Abstract
Purpose
To assess axillary lymph nodes in patients with breast cancer with diffusion-weighted MR imaging in combination with routine and dynamic contrast MR imaging.
Materials and methods
Prospective study was conducted on 65 enlarged axillary lymph nodes in 34 consecutive female patients (28–64 years: mean 51 years) with breast cancer. They underwent T2-weighted, dynamic contrast-enhanced and diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the breast and axilla using a single-shot echo-planar imaging with a b factor of 0500 and 1000 s/mm2. Morphologic and quantitative parameters included ADC value of the axillary lymph node which was calculated and correlated with surgical findings.
Results
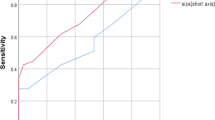
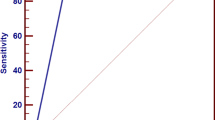
The mean ADC value of metastatic axillary lymph nodes was 1.08 ± 0.21 × 10−3 mm2/s and of benign lymph nodes was 1.58 ± 0.14 × 10−3 mm2/s. There was statistically difference in mean ADC values between metastatic and of benign axillary lymph nodes (P = 0.001). Metastatic nodes were associated with low ADC ≤ 1.3 (OR = 8.0), short axis/long axis (TS/LS) > 0.6 (OR = 7.0) and absent hilum (OR = 6.21). When ADC of 1.3 × 10−3 mm2/s was used as a threshold value for differentiating metastatic from benign axillary lymph nodes, the best result was obtained with an accuracy of 95.6 %, sensitivity of 93 %, specificity of 100 %, positive predictive value of 100 %, negative predictive value of 87.5 % and area under the curve of 0.974. Multivariate model involving combined ADC value and TS/LS improved the diagnostic performance of MR imaging with AUC of 1.00.
Conclusion
We concluded that combination of diffusion-weighted MR imaging with morphological and dynamic MR imaging findings helps for differentiation of metastatic from benign axillary lymph nodes.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ADC:
-
Apparent diffusion coefficient
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- NPV:
-
Negative predictive value
- ORs:
-
Odds ratios
- PPV:
-
Positive predictive value
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic
- TIC:
-
Time–intensity curves
- TS/LS:
-
Short axis to long axis
References
Dull BZ, Neuman HB. Management of the axilla. Surg Clin North Am. 2013;93:429–44.
Thompson AM. New standards of care in the management of the axilla. Curr Opin Oncol. 2012;24:605–11.
Rahbar H, Partridge S, Javid S, Lehman C. Imaging axillary lymph nodes in patients with newly diagnosed breast cancer. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2012;41:149–58.
Cools-Lartigue J, Meterissian S. Accuracy of axillary ultrasound in the diagnosis of nodal metastasis in invasive breast cancer: a review. World J Surg. 2012;36:46–54.
Tsai WC, Lin CK, Wei HK, Yu BL, Hung CF, Cheng SH, Chen CM. Sonographic elastography improves the sensitivity and specificity of axilla sampling in breast cancer: a prospective study. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2013;39:941–9.
Song SE, Seo BK, Lee SH, Yie A, Lee KY, Cho KR, Woo H, Cha SH, Kim B. Classification of metastatic versus non-metastatic axillary nodes in breast cancer patients: value of cortex-hilum area ratio with ultrasound. J Breast Cancer. 2012;15:65–70.
Nasu Y, Shikishima H, Miyasaka Y, Nakakubo Y, Ichinokawa K, Kaneko T. A study of the assessment of axillary lymph nodes before surgery for breast cancer using multidetector-row computed tomography. Surg Today. 2010;40:1023–6.
Keam B, Im S, Koh Y, Han S, Oh D, Cho N, Kim JH, Han W, Kang KW, Moon WK, Kim TY, Park IA, Noh DY, Chung JK, Bang YJ. Predictive value of FDG PET/CT for pathologic axillary node involvement after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Breast Cancer. 2013;20:167–73.
Scaranelo AM, Eiada R, Jacks LM, Kulkarni SR, Crystal P. Accuracy of unenhanced MR imaging in the detection of axillary lymph node metastasis: study of reproducibility and reliability. Radiology. 2012;262:425–34.
Ecanow J, Abe H, Newstead G, Ecanow D, Jeske J. Axillary staging of breast cancer: what the radiologist should know. Radiographics. 2013;33:1589–612.
Loiselle C, Eby P, Peacock S, Kim J, Lehman C. Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and invasive breast cancer: primary lesion kinetics correlated with axillary lymph node extracapsular extension. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2011;33:96–101.
Mortellaro V, Marshall J, Singer L, Hochwald S, Chang M, Copeland E, Grobmyer SR. Magnetic resonance imaging for axillary staging in patients with breast cancer. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009;30:309–12.
Seenu V, Kumar M, Sharma U, Gupta S, Mehta S, Jagannathan N. Potential of magnetic resonance spectroscopy to detect metastasis in axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer. Magn Reson Imaging. 2005;23:1005–10.
