Abstract
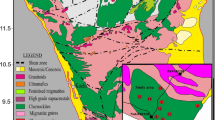
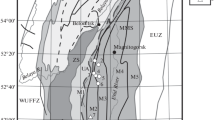
Seventy oriented basaltic samples were collected from six sites from the Wadi Budra and Farsh El Azraq areas of the west-central part of Sinai. Rock magnetic properties such as Curie temperatures and hysteresis parameters, as well as microscopic observations, point to magnetite as the main carrier of the remanent magnetization. The stress sensitivity of basaltic rocks is relatively low. High stress produces an increase in the remanent and induced magnetizations perpendicular to the applied stress axis and a decrease parallel to it. The change of magnetization during stress action ranges from 1.1% to 3.5% for a stress of 100 bar. The differential total magnetic intensity field with time (within 2 years) was observed through 80 magnetic observation points set up on both sites of the basaltic sheet at the studied area. The observed temporal variations of magnetization can be interpreted as stress loading parallel to the regional stress field in the order of 50 ± 20 bar, according to the stress sensitivity of the precursor basalt.
أحمد صالح
المعهد القومى للبحوث الفلكية و الجيوفيزيقية – حلوان – مصر. تم جمع سبعون عينة بازلت من ستة مواقع من وادى بودرا و فرش الأزرق فى الجزء الغربى من وسط سيناء . أثبتت دراسات الخواص المغناطيسية للصخورمثل درجة حرارة الكورى و منحنيات التخلف المغناطيسى بالأضافة الى الشواهد الميكروسكوبية ان معدن الماجنيتيت هو المعدن الرئيسى الحامل للمغناطيسية المتبقية . حساسية صخور البازلت للجهد المؤثر تكون منخفضة نسبيا . زيادة الجهد ينتج عنة زيادة فى قيمة المغناطيسية المتبقية و الحثية العمودية على محور الجهد المؤثر و نقصان فى قيمتها عندما تكون موازية لمحور الجهد المؤثر. تغير المغناطيسية أثناء زيادة الجهد يتراوح بين 1.1 الى 3.5 عندما يكون قيمة الجهد 100 بار . أختلاف شدة المجال المغناطيسى مع الوفت (خلال عامين) تم رصدة من خلال 80 محطة مغناطيسية تم وضعها على جانبى مكشف البازلت فى منطقة الدراسة. التغير الدورى الملاحظ للمغناطيسية قد فسر على انة ناتج عن جهد موازى لمجال الجهد الأقليمى و قيمتة 50 ± 20 بار بالنسبة الى حساسية جهد البازلت.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu El-Ata ASA (1988) The relation between the local tectonics of Egypt and the plate tectonics of the surrounding regions, using geophysical and geological data. Proceedings of 6th Annual Meeting of the. Egyptian Geophysical Society, pp 92–112
Ambraseys NN, Melville CP, Adam RD (1994) The seismicity of Egypt, Arabia and the Red Sea: a historical review. Cambridge University Press, UK
Badawy A (2001) The present-day stress field in Egypt. Annali di Geofisica 44(3):557–570
Ben-Menahem A, Nur A, Vered M (1976) Tectonics seismicity and structure of the Afro-Eurasian junction and the breaking of an incoherent plate. Phys Earth Planet Inter 12:1–50
Borradaile GJ (1992) Experimental deformation of two components IRM in magnetite bearing limestone: a model for the behaviour of NRM during n atural deformation. Phys Earth Planet Inter 70:64–77
Borradaile GJ (1994) Remagnetization of a rock analogue during experimental triaxial deformation. Phys Earth Planet Inter 83:147–163
Coleman RG, McGuire AV (1988) Magma systems related to the Red Sea opening. Tectonophysics 150:77–100
Day R, Fuller MD, Schmidt VA (1977) Hystersis properties of titanomagnetites. Grain size and compositional dependence. Earth Planet Inter 13:260–267
El-Fiky G (2005) GPS-derived velocity and crustal strain field in the Suez–Sinai area. Egypt Bull Earthq Res Inst Univ Tokyo 80:73–86
Eyal M, Eyal Y, Bartov Y, Steinitz G (1981) The tectonic development of the western margin of the Gulf of Aqaba rift. Tectonophysics 80:39–66
Hamano Y (1983) Experiments on the stress sensitivity of natural remanent magnetization. J Geomag Geoelectr 35:155–172
Hamano Y, Boyd R, Fuller M, Lanham M (1989) Induced susceptibility anisotropy of igneous rocks caused by uniaxial compression. J Geomag Geoelectr 41:203–220
Hurukawa N, Seto N, Inoue H, Nishigami K, Marzouk I, Megahed A, Ibrahim EM, Murakami H, Nakamura M, Haneda T, Sugiyama S, Ohkura T, Fujii Y, Hessain H, Ahmed AS, Mohammed H, Abdel-Fattah R, Mizoue M, Hashimoto S, Kobayasi M, Suetsugu D (2001) Seismological observations at the Gulf of Suez in Egypt. Bull Seism Soc Am 91(4):708–717
Jackson M, Borradaile G, Hudleston P, Banerjee S (1993) Experimental deformation of synthetic magnetite-bearing calcite sandstones: effects on remanence, bulk magnetic properties, and magnetic anisotropy. M Journal of Geophysical Research 98(1):383–401
Kebeasy RM (1990) Seismicity. In: Said R (ed) The geology of Egypt, chapter 5. A.A. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 51–59
Le Pichon X, Gaulier JM (1988) The rotation of Arabia and the Levant fault system. Tectonophysics 153:271–294
Mahmoud S (2003) Seismicity and GPS-derived crustal deformation in Egypt. Geodynamics 35:333–352
Maamoun M, Allam A, Megahed A (1984) Seismicity of Egypt. Bull HIAG 4:109–160
Meneisy MY (1986) Mesozoic igneous activity in Egypt. Qatar Univ Sci Bull 6:317–328
Meneisy MY (1990) Vulcanicity. In: Said R (ed) The geology of Egypt. A.A. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 157–172
Morgan P (1990) Egypt in framework of global tectonics. In: Said R (ed) The geology of Egypt. A.A. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 91–111
Mousa HE (1987) Geologic studies and genetic correlation of basaltic rocks in West Central Sinai. PhD thesis, Faculty of Science, Ain Shams University
Robion P, Borradaile GJ (2001) Stress remagnetization in pyrrhotite–calcite synthetic aggregates. Geophys J Int 144:96–104
Saleh A (2000) The effect of uniaxial compression on the behaviour of the remanent magnetization of the Mandisha basalt in the Bahariya Oasis, Egypt. E.G.S Proceedings of the 18th Annual Meeting, pp 139–152
Saleh A (2002) Stress dependence of magnetization and rock magnetism of the west central Sinai basalt, Egypt. Journal of the Faculty of Education 27:463–477
Steckler MS, Berthelot F, Lyberis N, Le Pichon X (1988) Subsidence in the Gulf of Suez: implications for rifting and plate kinematics. Tectonophysics 153:249–270
Acknowledgements
The author wishes to thank Axel Schult (Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences, Munich University, Munich, Germany) for his help and support. Laboratory measurements were carried out at the Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences, LMU University, Munich, Germany. The author is grateful to Daniel Miggins for helpful review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saleh, A. The effect of uniaxial compression in the behaviour of remanent and induced magnetizations for basaltic rocks from the western Sinai Peninsula, Egypt. Arab J Geosci 5, 1175–1184 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-010-0260-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-010-0260-9