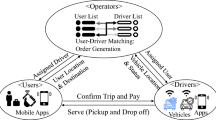
Abstract
In this paper, due to the inefficiency of implemented ride-sharing (RS) and demand responsive transport (DRT) systems in recent decades, these two systems are integrated in order to design a spatial system to manage numbers of single-passenger vehicles and, also, efficiently use public fleet capacity. In the designed system, after preparing and pre-processing on data, in the RS stage, the proposed system searches for fellow travellers for private vehicle users with priority given firstly to the applicants owning a private vehicle. And then, in the DRT stage, the remaining applicants are formed into DRT fellow traveller groups in which each DRT fellow traveller group is assigned an appropriate public vehicle and a parking lot. The proposed system is implemented based on real commuting trips taken in Tehran. The effectiveness of the system is mainly evaluated by comparing the decrease of mileage, gas consumption, and total travel time per vehicle.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amey AM, Attanucci J, Mishalani R (2011) Real-time ridesharing: opportunities and challenges in using mobile phone technology to improve rideshare services. Transp Res Rec: J Transp Res Board 2217:103–110
Bruni ME, Guerriero F, Beraldi P (2014) Designing robust routes for demand-responsive transport systems. Transp Res Part E: Logist Transp Rev 70:1–16
Chan Nelson, Shaheen Susan (2012) Ride Sharing in North America: past, present and future. Transp Rev 32(1):93–112. doi:10.1080/01441647.2011.621557
Chaube V, Kavanaugh AL, Pérez-Quinones MA (2010) Leveraging social networks to embed trust in rideshare programs. In: Proceedings of the Hawaii international conference on system sciences (HICSS), pp 1–8
Diana M, Quadrifoglio L, Pronello C (2009) A methodology for comparing distances traveled by performance-equivalent fixed-route and demand responsive transit services. Transp Plan Technol 32(4):377–399. doi:10.1080/03081060903119618
Edwards D, Watkins K (2013) Comparing fixed-route and demand-responsive feeder transit systems in real-world settings. Transp Res Rec 2352:128–135. doi:10.3141/2352-15
Faroqi H, Niaraki AS (2015) Multi-objective optimization based collision avoidance algorithm for an intelligence marine navigation. J Appl Sci 15:911–916
Faroqi H, Saadi Mesgari M (2016) Performance comparison between the multi-colony and multi-pheromone ACO algorithms for solving the multi-objective routing problem in a public transportation network. J Navig 69(01):197–210
Furuhata M, Dessouky M, Ordonez F, Brunet ME, Wang X, Koenig S (2013) Ridesharing: the state-of-the-art and future directions. Transp Res Part B: Methodol 57:28–46
Ghoseiri K, Haghani A, Hamedi M (2011) Real-time rideshare matching problem. Mid-Atlantic Universities Transportation Center, Berkeley
Ichoua S, Gendreau M, Potvin JY (2006) Exploiting knowledge about future demands for real-time vehicle dispatching. Transp Sci 40(2):211–225
Jacobson S, King D (2009) Fuel saving and ridesharing in the US: motivations, limitations, and opportunities. Transp Res Part D: Transp Environ 14(1):14–21. doi:10.1016/j.trd.2008.10.001
Kawasaki S, Higuchi M, Gamba J, Murakami H (2009) On modeling ubiquitous cloud: estimation of traffic. WSEAS Trans Math 8(9):530–540
Kelly K (2007) Casual carpooling-enhanced. J Public Transp 10(4):6, 119–130. doi:10.5038/2375-0901.10.4.6
Kowshik RR, Reddy PD, Gard J, Jovanis PP, Kitamura R (1994) Real-time rideshare matching using GIS. In: Proceedings of the IVHS America, vol 1(9), p 1
Kritikou Y, Dimitrakopoulos G, Dimitrellou E, Demestichas P (2009) A management scheme for improving transportation efficiency and contributing to the enhancement of the social fabric. Telem Inform 26(4):375–390. doi:10.1016/j.tele.2008.10.002
Laws R, Enoch MP, Ison SG, Potter S (2009) Demand responsive transport: a review of schemes in England and Wales. J Public Transp 12(1):19–37. doi:10.5038/2375-0901.12.1.2
Li X, Quadrifoglio L (2011) Vehicle optimal zone design for feeder transit services. Public Transp 3(1):89–104. doi:10.1007/s12469-011-0040-2
McCormack E, Nyerges T (1998) What transportation modeling needs from a GIS: a conceptual framework. Transp Plan Technol 21(1–2):5–23. doi:10.1080/03081069708717599
Miller HJ, Shaw SL (2001) Geographic information systems for transportation: principles and applications. Oxford University Press on Demand, Oxford
Seyedabrishami S, Hasanpour S (2012) Impact of carpooling on fuel saving in urban transportation: case study of Tehran. Proc-Soc Behav Sci 54:323–331
Steger C (2005) Improving modal choice and transport efficiency with the virtual ridesharing agency. In: Intelligent transportation systems, 2005. Proceedings. 2005 IEEE. IEEE, pp 994–999
TCTTS (2011) Tehran transportation and traffic. Tehran Comprehensive Transportation & Traffic Studies Co. 17-20
Thill JC (ed) (2000) Geographic information systems in transportation research. Pergamon, Oxford
Tjokroamidjojo D, Kutanoglu E, Taylor GD (2006) Quantifying the value of advance load information in truckload trucking. Transp Res Part E: Logist Transp Rev 42(4):340–357
White P (2008) Public transport: its planning, management and operation. Routledge, London
Wong KI, Han AF, Yuen CW (2014) On dynamic demand responsive transport services with degree of dynamism. Transportmetrica A: Transp Sci 10(1):55–73
Yoo J-B, Hong B-K (2008) Intelligent traffic control system based on ubiquitous technology. In: INFOS2008, 27–29 March 2008, Cairo-Egypt, pp 78–83
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by an Inha University research grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Faroqi, H., Sadeghi-Niaraki, A. GIS-based ride-sharing and DRT in Tehran city. Public Transp 8, 243–260 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12469-016-0130-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12469-016-0130-2