Abstract
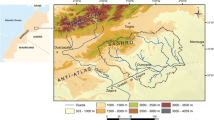
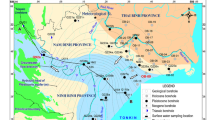
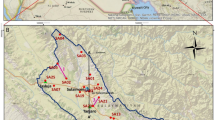
The hydrogeochemical and isotopic compositions of groundwaters of the Mio-Plio-Quaternary (MPQ) aquifer of the El Eulma area, Northeast Algeria were examined to determine the main factors controlling groundwater chemistry and salinity as well as its hydrogeochemical evolution. Groundwater occurs in different water-bearing formations belonging to Quaternary, Neogene, Upper Cretaceous and Jurassic age. Different geochemical interpretation methods were used to identify the geochemical characteristics. Groundwater of the MPQ aquifer has the highest salinity values (564.5 ≤ total dissolved solids ≤ 2,333 mg/L) in the study area due to the impact of saltwater of Chotts and/or Sebkha “Bazar” and agricultural activities. Plotting data in a Piper diagram showed that Cl and SO4 are the dominant anions, whereas Na is the most dominant cation, although sometimes replaced by Ca and/or Mg in the groundwaters. Dissolution of carbonate and sulphate minerals in the aquifer matrices and recharge areas as well as cation exchange is shown to modify the concentration of ions in groundwater. Groundwater-mineral equilibria showed the prevailing dissolution-precipitation reactions in the groundwater. The groundwaters are depleted in 2H and 18O and display an isotopic signature close to that of meteoric water with d-excess values indicating present-day precipitation over the region and reflect the contribution of vapour masses from Mediterranean Sea and Atlantic origin. The isotopic features suggest that most of the groundwaters at the study area result from mixing between recent recharge and an older component recharged under climatic conditions cooler than at present.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abid K, Dulinski M, Hadj Ammara F, Rozanski K, Zouari K (2012) Deciphering interaction of regional aquifers in Southern Tunisia using hydrochemistry and isotopic tools. Appl Geochem 27:44–55
Adams S, Titus R, Pietersen K, Tredouxc G, Harris C (2001) Hydrochemical characteristics of aquifers near Sutherland in the Western Karoo, South Africa. J Hydrol 241:91–103
Ahmadi R, Eric M, Ouali J (2013) Growth-strata geometry in fault-propagation folds: a case study from the Gafsa basin, southern Tunisian Atlas. Swiss J Geosci 106(1):91–107. doi:10.1007/s00015-013-0122-z
Andreo B, Linana C, Carrasco F, Jiménez de Cisneros C, Caballero F, Mudry J (2004) Influence of rainfall quantity on the isotopic composition (18O and 2H) of water in mountainous areas. Application for groundwater research in the Yunquera-Nieves karst aquifers (S Spain). Appl Geochem 19:561–574
APHA (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. APHA-AWWAWET, Washington, DC
Appelo CAJ, Postma D (1993) Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution. Balkema, Rotterdam
Avery A (1999) Infantile methemoglobinemia: reexamining the role of drinking water nitrates, Children Health Review. Environ Health Perspect 107(7):583–586
Ball JW, Nordstrom DK (1991) WATEQ4F—user’s manual with revised thermodynamic database and test cases for calculating speciation of major, trace and redox elements in natural waters. United States Geological Survey, Open-File Report, pp 90–129
Ben Moussa A, Bel Haj Salem S, Zouari K, Marc V, Jlassi F (2010) Investigation of groundwater mineralization in the Hammamet– Nabeul unconfined aquifer, north-eastern Tunisia: geochemical and isotopic approach. Environ Earth Sci. doi:10.1007/s12665-010-0616-1
