Abstract
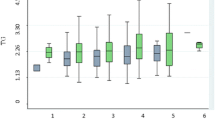
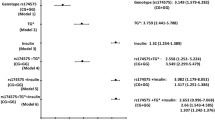
Elevated plasma triglyceride and non-esterified fatty acid concentrations may cause insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) is a rate-determining enzyme in lipid metabolism. A variant in the LPL gene has been identified which alters the penultimate amino acid Serine at 447 to a stop codon (S447X), and results in a truncated LPL molecule lacking the C-terminal dipeptide Ser–Gly. The present study was designed to evaluate the frequency of S447X variant in the LPL gene and its effect on the lipid and lipoprotein levels in type 2 diabetic subjects. The genotype frequency distributions of type 2 diabetes patients and controls were in Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium. Comparison of the genotype and allelic frequencies of S447X in subjects with type 2 diabetics compared to controls demonstrated no significant difference. In subjects with type 2 diabetics having hypertriglyceridemia (TG ≥ 150 mg/dl) compared to diabetics with TG level <150 mg/dl, significant difference in genotype frequency was found among these groups, while allelic frequency of X was significantly differed. Logistic regression analysis showed the negative association of LPL S447X variant with TG and VLDL cholesterol, while no association with total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol and LDL cholesterol was found. The lipid levels except for HDL cholesterol were found to be significantly lower in carriers for S447X than wild type in diabetes group. The decreased level of TG and TG rich lipoprotein in subjects with SNP S447X in LPL, predicts anti-atherogenic activity of carriers for S447X variant in general population as well as type 2 diabetic patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yusuf S, Hawken S, Ounpuu S, Dans T, Avezum A, Lanas F, et al. Effect of potentially modifiable risk factors associated with myocardial infarction in 52 countries (the INTERHEART study): case-control study. Lancet. 2004;364(9438):937–52.
Hokanson JE, Austin MA. Plasma triglyceride level is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease independent of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol level: a meta-analysis of population-based prospective studies. J Cardiovasc Risk. 1996;3(2):213–9.
Krauss RM. Atherogenicity of Triglyceride-Rich Lipoproteins. The American Journal of Cardiology 1998; 81 (4, Supplement 1):13B-17B.
Fortson MR, Freedman SN, Webster PD III. Clinical assessment of hyperlipidemic pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1995;90(12):2134–9.
Olivecrona G, Beisiegel U. Lipid binding of apolipoprotein CII is required for stimulation of lipoprotein lipase activity against apolipoprotein CII-deficient chylomicrons. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1997;17(8):1545–9.
Taskinen MR, Nikkila EA. High density lipoprotein subfractions in relation to lipoprotein lipase activity of tissues in man–evidence for reciprocal regulation of HDL2 and HDL3 levels by lipoprotein lipase. Clin Chim Acta. 1981;112(3):325–32.
Merkel M, Heeren J, Dudeck W, Rinninger F, Radner H, Breslow JL, et al. Inactive lipoprotein lipase (LPL) alone increases selective cholesterol ester uptake in vivo, whereas in the presence of active LPL it also increases triglyceride hydrolysis and whole particle lipoprotein uptake. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(9):7405–11.
Heeren J, Niemeier A, Merkel M, Beisiegel U. Endothelial-derived lipoprotein lipase is bound to postprandial triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and mediates their hepatic clearance in vivo. J Mol Med. 2002;80(9):576–84.
Wittrup HH, Tybjaerg-Hansen A, Nordestgaard BG. Lipoprotein lipase mutations, plasma lipids and lipoproteins, and risk of ischemic heart disease. A meta-analysis. Circulation. 1999;99(22):2901–7.
Kozaki K, Gotoda T, Kawamura M, Shimano H, Yazaki Y, Ouchi Y, et al. Mutational analysis of human lipoprotein lipase by carboxy-terminal truncation. J Lipid Res. 1993;34(10):1765–72.
Zhang H, Henderson H, Gagne SE, Clee SM, Miao L, Liu G, et al. Common sequence variants of lipoprotein lipase: standardized studies of in vitro expression and catalytic function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996;1302(2):159–66.