Korteweg MA, Zwanenburg JJ, Hoogduin JM, van den Bosch MA, van Diest PJ, van Hillegersberg R, Eijkemans MJ, Mali WP, Luijten PR, Veldhuis WB. Dissected sentinel lymph nodes of breast cancer patients: characterization with high-spatial-resolution 7-T MR imaging. Radiology. 2011;261:127–35.
Schipper RJ, Smidt ML, van Roozendaal LM, Castro CJ, de Vries B, Heuts EM, Keymeulen KB, Wildberger JE, Lobbes MB, Beets-Tan RG. Noninvasive nodal staging in patients with breast cancer using gadofosveset-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Invest Radiol. 2013;48:134–9.
Mullen R, Purdie CA, Jordan LB, McLean D, Whelehan P, Vinnicombe S, Brown DC, Evans A. Can additional histopathological examination of ultrasound-guided axillary lymph node core biopsies improve preoperative diagnosis of primary breast cancer nodal metastasis? Clin Radiol. 2013;68:704–7.
Brandão AC, Lehman CD, Partridge SC. Breast magnetic resonance imaging: diffusion-weighted imaging. Magn Reson Imaging Clin North Am. 2013;21:321–36.
Thomassin-Naggara I, De Bazelaire C, Chopier J, Bazot M, Marsault C, Trop I. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the breast: advantages and pitfalls. Eur J Radiol. 2013;82:435–43.
Razek AA, Gaballa G, Denewer A, Tawakol I. Diffusion weighted MR imaging of the breast. Acad Radiol. 2010;17:382–6.
Tan SL, Rahmat K, Rozalli F, Mohd-Shah N, Aziz Y, Yip C, Vijayananthan A, Ng KH. Differentiation between benign and malignant breast lesions using quantitative diffusion weighted sequence on 3 T MRI. Clin Radiol. 2014;69:63–71.
El Khouli R, Jacobs M, Mezban S, Huang P, Kamel I, Macura K, Bluemke DA. Diffusion-weighted imaging improves the diagnostic accuracy of conventional 3.0-T breast MR imaging. Radiology. 2010;256:64–73.
Parsian S, Rahbar H, Allison KH, Demartini WB, Olson ML, Lehman CD, Partridge SC. Nonmalignant breast lesions: ADCs of benign and high-risk subtypes assessed as false-positive at dynamic enhanced MR imaging. Radiology. 2012;265:696–706.
Heusner TA, Kuemmel S, Koeninger A, Hamami ME, Hahn S, Quinsten A, Bockisch A, Forsting M, Lauenstein T, Antoch G, Stahl A. Diagnostic value of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DWI) compared to FDG PET/CT for whole-body breast cancer staging. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010;37:1077–86.
Razek AA, Gaballa G, Denewer A, Nada N. Invasive ductal carcinoma: correlation of apparent diffusion coefficient value with pathological prognostic factors. NMR Biomed. 2010;23:619–23.
Razek AA, Elkammary S, Elmorsy A, Elshafey M, Elhadedy T. Characterization of mediastinal lymphadenopathy with diffusion-weighted imaging. Magn Reson Imaging. 2011;29:167–72.
Cheng J, Wang Y, Deng J, McCarthy R, Wang G, Wang H, Ye Y. Discrimination of metastatic lymph nodes in patients with gastric carcinoma using diffusion-weighted imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2013;37:1436–44.
Razek AAA, Soliman NY, Elkhammary S, Alsharaway MK, Tawfik A. Role of diffusion-weighted MR imaging in cervical lymphadenopathy. Eur Radiol. 2006;16:1468–77.
Mir N, Sohaib SA, Collins D, Koh DM. Fusion of high b-value diffusion-weighted and T2-weighted MR images improves identification of lymph nodes in the pelvis. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2010;54:358–64.
Luo N, Su D, Jin G, Liu L, Zhu X, Xie D, Liu Y. Apparent diffusion coefficient ratio between axillary lymph node with primary tumor to detect nodal metastasis in breast cancer patients. Magn Reson Imaging. 2013;38:824–8.
Kamitani T, Hatakenaka M, Yabuuchi H, Matsuo Y, Fujita N, Jinnouchi M, Nagao M, Shirahane K, Tokunaga E, Honda H. Detection of axillary node metastasis using diffusion-weighted MRI in breast cancer. Clin Imaging. 2013;37:56–61.
Fornasa F, Nesoti VM, Bovo C, Bonavina GM. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in the characterization of axillary lymph nodes in patients with breast cancer. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012;36:858–64.
He N, Xie C, Wei W, Pan C, Wang W, Lv N, Wu P, et al. A new, preoperative, MRI-based scoring system for diagnosing malignant axillary lymph nodes in women evaluated for breast cancer. Eur J Radiol. 2012;81:2602–12.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Razek, A.A.K.A., Lattif, M.A., Denewer, A. et al. Assessment of axillary lymph nodes in patients with breast cancer with diffusion-weighted MR imaging in combination with routine and dynamic contrast MR imaging. Breast Cancer 23, 525–532 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-015-0598-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-015-0598-7