Abstract
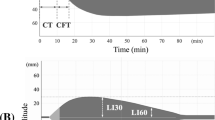
The prothrombotic state in type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) has been reported as a plausible cause of vascular complications. Rotational thromboelastometry (ROTEM) assay enables the global assessment of coagulation status. This study aimed to assess hypercoagulability in children with T1DM using ROTEM. A total of 43 T1DM children (20 females and 23 males) aged 2–18 years and age- and sex-matched 30 healthy control subjects were enrolled in the study group. ROTEM assays [intrinsic TEM (INTEM) and extrinsic TEM (EXTEM)] were used to measure and analyze coagulation time (CT), clot formation time, maximum clot firmness (MCF). Glycated hemoglobin levels (HbA1c), diabetic complications, platelet count, prothrombin time (PT), activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), fibrinogen, and dimerized plasmin fragment D (D-dimer) were determined in the study group. The mean duration of T1DM diagnosis was 3.15 ± 2.49 years, and the mean HbA1c level was 8.94 ± 1.88% (74.29 ± 20.59 mmol/mol). None of the patients had macrovascular complications. Nephropathy was present in five patients. In the T1DM group, EXTEM-CT [80.00 (66.75−108.50)] was significantly lower, and EXTEM-MCF [65.00 (64.00−70.00)] and INTEM-MCF [65.00 (62.00−68.00)] were significantly higher than in the controls (p < 0.001, p = 0.026, and p = 0.004, respectively). However, the duration of T1DM and the degree of metabolic control had no influence on these parameters. Platelet count, PT, aPTT, fibrinogen and D-dimer levels were comparable between the diabetic patients and the control group. There were statistically significant correlations between fibrinogen level and INTEM-MCF and EXTEM-MCF (p < 0.001, p = 0.002 and r = 0.545, r = 0.454, respectively) This study shows that decreased levels of CT and increased levels of MCF suggest hypercoagulability in patients with T1DM. Further studies are needed to confirm our findings on a larger number of diabetic patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haitas B, Barnes AJ, Cederholm-Williams SA, Moore J, Shogry ME, Turner RC (1984) Abnormal endothelial release of fibrinolytic activity and fibronectin in diabetic microangiopathy. Diabetologia 27:493–496
Carmassi F, Morale M, Puccetti R, De Negri F, Monzani F, Navalesi R, Mariani G (1992) Coagulation and fibrinolytic system impairment in insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Thromb Res 67:643–654
Blann AD, Lip GY (1998) Endothelial integrity, soluble adhesion molecules and platelet markers in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Med 15:634–642
Rigla M, Mateo J, Fontcuberta J, Souto JC, de Leiva A, Pérez A (2000) Normalisation of tissue factor pathway inhibitor activity after glycaemic control optimisation in type 1 diabetic patients. Thromb Haemost 84:223–227
Targher G, Bertolini L, Zoppini G, Zenari L, Falezza G (2005) Increased plasma markers of inflammation and endothelial dysfunction and their association with microvascular complications in type 1 diabetic patients without clinically manifest macroangiopathy. Diabet Med 22:999–1004
Yngen M, Ostenson CG, Hu H, Li N, Hjemdahl P, Wallén NH (2004) Enhanced P-selectin expression and increased soluble CD40 Ligand in patients with Type 1 diabetes mellitus and microangiopathy: evidence for platelet hyperactivity and chronic inflammation. Diabetologia 47:537–540
Hartert H (1948) Blutgerinnungsstudien mit der thrombelatographie, einem neuen untersuchungs verfahren. Klinische Wochenschr 26:577–583
Traverso CI, Caprini JA, Arcelus JI (1995) The normal thromboelastogram and its interpretation. Semin Thromb Hemost 21(Suppl 4):7–13
Spiel AO, Mayr FB, Firbas C, Ouehenberger P, Jilma B (2005) Validation of rotation thromboelastography in a model of systemic activation of fibrinolysis and coagulation in humans. J Thromb Haemost 4:411–416
Da Luz LT, Nascimento B, Shankarakutty AK, Rizoli S, Adhikari NK (2014) Effect of thromboelastography (TEG®) and rotational thromboelastometry (ROTEM®) on diagnosis of coagulopathy, transfusion guidance and mortality in trauma: descriptive systematic review. Crit Care 18:518
Mallett SV (2015) Clinical utility of viscoelastic tests of coagulation (TEG/ROTEM) in patients with liver disease and during liver transplantation. Semin Thromb Hemost 41:527–537