Ben Sâad A (2012) Étude toxicologique des eaux souterraines de la région de Berka (bassin minier de Moularés). Sud Ouest Tunisien. Master-Pro. Faculté de Médicine de Sfax. 150p
Bengtsm G, Annadotter H (1989) Nitrate reduction in a groundwater microcosm determined by 15 N gas chromatograph mass spectrometry. Appl Environ Microbiol 55(11):2861–2870
Bouaziz S, Barrier E, Soussi M, Turki MM, Zouari H (2002) Tectonic evolution of the northern African margin in Tunisia from paleostress data and sedimentary record. Tectonophysics 357:227–253
Celle-Jeanton H, Travy Y, Blavoux B (2001) Isotopic typology of the precipitation in the Western Mediterranean region at three different time scales. Geophys Res Lett 28:1215–1218
Clark ID, Fritz P (1997) Environmental isotopes in hydrogeology. Lewis Publishers, New York
Coplen TB (1996) New guidelines for reporting stable hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen isotope-ratio data. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 60:3359–3360
Craig H (1961) Isotopic variations in meteoric water. Science 133:1702–1703
Cruz Sanjuliàn J, Araguàs L, Rozanski K, Cardenal J, Hidalgo MC, Garcia Lopez S, Martinez Garrido JC, Moral F, Olias M (1992) Sources of precipitation over South-Eastern Spain and groundwater recharge. An isotopic study. Tellus 44B:226–236
Dansgaard W (1964) Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 16:436–468
Daoud D (1995) Caractérisation géochimique et isotopique des eaux souterraines et estimation du taux d’évaporation dans le bassin du Chott Chergui (zone semi-aride), Algérie. Ph.D. thesis, University of Paris-Sud, Orsay, p. 256
Demdoum A (1996) Étude hydrogéologique de la plaine d’El Eulma et le problème de la qualité des eaux, Thèse; Magister, Uni Constantine, p. 205
Demdoum A (2009) Étude hydrogéochimique, isotopique et impact de la pollution sur les eaux de la région d’El Eulma. Thèse Doctorat Univ.de Constantine
Demdoum A, Hadji R, Djebbar M (2012) Caractérisation hydrochimique et apport isotopique sur la salinité du bassin d’El Eulma (Algérie Nord Orientale). Watmed6. 20-22 Nov. Sousse-Tunisia
Dissanayake CB, Weerasooriya SVR (1987) Medical geochemistry of nitrates and human cancer in Sri Lanka. Int J Environ stud 30:145–156
Edmunds WM, Guendouz A, Mamou A, Moulla A, Shand P, Zouari K (2003) Groundwater evolution in the Continental Intercalaire aquifer of southern Algeria and Tunisia: trace element and isotopic indicators. Appl Geochem 18:805–822
ERESS (1972) Etude des resources en eau du Sahara Septentrional [Study of water resources of the Septentrional Sahara]. UNESCO, Paris
Fontes J.C, Zuppi G.M (1976) Isotopes and water chemistry in sulphide-bearing springs of central Italy” In Conference on interpretation of environmental isotope and hydrochemical data in groundwater hydrology, Vienna, Austria, Panel Proceedings Series, IAEA, STI/PUB/429, pp. 143-158
Fontes JC, Coque R, Dever L, Filly A, Mamou A (1983) Paléohydrologie isotopique de l’wadi el Akarit (Sud Tunsien) au Pléistocène Supérieur et à l’Holocène [Isotopic Paleohydrology of Wadi el Akarit (Southern Tunsien) during the Late Pleistocene and Holocene]. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 43:41–61
Ford DC, Williams PW (1989) Karst geomorphology and hydrology. Unwin Hyman, London, p 601
Freeze RA, Cherry JA (1979) Groundwater. Prentice-Hall, Englewoods Cliff, NJ
Fretwell BA, Burgess WG, Barker JA, Jefferies NL (2005) Redistribution of contaminants by a fluctuating water table in a micro-porous, double porosity aquifer: field observations and model simulations. J Contam Hydrol 78(1–2):27–52