Franceschini G, Vecchio G, Gianfranceschi G, Magani D, Sirtori CR. Apolipoprotein AIMilano. Accelerated binding and dissociation from lipids of a human apolipoprotein variant. J Biol Chem. 1985;260(30):16321–5.
Margaglione M, Cappucci G, d’Addedda M, Colaizzo D, Giuliani N, Vecchione G, et al. PAI-1 plasma levels in a general population without clinical evidence of atherosclerosis: relation to environmental and genetic determinants. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1998;18(4):562–7.
Iacoviello L, Di Castelnuovo A, De Knijff P, D’Orazio A, Amore C, Arboretti R, et al. Polymorphisms in the coagulation factor VII gene and the risk of myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1998;338(2):79–85.
Allain CC, Poon LS, Chan CS, Richmond W, Fu PC. Enzymatic determination of total serum cholesterol. Clin Chem. 1974;20(4):470–5.
Bucolo G, David H. Quantitative determination of serum triglycerides by the use of enzymes. Clin Chem. 1973;19(5):476–82.
Warnick GR, Nauck M, Rifai N. Evolution of method for measurement of HDL cholesterol: from ultracentrifugation to homogenous assays. Clin Chem. 2001;47(9):1579–96.
Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem. 1972;18:499–502.
Miller SA, Dykes DD, Polesky HF. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988;16(3):1215.
Groenemeijer BE, Hallman MD, Reymer PWA, Gagné E, Kuivenhoven JA, Bruin T et al on behalf of the REGRESS Study Group. Genetic variant showing a positive interaction with β-blocking agents with a beneficial influence on lipoprotein lipase activity, HDL cholesterol, and triglyceride levels in coronary artery disease patients. The Ser447-stop substitution in the lipoprotein lipase gene. Circulation. 1997; 95:2628–635.
Goldberg IJ. Lipoprotein lipase and lipolysis: central roles in lipoprotein metabolism and atherogenesis. J Lipid Res. 1996;37:693–707.
Jemaa R, Fumeron F, Poirier O, Lecerf L, Evans A, Arveiler D, et al. Lipoprotein lipase gene polymorphisms: associations with myocardial infarction and lipoprotein levels, the ECTIM study. Etude Cas Temoin sur l’Infarctus du Myocarde. J Lipid Res. 1995;36(10):2141–6.
Wion KL, Kirchgessner TG, Lusis AJ, Schotz MC, Lawn RM. Human lipoprotein lipase complementary DNA sequence. Science. 1987;235:1638–41.
Rip J, Nierman MC, Ross CJ, Jukema JW, Hayden MR, Kastelein JJP, et al. Lipoprotein lipase S447X: A naturally occurring gain-of-function mutation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26:1236–45.
Chen W, Srinivasan SR, Elkasabany A, Ellsworth DL, Boerwinkle E, Berenson GS. Influence of lipoprotein lipase serine 447 stop polymorphism on tracking of triglycerides and HDL cholesterol from childhood to adulthood and familial risk of coronary artery disease: the Bogalusa heart study. Atherosclerosis. 2001;159(2):367–73.
Stanslas J, Vasudevan NR, Ismail P, Shamsudin, Zamanian M: Lipoprotein lipase gene polymorphism (S447X) is not associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus patients among Malaysian population. http://www.persatuangenetikmalaysia.com/files/congress07/04Poster14.pdf.
Vasudevan R, Ismail P, Stanslas J, Shamsudin N. Analysis of three genetic polymorphisms in Malaysian essential hypertensive and type 2 diabetic subjects. Afr J Biotechnol. 2009;8(10):2069–75.
Anagnostopoulou KK, Kolovou GD, Kostakou PM, Mihas C, Hatzigeorgiou G, Marvaki C, et al. Sex-associated effect of CETP and LPL polymorphisms on postprandial lipids in familial hypercholesterolaemia. Lipids Health Dis. 2009;8:24.
Lee J, Tan CS, Chia KS, Tan CE, Chew SK, Ordovas JM, et al. The lipoprotein lipase S447X polymorphism and plasma lipids: interactions with APOE polymorphisms, smoking, and alcohol consumption. J Lipid Res. 2004;45(6):1132–9.