Yürekli BP, Ozcebe OI, Kirazli S, Gürlek A (2006) Global assessment of the coagulation status in type 2 diabetes mellitus using rotation thromboelastography. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 17:545–549
Reissell E, Lalla M, Höckerstedt K, Lindgren L (1994) Coagulation abnormalities in diabetic patients undergoing renal transplantation. Ann Chir Gynaecol 83:251–255
Burke GW, Ciancio G, Figueiro J, Buigas R, Olson L, Roth D, Kupin W, Miller J (2004) Hypercoagulable state associated with kidney–pancreas transplantation. Thromboelastogram-directed anti-coagulation and implications for future therapy. Clin Transplant 18:423–428
Rewers M, Pihoker C, Donaghue K, Hanas R, Swift P, Klingensmith GJ (2009) Assessment and monitoring of glycemic control in children and adolescents with diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes 10(Suppl 12):71–81
Neyzi O, Furman A, Bundak R, Gunoz H, Darendeliler F, Bas F (2006) Growth references for Turkish children aged 6 to 18 years. Acta Paediatr 95:1635–1641
Bundak R, Furman A, Gunoz H, Darendeliler F, Bas F, Neyzi O (2006) Body mass index references for Turkish children. Acta Paediatr 95:194–198
National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents (2004) The fourth report on the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics 114:555–576
Chitlur M, Rivard GE, Lillicrap D, Mann K, Shima M, Young G (2014) Factor VIII, Factor IX, and Rare Coagulation Disorders Subcommittee of the Scientific and Standardisation Committee of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis. Recommendations for performing thromboelastography/thromboelastometry in hemophilia: communication from the SSC of the ISTH. J Thromb Haemost 12:103–106
Neal WA (2007) Disorders of lipoprotein metabolism and transport. In: Klieigman RM, Behrman RE, Jenson HB, Stanton BF (eds) Nelson textbook of pediatrics, 18th edn. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 580–592
Spiezia L, Marchioro P, Radu C, Rossetto V, Tognin G, Monica C, Salmaso L, Simioni P (2008) Whole blood coagulation assessment using rotation thrombelastogram thromboelastometry in patients with acute deep vein thrombosis. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 19:355–360
Nielsen VG, Geary BT, Baird MS (2000) Evaluation of the contribution of platelets to clot strength by thromboelastography in rabbits: the role of tissue factor and cytochalasin D. Anesth Analg 91:35–39
Zuckerman L, Cohen E, Vagher JP, Woodward E, Caprini JA (1981) Comparison of thrombelastography with common coagulation tests. Thromb Haemost 46:752–756
Rossetto V, Spiezia L, Senzolo M, Rodriguez-Castro KI, Maggiolo S, Simioni P (2013) Whole blood rotation thromboelastometry (ROTEM) profiles in subjects with non-neoplastic portal vein thrombosis. Thromb Res 132:e131–e134
Sibal L, Aldibbiat A, Agarwaletal SC (2009) Circulating endothelial progenitorcells, endothelial function, carotid intima-media thickness and circulating markers of endothelial dysfunction in people with type 1 diabetes without macrovascular disease or microalbuminuria. Diabetologia 52:1464–1473
Sobol AB, Watala C (2000) The role of platelets in diabetes-related vascular complications. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 50:1–16
Singh A, Boden G, Homko C, Gunawardana J, Rao AK (2012) Whole-blood tissue factor procoagulant activity is elevated in type 1 diabetes: effects of hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia. Diabetes Care 35:1322–1327
Ce GV, Rohde LE, da Silva AM, Puñales MK, de Castro AC, Bertoluci MC (2011) Endothelial dysfunction is related to poor glycemic control in adolescents with type 1 diabetes under 5 years of disease: evidence of metabolic memory. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96:1493–1499
Smulders RA, Stehouwer CD, Schalkwijk CG, Donker AJ, van Hinsbergh VW, TeKoppele JM (1998) Distinct associations of HbA1c and the urinary excretion of pentosidine, an advanced glycosylation end-product, with markers of endothelial function in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Thromb Haemost 80:52–57
Hu H, Li N, Yngen M, Ostenson CG, Wallén NH, Hjemdahl P (2004) Enhanced leukocyte-platelet cross-talk in type 1 diabetes mellitus: relationship to microangiopathy. J Thromb Haemost 2:58–64
Tschoepe D, Driesch E, Schwippert B, Nieuwenhuis HK, Gries FA (1995) Exposure of adhesion molecules on activated platelets in patients with newly diagnosed IDDM is not normalized by near-normoglycemia. Diabetes 44:890–894