Gat I, Gonfiantini R (1981) Stable isotope hydrology: deuterium and oxygen-l8 in the water cycle. Int. Atom. Energy Agency, Vienna, Tech. Rep. Ser. 210, 1-339
Gonfiantini R, Conrad G, Fontes J.C, Sauzy G, Payne B.R (1974) Etude isotopique de la nappe du Continental Intercalaire et ses relations avec les autres nappes du Sahara Septentrional [Isotopic study of the Continental Intercalaire aquifer and its relations with the other aquifers of the Septentrional Sahara]. In: Isotope techniques in groundwater hydrology, vol I. IAEASM-182/25, IAEA, Vienna, pp 227-241
Guendouz A, Moulla AS (1996) Drainance de la nappe profonde du Continental Intercalaire vers les aquifères superficiels à Ourgala: arguments isotopiques. Colloque International sur l’utilisation des techniques isotopiques dans les domaines des ressources en eau et en sol, Mahdia (Tunisie)
Guendouz A, Moulla AS, Edmunds W, Shand P, Poole J, Zouari K, Mamou A (1997) Paleoclimatic information contained in groundwater of the Grand Erg Oriental. N. Africa. Proceeding symposium. IAEA, Vienna, p 349
Guendouz A, Moulla AS, Remini B, Michelot JL (2003) Hydrochemical and isotopic behaviour of a Saharan phreatic aquifer suffering severe natural and anthropic constraints (case of Oued-Souf region, Algeria). J Hydrol 14:955–968
Hamed Y (2004) Caractérisation hydrogéologique, hydrochimique et isotopique des eaux souterraines de la région du Kef (Nord Ouest Tunisien). Mémoire DEA. Faculté de Sciences de Sfax, 180p.
Hamed Y (2009a) Caractérisation hydrogéologique, hydrochimique et isotopique du système aquifère de Moularés-Tamerza. Ph.D. thesis, University of Sfax, pp 280
Hamed Y (2012) Monthly isotopes (δ18O and δD) variations of meteoric waters in El Kef region, Northwestern Tunisia: implications for changes of moisture sources. International colloque Annaba 20-22 Nov, 2012-Algeria
Hamed Y, Dassi L, Ahmadi R, Ben Dhia H (2008) Geochemical and isotopic study of the multilayer aquifer system in the Moulares-Redayef basin, southern Tunisia. Hydrological Sciences–Journal-des Sciences Hydrologiques 53(6):1241–1252
Hamed Y, Hadji R, Ben Dhia H, Ali W (2012a) Groundwater evolution in the Continental Intercalaire aquifer of southern Tunisia and a part of Algeria: hydrochemical and isotopic indicators. International colloque-Watmed6, 10-12 October. Sousse-Tunisia
Hamed Y, Mokadem N, Ben Dhia H (2012b) Hydrochemical changes induced by overexploitation of groundwater in North Africa: a case study of south Gafsa basin (SW Tunisia). International colloque- Annaba 20-22 Nov, 2012-Algeria
Hamed Y, Awad S, Ben Sâad A (2013a) Nitrate contamination in groundwater in the Sidi Aïch-Gafsa Oases region, Southern Tunisia. J Environ Earth Sci. doi:10.1007/s12665-013-2445-5
Hamed Y, Ahmadi R, Hadji R, Mokadem N, Ben Dhia H, Ali W (2013b) Groundwater evolution in the Continental Intercalaire aquifer of southern Tunisia and a part of Algeria: hydrochemical and isotopic indicators. Desalin Water Treat. doi:10.1080/19443994.2013.806221
Hamed Y, Abdeslam D, Al-Gamal S.A, Bouri S, Ben Dhia H (2013c) Groundwater recharge areas of the Continental Intercalaire aquifer-hydrogeochemical and environmental isotopes: case of Southern Tunisia and Algeria. The 3rd International colloque-Tebessa, 20-21 Novmber. Tebessa-Algeria
Hem J.D (1989) The study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water. 3rd edn. USGS Water-Supply Paper 2254, US Geological Survey
Hess JW, White WB (1988) Storm response of the karstic carbonate aquifer of south central Kentucky. J Hydrol 99:235–252
