Abstract
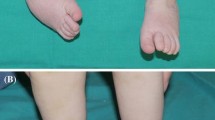
An Italian team of orthopaedic surgeons joined Eritrean colleagues to perform a clinical study in ambulating children affected by neglected idiopathic congenital talipes equinovarus (clubfoot). This study reports the surgical strategy as well as clinical outcomes, early complications and relapse at a mid-term follow-up. Four expeditions of 7 days were organized between 2012 and 2015 from Italy to the Halibet Hospital of Asmara in Eritrea. In each expedition were included two experienced surgeons, two assistants and one anaesthesiologist. During these expeditions, a total of 468 patients were evaluated together with Eritrean colleagues and 45 cases of neglected talipes equinovarus in ambulating children were diagnosed and selected for surgery. Follow-up range was 1–3 years. During the four expeditions, the Eritrean team of orthopaedic surgeons learned to manage most cases of neglected talipes equinovarus. No major complications were reported. Sixteen feet were considered excellent, 25 good and four poor. No overcorrections were observed. Neglected congenital talipes equinovarus is the result of delayed treatment of congenital deformity in developing countries, and its treatment often requires extensive surgery. Collaboration with foreign expert surgeons may help local doctors to learn how to treat this disease. The current study demonstrates that surgical expeditions in developing countries, when organized in collaboration with local doctors, help to manage on site this severe deformity.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ponseti IV, Smoley EN (1963) Congenital clubfoot: the results of treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am 45:261–344
Masse P (1977) Le traitement du pied bot par la methode ‘‘fonctionelle’’. Cahier d’enseignement de la SOFCOT, vol 3. Expansion Scientifique, Paris, France, pp 51–56
Morcuende JA, Abbasi D, Dolan LA, Ponseti IV (2005) Results of an accelerated Ponseti protocol for clubfoot. J Pediatr Orthop 25:623–626
Colburn M, Williams M (2003) Evaluation of the treatment of idiopathic clubfoot by using the Ponseti method. J Foot Ankle Surg 42:259–267
Gupta A, Singh S, Patel P, Patel J, Varshney MK (2008) Evaluation of the utility of the Ponseti method of correction of clubfoot deformity in a developing nation. Int Orthop 32:75–79
Jowett CR, Morcuende JA, Ramachandran M (2011) Management of congenital talipes equinovarus using the Ponseti method: a systematic review. J Bone Joint Surg Br 93:1160–1164
Changulani M, Garg NK, Rajagopal TS, Bass A, Nayagam SN, Sampath J, Bruce CE (2006) Treatment of idiopathic clubfoot using the Ponseti method. Initial experience. J Bone Joint Surg Br 88:1385–1387
Herold HV, Torok G (1973) Surgical correction of neglected clubfoot in the older child and adult. J Bone Joint Surg Am 55:1385–1395
Loza ME, Bishay SN, El-Barbary HM, Hanna AA, Tarraf YN, Lotfy AA (2010) Double column osteotomy for correction of residual adduction deformity in idiopathic clubfoot. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 92:673–679
Turco VJ (1971) Surgical correction of the resistant club foot. One-stage posteromedial release with internal fixation: a preliminary report. J Bone Joint Surg Am 53:477–497
Turco VJ (1979) Resistant congenital club foot one-stage posteromedial release with internal fixation. A follow-up report of a fifteen-year experience. J Bone Joint Surg Am 61:805–814
Mahadev A, Munajat I, Mansor A, Hui JH (2009) Combined lateral and transcuneiform without medial osteotomy for residual clubfoot for children. Clin Orthop Relat Res 467:1319–1325
Hassan FO, Jabaiti S, El Tamini T (2010) Complete subtalar release for older children who had recurrent clubfoot deformity. Foot Ankle Surg 16:38–44