el Khawand C, Jamart J, Donckier J, Chatelain B, Lavenne E, Moriau M, Buysschaert M (1993) Hemostasis variables in type I diabetic patients without demonstrable vascular complications. Diabetes Care 16:1137–1145
Reverter JL, Reverter JC, Tàssies D, Rius F, Monteagudo J, Rubiés-Prat J, Escolar G, Ordinas A, Sanmarti A (1997) Thrombomodulin and induced tissue factor expression on monocytes as markers of diabetic microangiopathy: a prospective study on hemostasis and lipoproteins in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Am J Hematol 56:93–99
Fasching P, Veitl M, Rohac M, Streli C, Schneider B, Waldhäusl W, Wagner OF (1996) Elevated concentrations of circulating adhesion molecules and their association with microvascular complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81:4313–4317
Elhadd TA, Kennedy G, Hill A, McLaren M, Newton RW, Greene SA, Belch JJ (1999) Abnormal markers of endothelial cell activation and oxidative stress in children, adolescents and young adults with type 1 diabetes with no clinical vascular disease. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 15:405–411
Romano M, Pomilio M, Vigneri S, Falco A, Chiesa PL, Chiarelli F, Davì G (2001) Endothelial perturbation in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes: association with markers of the inflammatory reaction. Diabetes Care 24:1674–1678
Di Benedetto P, Baciarello M, Cabetti L, Martucci M, Chiaschi A, Bertini L (2003) Thrombelastography. Present and future perspectives in clinical practice. Minerva Anestesiol 69:501–515
Luddington RJ (2005) Thrombelastography/thromboelastometry. Clin Lab Haematol 27:81–90
Chen A, Teruya J (2009) Global hemostasis testing thromboelastography: old technology, new applications. Clin Lab Med 29:391–407
Akay OM, Ustuner Z, Canturk Z, Mutlu FS, Gulbas Z (2009) Laboratory investigation of hypercoagulability in cancer patients using rotation thrombelastography. Med Oncol 26:358–364
Turhan AB, Bör Ö, Akay OM, Akgün NA (2014) Thromboelastometry profile in children with beta-thalassemia. Int J Hematol 99:407–412
Yaşar Bilge NŞ, Akay OM, Kaşifoğlu T, Kuş G, Korkmaz C (2013) The role of hemostatic mechanisms in the development of thrombosis in Behcet’s disease: an analysis by modified rotation thromboelastogram (ROTEM). Clin Rheumatol 32:1815–1818
Ustuner Z, Akay OM, Keskin M, Kuş E, Bal C, Gulbas Z (2012) Evaluating coagulation disorders in the use of bevacizumab for metastatic colorectal cancer by thrombelastography. Med Oncol 29:3125–3128
Seljeflot I, Larsen JR, Dahl-Jorgensen K, Hanssen KF, Arnesen H (2006) Fibrinolytic activity is highly influenced by long-term glycemic control in type 1 diabetic patients. J Thromb Haemost 4:686–688
Davì G, Chiarelli F, Santilli F, Pomilio M, Vigneri S, Falco A, Basili S, Ciabattoni G, Patrono C (2003) Enhanced lipid peroxidation and platelet activation in the early phase of type 1 diabetes mellitus: role of interleukin-6 and disease duration. Circulation 107:3199–3203
Delis S, Ciancio G, Casillas J, Figueiro J, Garcia A, Miller J, Burke GW (2002) Diabetic muscle infarction after simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplant. Clin Transplant 16:295–300
Konieczynska M, Fil K, Bazanek M, Undas A (2014) Prolonged duration of type 2 diabetes is associated with increased thrombin generation, prothrombotic fibrin clot phenotype and impaired fibrinolysis. Thromb Haemost 111(4):685–693
Pretorius E, Bester J (2016) Viscoelasticity as a measurement of clot structure in poorly controlled type 2 diabetes patients: towards a precision and personalized medicine approach. Oncotarget. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.10618
Tran TH, Al-Harfi I, Harle CC, Kahr WH, Morrison GC, Kornecki A (2013) Coagulation assessment in children with diabetic ketoacidosis. Pediatr Crit Care Med 14:256–260
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Binay, C., Bozkurt Turhan, A., Simsek, E. et al. Evaluation of Coagulation Profile in Children with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Using Rotational Thromboelastometry. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus 33, 574–580 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12288-017-0793-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12288-017-0793-0