Inoubli A (2014) Hydrogeological and geochemistry studies of the aquifers of Sra Ouertane basin (NW Tunisia). Master. Sciences Faculty of Bizerte. p140
International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) (1981) Statistical treatment of environmental isotope data in precipitation, IAEA Technical Report Series No. 206, IAEA, Vienna
Jallouli C, Mickus K (2000) Regional gravity analysis of the crustal structure of Tunisia. J Afr Earth Sci 30:63–78
Jedoui Y, Kallel K, Labeyrie L, Reyss J.L, Montacer M, Michel Fontugne M (2001) Variabilité climatique rapide lors du dernier Interglaciaire (stade isotopique marin 5e), enregistrée dans les sédiments littoraux du Sud-Est tunisien. Abrupt climatic variability of the Last Interglacial (marine isotopic 5e substage) recorded in the coastal sediments of southeastern Tunisia. Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences - Series IIA - Earth and Planetary Science. Volume 333, Issue 11, 15 December 2001, Pages 733-740
Kallel N, Duplessy JC, Labeyrie L, Fontugne M, Paterne M, Montacer M (2000) Mediterranean pluvial periods and sapropel formation during the last 200 000 years. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 157:45–58
Kamel S, Younes H, Chkir N, Zouari K (2008) The hydrogeochemical characterization of ground waters in Tunisian Chott’s region. Environ Geol 54:843–854
Kirchner J.O.G (1994) Investigation into the contribution of ground water to the salt load of the Breede River, using natural isotopes and chemical tracers. Report No. 344/1/95. Water Research Commission, Pretoria
Mahler B.J, Garner B.D, Musgrove M, Guilfoyle A, Rao M (2006) Recent (2003-05) water quality of Barton Springs, Austin, Texas, with emphasis on factors affecting variability. U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2006-5299. p. 83
Mamou A (1990) Caractéristiques, evaluation, gestion des ressources en eau du Sud Tunisien [Characterisation, evaluation and management of the water resources of southern Tunisia]. Ph.D. thesis, University of Paris South, France
McMahon P (2001) Aquifer/aquitard interfaces: mixing zones that enhance biogeochemical reactions. Hydrogeol J 9(1):34–43
Mokadem N (2012) Hydrogeochemical and isotope evidence of groundwater evolution in El Guettar oasis area, Southwest Tunisia. pp. 180-Master. Faculty of Sciences of Sfax-Tunisia
Mokadem N, Hamed Y, Ben Sâad A, Gargouri I (2013) Atmospheric pollution in North Africa (ecosystems-atmosphere interactions): a case study in the mining basin of El Guettar-M’Dilla (southwestern Tunisia). Arab J Geosci. doi:10.1007/s12517-013-0852-2
Mook WG, De Vries JJ (2000) Environmental isotopes in the hydrological cycle: principles and applications. IHP-V no. 39, UNESCO, Paris
Ophori DU, Toth J (1988) Patterns of groundwater chemistry, Ross Creek Basin, Alberta, Canada. Groundw 27(1):20–55
Outtani F, Addoum B, Mercier E, de Lamotte DF, Andrieux J (1995) Geometry and kinematics of the South Atlas Front, Algeria and Tunisia. Tectonophysics 249:233–248
Piper AM (1944) A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses. Trans. Am Geophys Union 25:914–923
Post V (2003) Groundwater salinization processes in the coastal area of the Netherlands due to transgressions during the Holocene. PhD Thesis, Free Univ., The Netherlands
Rightmire CT (1978) Seasonal variation in pCO2 and 13C content of soil atmosphere. Water Resour Res 14:691
Rindsberger M, Magaritz M, Carmi I, Gilad D (1983) The relation between air mass trajectories and the water isotope composition in the Mediterranean Sea area. Geophys Rev Lett 10:43–46