Fujiwara S, Kotani K, Sano Y, Matsuoka Y, Tsuzaki K, Komichi M, et al. S447X polymorphism in the lipoprotein lipase gene and the adiponectin level in the general population: Results from the Mima study. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2008;16(3):188–93.
Brousseau ME, Goldkamp AL, Collins D, Demissie S, Connolly AC, Cupples LA, et al. Schaefer Polymorphisms in the gene encoding lipoprotein lipase in men with low HDL-C and coronary heart disease: the veterans affairs HDL intervention trial. J Lipid Res. 2004;45:1885–91.
Kuivenhoven JA, Groenemeyer BE, Boer JMA, Reymer PWA, Berghuis R, Bruin T, et al. S447X mutation in lipoprotein lipase is associated with elevated HDL cholesterol levels in 295Normolipidemic males. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1997;17:595–9.
Hall S, Talmud PJ, Cook DG, Wicks PD, Rothwell MJ, Strazzullo P, et al. Frequency and allelic association of common variants in the lipoprotein lipase gene in different ethnic groups: the Wandsworth Heart and Stroke Study. Genet Epidemiol. 2000;18:203–16.
Yang T, Pang CP, Tsang MW, Lam CW, Poon PMK, Chan LYS, et al. Pathogenic mutations of the lipoprotein lipase gene in Chinese patients with hypertriglyceridemic type 2 diabetes. Hum Mutat. 2003;21(4):453.
Mailly F, Tugrul Y, Reymer PW, Bruin T, Seed M, Groenemeyer BF, et al. A common variant in the gene for lipoprotein lipase (Asp9 → Asn). Functional implications and prevalence in normal and hyperlipidemic subjects. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1995;15:468–78.
Gerdes C, Fisher RM, Nicaud V, Boer J, Humphries SE, Talmud PJ, et al. Lipoprotein lipase variants D9 N and N291S are associated with increased plasma triglyceride and lower high-density lipoprotein cholesterol concentrations: studies in the fasting and postprandial states: the European Atherosclerosis Research Studies. Circulation. 1997;96:733–40.
Hata A, Robertson M, Emi M, Lalouel JM. Direct detection and automated sequencing of individual alleles after electrophoretic strand separation: identification of a common nonsense mutation in exon 9 of the human lipoprotein lipase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990;18:5407–11.
Hans HW, Anne TH, Børge GN. Lipoprotein lipase mutations, plasma lipids and lipoproteins, and risk of ischemic heart disease a meta-analysis. Circulation. 1999;99:2901–7.
Muñoz-Barriosab S, Guzmán-Guzmána IP, Muñoz-Valleb JF, Salgado-Bernabéa AB, Salgado-Goytiaa L, Parra-Rojasa I. Association of the HindIII and S447X polymorphisms in LPL gene with hypertension and type 2 diabetes in Mexican families. Dis Markers. 2012;33:313–20.
Ranganathan G, Unal R, Pokrovskaya ID, Tripathi P, Rotter JI, Goodarzi MO, et al. The lipoprotein lipase (LPL) S447X gain of function variant involves increased mRNA translation. Atherosclerosis. 2012;221(1):143–7.
Wierzbicki AS, Viljoen A. Alipogene tiparvovec: gene therapy for lipoprotein lipase deficiency. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2013;13(1):7–10.
Stroes ES, Nierman MC, Meulenberg JJ, Franssen R, Twisk J, Henny CP, et al. Intramuscular administration of AAV1-lipoprotein lipase S447X lowers triglycerides in lipoprotein lipase-deficient patients. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2008;28(12):2303–4.
Funding
This study was not funded by any funding agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
A. A. Momin, M. P. Bankar, G. M. Bhoite declares that that have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Momin, A.A., Bankar, M.P. & Bhoite, G.M. Study of Common Genetic Variant S447X in Lipoprotein Lipase and Its Association with Lipids and Lipoproteins in Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Ind J Clin Biochem 31, 286–293 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-015-0531-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-015-0531-z