Abstract
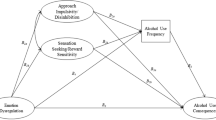
An increasing percentage of college students report being affected by ADHD behaviors, and this population is at increased risk of experiencing negative consequences associated with alcohol consumption. However, specific factors motivating alcohol consumption and contributing to negative outcomes among these individuals are not well understood. Recent work suggests alcohol expectancies may interact with ADHD behaviors to influence negative drinking-related outcomes among those with elevated inattention and/or hyperactivity-impulsivity. Seven-hundred-forty emerging adults (M age = 19.13 [SD = 2.25] years; 72.1% female; 85.8% Caucasian) enrolled in two public universities in the Southeast and Midwest USA completed the Brief Comprehensive Effects of Alcohol Survey (B-CEOA) and provided self-reports of ADHD symptoms and drinking-related outcomes. Multiple mediation analyses were conducted to evaluate effects of ADHD behaviors (i.e., hyperactivity-impulsivity, and inattention) and related impairment in major life domains (e.g., social interactions, occupational and educational activities, fulfillment of daily responsibilities) on drinking-related outcomes via positive and negative alcohol expectancies, controlling for sex, age, co-occurring oppositional behaviors, and data collection site. Inattention, hyperactivity-impulsivity, and impairment directly predicted both personal and social problems consequent to alcohol use. Effects of ADHD behaviors and impairment on drinking-related personal and social problems were partially mediated by positive expectancies. Findings are consistent with and extend prior work supporting a role of positive alcohol expectancies in alcohol-related negative outcomes among college students experiencing mild to moderate symptoms of ADHD.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association (2013) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 5th edn. American Psychiatric Association, Washington
Baer J, Stacy A, Larimer M (1991) Biases in the perception of drinking norms among college students. J Stud Alcohol 52:580–586
Baker L, Prevatt F, Proctor B (2012) Drug and alcohol use in college students with and without ADHD. J Atten Disord 16:255–263
Barkley R (1997) Behavioral inhibition, sustained attention, and executive functions: constructing a unifying theory of ADHD. Psychol Bull 121:65–94
Barkley R, Murphy K (2006) Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: a clinical workbook, 3rd edn. Guilford Press, New York
Biederman J, Monuteaux M, Mick E, Spencer T, Wilens T, Klein K, Faraone S (2006) Psychopathology in females with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a controlled, five-year prospective study. Biol Psychiatry 60:1098–1105
Bitsakou P, Psychogiou L, Thompson M, Sonuga-Barke EJS (2009) Delay aversion in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: an empirical investigation of the broader phenotype. Neuropsychologia 47:446–456. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2008.09.015
Castellanos F, Sonuga-Barke Eo, Milham M, Tannock R (2006) Characterizing cognition in ADHD: beyond executive dysfunction. Trends Cogn Sci 10:117–123
Collins L, Graham J, Flaherty B (1998) An alternative framework for defining mediation. Multivar Behav Res 33:295–312
Corbin W, Iwamoto D, Fromme K (2011) A comprehensive longitudinal test of the acquired preparedness model for alcohol use and related problems. J Stud Alcohol Drugs 72:602–610
Dattilo L, Murphy K, Van Eck K, Flory K (2013) Do ADHD symptoms moderate the relation between positive alcohol expectancies and alcohol-related outcomes? Atten Deficit Hyperact Disord ADHD 5:93–104
Dawson D, Grant B, Stinson F, Chou P (2004) Another look at heavy episodic drinking and alcohol use disorders among college and noncollege youth. J Stud Alcohol 65:477–488
DuPaul G, Weyandt L, O’Dell S, Varejo M (2009) College students with ADHD: current status and future directions. J Atten Disord 13:234–250
Fritz MS, MacKinnon DP (2007) Required sample size to detect the mediated effect. Psychol Sci 18:233–239
Fromme K, Stroot E, Kaplan D (1993) Comprehensive effects of alcohol: development and psychometric assessment of a new expectancy questionnaire. Psychol Assess 5:19–26
Gershon J (2002) A meta-analytic review of gender differences in ADHD. J Atten Disord 5:143–154
Ham L, Hope D (2003) College students and problematic drinking: a review of the literature. Clin Psychol Rev 23:719–759
Ham L, Stewart S, Norton P, Hope D (2005) Psychometric assessment of the comprehensive effects of alcohol questionnaire: comparing a brief version to the original full scale. J Psychopathol Behav Assess 27:141–158
Hartung C, Lefler E, Canu W, Stevens A, Jaconis M, LaCount P, Shelton C, Leopold D, & Willcutt E (2016) DSM-5 and other symptom thresholds for ADHD: Which is the best predictor of impairment in college students?. J Atten Disord. doi:10.1177/1087054716629216
Jones B, Corbin W, Fromme K (2001) A review of expectancy theory and alcohol consumption. Addictions 96:57–72
Katz N, Petscher Y, Welles T (2009) Diagnosing attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in college students: an investigation of the impact of informant ratings on diagnosis and subjective impairment. J Atten Disord 13:277–283
