pore water pressure. Arab J Geosci 4(7–8):1095–1101
Arora KR (2008) Soil mechanics and foundation engineering (geotechnical engineering), 8th edition. Lomus offset press, Delhi, 953p
Ayedun CA, Durodola OD, Akinjare OA (2012) An empirical ascertainment of the causes of building failure and collapse in Nigeria. Mediterr J Soci Sci 3(1):313–322
Badejo E (2009) Engineers, others urge multi-disciplinary approach to curb building collapse. Guardian Newsp. 15–17
Bazant PZ, Verdure M (2007) Discussion of “Mechanics of progressive collapse: learning from World Trade Centre and building demolitions”. J Eng Mech 133(3):308–319
Bell FG (2007) Engineering geology, 2nd edn. Elsevier, London, pp 207–248
Bish DL, Reynolds RC (1989) Sample preparation for x-ray diffraction. In: Bish DL, Post JE (eds) Modern powder diffraction. Mineralogical Society of America, Washington, DC, pp 73–100
Blyth FGH, De Feritas MH (1984) A geology for engineers. Arnold Intern Students’s ed., 7th edn. Arnold Publishing, London, 325p
Chabrillat S, Goetz AFH, Krosley L, Olsen HW (2002) Use of hyper spectral images in the identification and mapping of expansive clay soils and the role of spatial resolution. Remote Sens Environ 82:431–445
De-Swardt AM, Casey OP (1963) The coal resources of Nigeria. Bull Geol Survey of Nigeria, 28
Dobrin MB, Savit CH (1988) Introduction to geophysical prospecting, 4th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, 867p
Ede AN (2010) Building collapse in Nigeria: the trend of casualties in the last decade (2000–2010). Int J Civ Environ Eng 10(6):32–42
Eltaif NI, Gharaibeh MA (2008) Impact of alum on crust prevention and aggregation of calcareous soil: laboratory studies. Soil Use Manag 24(4):424–426
Emesiobi FC (2002) Research testing and quality control of materials I. Civil and highway engineering. The Blueprint Limited, Port-Harcourt, Rivers State
Fanis MS (2011) Geophysical characteristics of Wadi Hanifah water system, Riyadh Saudi Arabia. Arab J Geosci 4:1051–1066
Farmer BA (1973) Clay mineralogy. KPL publishing co. Ltd, Canada, 342P
Fatoba JO, Salami BM, Adesida A (2013) Structural failure investigation using electrical resistivity method: a case study of Amafor Ihuokpala, Enugu, Southeastern Nigeria. J Geol Min Res 5(8):208–215
Folagbade SO (2001) Case studies of building collapse in Nigeria. Proceedings of a Workshop on Building Collapse, Causes, Prevention and Remedies, The Nigerian Institute of Building, Ondo State Chapter, 23–24
Fouzan A, Muawia AD (2013) The study of cracks and fissures phenomenon in Central Saudi Arabia by applying geotechnical and geophysical techniques. Arab J Geosci. 1–8
Igwe O, Fukuoka H (2014) The effect of water-saturation on the stability of problematic slopes at the Iva Valley area, Southeast Nigeria. Arab J Geosci. doi:10.1007/s12517-014-1398-7
Kogbe CA (1981) Attempt to correlate the stratigraphic sequence in the middle Benue basin with those of the Anambra and upper Benue basins. Earth Evol Sci 1(2):139–148
Lazzari M, Geraldi E, Lapenna V, Loperte A (2006) Natural hazards vs human impact: an integrated methodological approach in geomorphological risk assessing on Tursi historical site, southern Italy. Landslides 3(4):275–287, Springer-Verlag
Lazzari M, Loperte A, Perrone A (2010) Near surface geophysics techniques and geomorphological approach to reconstruct the hazard cave map in historical and urban areas. Adv Geosci 24:35–44
Manasseh J, Olufemi AI (2004) Effect of lime on the geotechnical properties of Igumale shale. Electron J Geotech Eng 7:230–241
Matawal DS (2012) The challenges of building collapse in Nigeria. Proceedings of National Technical Workshop on Building Collapse in Nigeria: curbing the incidences of building collapse in Nigeria, 3–54
McCarthy DF (1999) Essentials of soil mechanics and foundations. Cited in Criteriurn McCarthy
Monanu S, Inyang F (1975) Climatic regimes. In: Ofomata GEK (ed) Nigeria in maps. Ethiope Publ. House, Benin, pp 27–29
Moore DM, Reynolds RCJ (1997) X-ray diffraction and the identification and analysis of clay minerals, 2nd edn. Oxford Univ Press, New York
Murat C (1972) Stratigraphy and paleogeography of the Cretaceous and Lower Tertiary in South-Eastern Nigeria. In: Whiteman AJ, Dessauvagie TFJ (eds) African geology. Ibadan University Press, pp 251–266
Obaje NG (1994) Coal petrography, microfossils and paleoenvironments of Cretaceous coal measures in the Middle Benue Trough of Nigeria. Tuebinger Mikropalaeontologische Mitteilungen 11:1–165
Obi GC, Okogbue CO, Nwajide CS (2001) Evolution of the Enugu Cuesta: a tectonically driven erosional process. Glob J Pure Appl Sci 7:321–330
Obiora SC, Umeji AC (2004) Petrographic evidence for regional burial metamorphism of the sedimentary rocks in the Lower Benue Rift. J Afr Earth Sci 3:269–277
Oboh-Ikuenobe EF, Obi GC, Jaramillo AC (2005) Lithofacies, palynofacies, and sequence stratigraphy of Palaeogene strata in Southeastern Nigeria. Afr Earth Sci 41:79–101
Oyedele KF, Oladele S, Adedoyin O (2011) Application of geophysical and geotechnical methods to site characterization for construction purposes at Ikoyi, Lagos, Nigeria. J Earth Sci Geotech Eng 1(1):87–100
Palacky GV (1987) Resistivity characteristics of geologic targets. Electromagnetic Methods Appl Geophys 1:1351
Reijers, TJA (1996) Selected chapters on geology. SPDC pub. 197p
Reyment RA (1965) Aspects of the geology of Nigeria. Ibadan University Press, Nigeria, 145p
Shaaban F, Ismail A, Massoud U, Mesbah H, Lethy A, Abbas MA (2013) Geotechnical assessment of ground conditions around a tilted building in Cairo, Egypt using geophysical approaches. Arab J Geosci 6(12):4961–4972
Sowers GB, Sower GE (1970) Introductory soil mechanics and foundations. Macmillan Book Publishing Company, London, 337p
Todd DK (1980) Groundwater hydrology, 2nd edn. John Wiley and Sons Inc, New York, 535p
Uduji ER, Okagbue CO, Onyeobi TUS (1996) Geotechnical properties of soils derived from the Awgu and Mamu formations in the Awgu-Okigwe area of south-eastern Nigeria and their relations to engineering problems. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech 33:117–123
Underwood LB (1967) Classification and identification of shales. Proc Am Soc Civ Eng J Soil Mech Foundn Div 93:97–116
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Una, C.O., Igwe, O., Maduka, R. et al. Integrating geotechnical and geophysical techniques in assessing frequent building collapse in Akpugo, Nkanu West L.G.A., Enugu State, Nigeria. Arab J Geosci 8, 10951–10960 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-1946-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-1946-9