Codivilla A (1905) On the means of lengthening, in the lower limbs, the muscles and tissues which are shortened through deformity. Am J Orthop Surg 22:353–369
Kuo KN, Smith PA (2009) Correcting residual deformity following clubfoot releases. Clin Orthop Relat Res 467:1326–1333
Thompson G, Hoyen H, Barthel T (2009) Tibialis anterior tendon transfer after clubfoot surgery. Clin Orthop Relat Res 467:1306–1313
Elgeidi A, Abulsaad M (2014) Combined double tarsal wedge osteotomy and transcuneiform osteotomy for correction of resistant clubfoot deformity (the “bean-shaped” foot). J Child Orthop 8:399–404
Holt JB, Oji DE, Yack HJ, Morcuende JA (2015) Long-term results of tibialis anterior tendon transfer for relapsed idiopathic clubfoot treated with the Ponseti method: a follow-up of thirty-seven to fifty-five years. J Bone Joint Surg Am 97:47–55
Faldini C, Traina F, Di Martino A, Nanni M, Acri F (2013) Can selective soft tissue release and cuboid osteotomy correct neglected clubfoot? Clin Orthop Relat Res 471:2658–2665
Dietz F (2002) The genetics of idiopathic clubfoot. Clin Orthop Relat Res 401:39–48
Owen RM, Kembhavi G (2012) A critical review of interventions for clubfoot in low and middle-income countries: effectiveness and contextual influences. J Pediatr Orthop B 21:59–67
Laaveg SJ, Ponseti IV (1980) Long-term results of treatment of congenital club foot. J Bone Joint Surg Am 62:23–31
Ippolito E, Farsetti P, Caterini R, Tudisco C (2003) Long-term comparative results in patients with congenital clubfoot treated with two different protocols. J Bone Joint Surg Am 85:1286–1294
Zhao D, Li H, Zhao L, Liu J, Wu Z, Jin F (2014) Results of clubfoot management using the Ponseti method: do the details matter? A systematic review. Clin Orthop Relat Res 472:1329–1336
Siapkara A, Duncan R (2007) Congenital talipes equinovarus: a review of current management. J Bone Joint Surg Br 89:995–1000
Uglow MG, Kurup HV (2010) Residual clubfoot in children. Foot Ankle Clin 15:245–264
Mehrafshan M, Rampal V, Seringe R, Wilcart P (2009) Recurrent clubfoot deformity following previous soft-tissue release: mid-term outcome after revision surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Br 91:949–954
Hallaj-Moghadam M, Moradi A, Ebrahimzadeh MH (2015) Clinical outcome of posteromedial versus posteromedial-lateral release for clubfoot. J Pediatr Orthop B 24:24–27
Radler C (2013) The Ponseti method for the treatment of congenital club foot: review of the current literature and treatment recommendations. Int Orthop 37:1747–1753
Verma A, Mehtani A, Sural S, Maini L, Gautam VK, Basran SS, Arora S (2012) Management of idiopathic clubfoot in toddlers by Ponseti’s method. J Pediatr Orthop B 21:79–84
Lourenco AF, Morcuende JA (2007) Correction of neglected idiopathic club foot by the Ponseti method. J Bone Joint Surg Br 89:378–381
Garg S, Dobbs MB (2008) Use of the Ponseti method for recurrent clubfoot following posteromedial release. Indian J Orthop 42:68–72
Dobbs MB, Gurnett CA (2009) Update on clubfoot: etiology and treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res 467:1146–1153
Bor N, Herzenberg JE, Frick S (2006) Ponseti management of clubfoot in older infants. Clin Orthop Relat Res 444:224–228
Cosma DI, Vasilescu DE (2014) Ponseti treatment for clubfoot in Romania: a 9-year single-centre experience. J Pediatr Orthop B 23:512–516
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to thank Dr. Franco Riboldi for having carried on this project and Prof. Alessandro Faldini for his invaluable teaching.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Faldini, C., Prosperi, L., Traina, F. et al. Surgical treatment of neglected congenital idiopathic talipes equinovarus after walking age in Eritrea: an Italo-Eritrean cooperation. Musculoskelet Surg 100, 133–137 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12306-016-0398-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12306-016-0398-z