Kilbey M, Downey K, Breslau N (1998) Predicting the emergence and persistence of alcohol dependence in young adults: the role of expectancy and other risk factors. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 6:149–156
Knight J, Weschler H, Kuo M, Seibring M, Weitzman E, Shuckit M (2002) Alcohol abuse and dependence among U.S. college students. J Stud Alcohol 63:263–270
Kolla N, van der Maas M, Toplak M, Erickson P, Mann R, Seeley J, Vingilis E (2016) Adult attention deficit hyperactivity disorder symptom profiles and concurrent problems with alcohol and cannabis: sex differences in a representative, population survey. BMC Psychiatry 16:50–58
Lau-Barraco C, Braitman AL, Leonard KE, Padilla M (2012) Drinking buddies and their prospective influence on alcohol outcomes: alcohol expectancies as a mediator. Psychol Addict Behav 26:747–758
Lee S, Humphreys K (2014) Interactive association of dopamine receptor (DRD4) genotype and ADHD on alcohol expectancies in children. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 22:100–109
Lee S, Humphreys K, Flory K, Liu R, Glass K (2011) Prospective association of childhood attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and substance use and abuse/dependence: a meta-analytic review. Clin Psychol Rev 31:328–341
Maddock J, LaForge R, Rossi J, O’Hare T (2001) The college alcohol problems scale. Addict Behav 26:385–398
Marcus D, Barry T (2011) Does attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder have a dimensional latent structure? a taxometric analysis. J Abnorm Psychol 120:427–442
Martel M, von Eye A, Nigg J (2010) Revising the latent structure of ADHD: is there a ‘g’ factor? J Child Psychol Psychiatry 51:905–914
Mesman G (2015) The relation between ADHD symptoms and alcohol use in college students. J Atten Disord 19:694–702
Miller W, Marlatt G (1987) The brief drinker profile. Psychological Assessment Resources, Odessa
Murphy P, Schachar R (2000) Use of self-ratings in the assessment of symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in adults. Am J Psychiatry 157:1156–1159
Muthén L, Muthén B (1998–2012). Mplus user’s guide. 7th edn. Muthén & Muthén, Los Angeles
Nehlin C, Nyberg F, Öster C (2015) The patient’s perspective on the link between ADHD and substance use: a qualitative interview study. J Atten Disord 19:343–350
Nolen-Hoeksema S (2004) Gender differences in risk factors and consequences for alcohol use and problems. Clin Psychol Rev 24:981–1010
Pabst A, Kraus L, Piontek D, Mueller S, Demmel R (2013) Direct and indirect effects of alcohol expectancies on alcohol-related problems. Psychol Addict Behav 28:20–30
Pederson S, Harty S, Pelham W, Gnagy E, Molina B (2014) Differential associations between alcohol expectancies and adolescent alcohol use as a function of childhood ADHD. J Stud Alcohol Drugs 75:145–152
Preacher K, Hayes A (2008) Asymptotic and resampling strategies for assessing and comparing indirect effects in multiple mediator models. Behav Res Methods 40:879–891
Rodriguez C, Span S (2008) ADHD symptoms, anticipated hangover symptoms, and drinking habits in female college students. Addict Behav 33:1031–1038
Rooney M, Chronis-Tuscano A, Yoon Y (2012) Substance use in college students with ADHD. J Atten Disord 16:221–234
Scott-Sheldon L, Terry D, Carey K, Garey L, Carey M (2012) Efficacy of expectancy challenge interventions to reduce college student drinking: a meta-analytic review. Psychol Addict Behav 26:393–405
Shiels K, Hawk L (2010) Self-regulation in ADHD: the role of error processing. Clin Psychol Rev 30:951–961
Sonuga-Barke E (2005) Causal models of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: from common simple deficits to multiple developmental pathways. Biol Psychiat 57:1231–1238
Squeglia L, Brammer W, Ray L, Lee S (2016) Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) symptoms predict alcohol expectancy development. J Child Adolesc Subst Abus 25:169–179
Weafer J, Fillmore M, Milich M (2011) Increased sensitivity to the disinhibiting effects of alcohol in adults with ADHD. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 17:113–121
Weyandt L, DuPaul G (2008) ADHD in college students: developmental findings. Dev Disabil 14:311–319
Zamboanga B (2006) From the eyes of the beholder: alcohol expectancies and valuations as predictors of hazardous drinking behaviors among female college students. Am J Drug Alcohol Abus 32:599–605
Zamboanga BL, Bean JL, Pietras AC, Pabόn LC (2005) Subjective evaluations of alcohol expectancies and their relevance to drinking game involvement in female college students. J Adolesc Health 37:77–80
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Molly Nikolas has received research grants from Shire Pharmaceutical. Alexis Elmore and Will Canu declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standard
All study procedures were conducted in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elmore, A., Nikolas, M. & Canu, W. Positive alcohol expectancies mediate associations between ADHD behaviors and alcohol-related problems among college students. ADHD Atten Def Hyp Disord 10, 65–75 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12402-017-0231-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12402-017-0231-z