Abstract
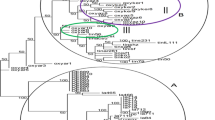
Safflower (Carthamus tinctorious L.) is valued as a source of high quality vegetable oil. 20 ISSR primers were used to assess the genetic diversity of 18 accessions of safflower collected from different geographical regions of Iran. The ISSR primers combinations revealed 57.6 % polymorphism, among 338 genetic loci amplified from the accessions. The sum of effective number of alleles and observed number of alleles were 29.76 and 36.77, respectively. To understand genetic relationships among these cultivars, Jacquards’ similarity coefficient and UPGMA clustering algorithm were applied to the ISSR marker data set. ISSR markers grouped accessions into two main clusters and four sub clusters. Also, the principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) supported the cluster analysis results. The results showed these genotypes have high genetic diversity, and can be used for alternative safflower breeding program.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amiri RM, Azdi SB, Ghanadha MR, Abd MC (2001) Detection of DNA polymorphism in landrace populations of safflower in Iran using RAPD-PCR technique. Iran J Agri Sci 32:737–745
Amsellem L, Noyer JL, Lebourgeois T, Hossaertmckey M (2000) Comparison of genetic diversity of the invasive weed Rubus alceifolius Poir. (Rosaceae) in its native range and in areas of introduction, using amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) markers. Mol Ecol 9:443–455
Arzani A, Rezaei AM (2011) Genetic variation in safflower (Carthamus tinctorious L.) for seed quality-related traits and Inter-Simple Sequence Repeat (ISSR) markers. Int J Mol Sci 12:2664–2677. doi:10.3390/ijms12042664
Ash GJ, Raman R, Crump NS (2003) An investigation of genetic variation in Carthamus lanatus in New South Wales, Australia, using intersimple sequence repeats(ISSR) analysis. Weed Res (Oxford) 43:208–213
Belaj A, Satovic Z, Cipriani G, Baldoni L, Testolin R, Rallo L, Trujillo I (2003) Comparative study of the discriminating capacity of RAPD, AFLP and SSR markers and of their effectiveness in establishing genetic relationships in olive. Theor Appl Genet 107:736–744
Blair MW, Panaud O, Mccouch SR (1999) Inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) amplification for analysis of microsatellite motif frequency and fingerprinting in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 98:780–792
Casaoli M, Mattion C, Cherubini M, Villani F (2001) A genetic linkage map of European chestnut (Castanea sativa Mill.) based on RAPD, ISSR and isozyme markers. Theor Appl Genet 102:1190–1199
Cekic C, Battey NH, Wilkinson MJ (2001) The potential of ISSR-PCR primer-pair combinations for genetic. Theor Appl Genet 103:540–546
Chapman MA, Burke JM (2007) DNA sequence diversity and the origin of cultivated safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.; Asteraceae). BMC Plant Biol. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-7-60
Godwin ID, Aitken EAB, Smith LW (1997) Application of inters simple sequence repeat (ISSR) markers to plant genetics. Electrophoresis 18:1524–1528
Guo ML, Jiang W, Zhang ZZ, Zhang G, Mao JF, Yin M, Su ZW (2003) Randomly amplified polymorphic DNA technique in molecular identification of germplasms of Carthamus tinctorius L. Acad J Sec Mil Med Univ 24(10):1116–1119 (In Chinese)
Hollngsworth PM, Tebbitt M, Watson KS, Gornall RJ (1998) Conservation genetics of an artic species, Saxifgra rivularis L. Bot J Linn Soc 128:1–14
Knowles PF (1969) Centers of plant diversity and conservation of crop germplasm: safflower. Econ Bot 23:324–329
Knowles PF, Ashri A (1995) Evolution of crop plants, 2nd edn. Longman, Harlow 31:47–50
Mary SS, Gopalan A (2006) Dissection of genetic attributes yield traits of fodder cowpea in F3 and F4. J Appl Sci Res 2(6):805–808
Mengoni A, Gor A, Bazzicalupo M (2000) Use of RAPD and microsatellite (SSR) variation to assess genetic relationships among populations of tetraploid alfalfa, Medicago sativa. Plant Breed 119:311–317
Mohammadi R, Pourdad SS (2009) Estimation, interrelationships and repeatability of genetic variability parameters in spring safflower using multi-environment trial data. Euphytica 165(3):313–324
Nagaoka T, Ogihara Y (1997) Applicability of inter-simple sequence repeat markers in wheat for use as DNA markers in comparison to RFLP and RAPD markers. Theor Appl Genet 94(5):597–602
Peakall R, Smouse PE (2007) GenAlEx V6.1: genetic analysis in excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Mol Ecol Notes 6:288–295
Potter D, Gao FY, Aliello G, Leslie C, McGranahan G (2002) Intersimple sequence repeat markers for fingerprinting and determining genetic relationships of walnut (Juglans regia) cultivars. Am Soc Horticult Sci 127(1):75–81
Rohlf FG (2000) NTsys-pc numerical taxonomy and multivariate system version 2.0. Appl Biostat. Inc, New York
Saghai-Maroof MA, Biyashev RM, Yang GP, Zhang Q, Allard RW (1984) Extraordarily polymorphic microsatellite DNA in barly: species diversity, chromosomal locations, and population dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci 91:5466–5470
Sehgal D, Rajpal VR, Raina SN, Sasanuma T, Sasakuma T (2009) Assaying polymorphism at DNA level for genetic diversity diagnostics of the safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) world germplasm resources. Genetics 135:457–470
Sneath PHA, Sokal RR (1973) Numerical Taxonomy: The principles and practice of. Numerical classification. San Francisco: Freeman 573:566–576
Tanyolac B (2003) Inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) and RAPD variation among wild barely (Hordeum vulgare subsp. spontaneum) populations from west Turkey. Genet Resour Crop Evol 50(6):611–614
Wang Z, Weber JL, Zhang G, Tanksley SD (1994) Survey of plant short tandem DNA repeats. Theor Appl Genet 88:1–6
Wu W, Zheng YL, Chen L, Wei YM, Yang RW, Yan ZH (2005) Evaluation of genetic relationships in the genus Houttuynia Thunb. in China based on RAPD and ISSR markers. Biochem Syst Ecol 33:1141–1157
Yang YX, Wu W, Zheng YL, Chen L, Liu RJ, Huang CY (2007) Genetic diversity and relationships among safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) analyzed by inter-simple sequence repeats (ISSRs). Genet Resour Crop Evol 54:1043–1051
Yeh FC, Yang RC, Boyle T (1999) POPGENE, the user-friendly shareware for population genetic analysis. Molecular biology and biotechnology center, University of Alberta, Canada
Zietkiewicz E, Rafalski A, Labuda D (1994) Genome fingerprinting by simple sequence repeat (SSR)-anchored polymerase chain reaction amplification. Genomics 20:176–183
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panahi, B., Ghorbanzadeh Neghab, M. Genetic characterization of Iranian safflower (Carthamus tinctorius) using inter simple sequence repeats (ISSR) markers. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 19, 239–243 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-012-0155-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-012-0155-1