Ronen D, Magaritz M, Gvirtzman H, Garner W (1987) Microscale chemical heterogeneity in groundwater. J Hydrol 92(1–2):173–178
Rouabhia A, Baali F, Kherici N, Djabri L (2004) Vulnérabilité et risque de pollution des eaux souterraines de la nappe des sables miocènes de la plaine d’El MA EL Abiod (Algérie), Revue Sécheresse Vol.15, n°4
Rouabhia A, Baali F, Fehdi Ch, Kherici N, Djabri L (2008a) Hydrochemical and isotopic investigation of a sandstone aquifer groundwater in a semi arid region, El Ma El Abiod, Algeria. Journal of environmental geology (Springer) Environ Geol. n°254. doi 10.1007/s00254-008-1451-5
Rozanski K, Araguàs L, Gonfiantini R (1993) Isotopic patterns in modern global precipitation. In: Continental isotope indicators of climate. American Geophysical Union (monograph)
Sanford WE (1997) Correcting for diffusion in carbon-14 dating of ground water. Ground Water 35:357–361
Talma AS (1981) Chemical changes in groundwater and their reaction rates. Trans Geol Soc S A 84:99–105
Tarki M, Dassi L, Hamed Y, Jedoui Y (2010) Geochemical and isotopic composition of groundwater in the Complex Terminal aquifer in southwestern Tunisia, with emphasis on the mixing by vertical leakage. Environ Earth Sci. doi:10.1007/s12665-010-0820-z
Trabelsi R (2009) Caractérisation hydrogéologique et géochimique du système aquifère de la Djeffara (SE Tunisien): Modélisation et intrusion marine. Thèse de Doctorat, Ecole Nationale d’Ingénieurs de Sfax, Tunisie
Van der Weijden CH, Pacheco FAL (2003) Hydrochemistry, weathering and weathering rates on Madeira Island. J Hydrol 283:122–145
WHO (2006) World Health Organization. Guidelines for drinking water quality, 3rd edn, incorporating first addendum. Available at http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/dwq/gdwq3rev/ en/index.html.
Yermani M, Chkir N, Zouari K, Michelot J.L, Moumni L (2002) Environmental tracers as indicators of water fluxes through the unsaturated zone in semiarid regions: the case of Gafsa Plain (southern Tunisia). J Environ Hydrol 17, paper 31
Zouari K, Mamou A (1997) Les systèmes aquifères du Sud tunisien: Caractéristiques hydrochimiques et isotopiques, conditions de recharge et optimisation de la gestion. Actes du congrès International, Marrakech, pp 41–44
Zouari K, Chkir N, Ouda B (2003) Palaeoclimatic variation in Meknassi basin (central Tunisia) during Holocene period using multidisciplinary approaches. International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, pp 80–128
Zouari K, Trabelsi R, Abid K (2005) Chemical and isotopic composition of rain water of the Station of Sfax, Tunisia. Workshop on Chemical and isotopic composition of rain water of some Arab countries, Beruit, Lebanon, 25-26 December
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our appreciation to Abdullah M. Al-Amri, the Editor-in-Chief of the journal, and three anonymous reviewers for their helpful and thoughtful review, their enthusiasm and support to this work. The authors gratefully acknowledge the contributions of the staff members of Setif (Algeria), Sfax and Gabes (Tunisia) universities for their help during field work. We also thank the staff at the Laboratory of Turin (Italy) and the Water, Energy and Environment Laboratory of the National Engineering School of Sfax (ENIS-Tunisia) for their help and assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Demdoum, A., Hamed, Y., Feki, M. et al. Multi-tracer investigation of groundwater in El Eulma Basin (northwestern Algeria), North Africa. Arab J Geosci 8, 3321–3333 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1377-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1377-z